leetcode everyday
day 1 2024-02-27
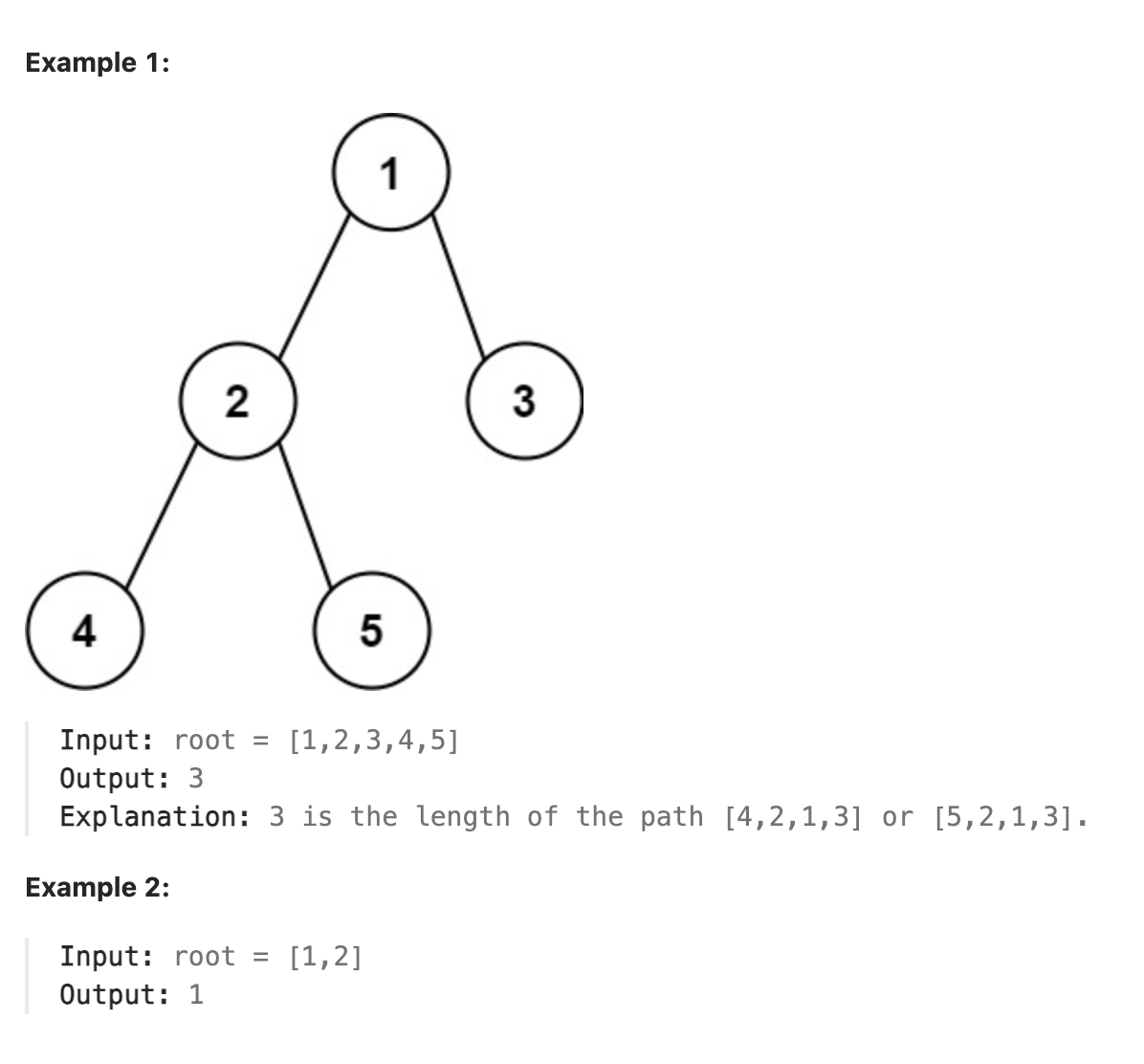
543 Diameter of Binary Tree
Given the root of a binary tree, return the length of the diameter of the tree.
The diameter of a binary tree is the length of the longest path between any two nodes in a tree. This path may or may not pass through the root.
The length of a path between two nodes is represented by the number of edges between them.
题解
读题, 题目要求寻找二叉树中任意两节点之间的最大距离. 这时这个二叉树更像是一个图的性质而不是树, 即寻找图中任意两节点之间的最大距离. 考虑任意一点到另一点的距离等于其到另一点的父节点的距离减一, 则使用一个二维数组保存每个节点的两个属性:
- 以该节点为根节点且经过该节点的最大直径
- 以该节点为根节点的子树中叶子节点到该节点的最大距离
属性1可以通过将该节点的两个子节点的属性2加和并加1来计算. 属性2取两个子节点属性2的最大值并加1来计算. 最后遍历数组求得数组中属性1的最大值即可. 有一点动态规划的思想.
题目中并没有提供二叉树的节点总数, 则可以使用动态创建的方法, 在遍历过程中每遇到新节点就在二维数组中增加一项. 这里使用递归来对树进行后序遍历, 对空节点, 设置其属性2的值为-1, 这样保证叶子节点的属性2的值为0.
解题时遇到一个小bug, 使用了一个全局切片(数组)来保存变量时, 第一个测试用例的数据会保留到测试第二个测试用例的过程中, 这大概是因为leetcode的测试是对每个用例直接调用给出的解题入口函数, 因此需要在解题函数中将使用的全局变量初始化一下, 将数组设置为空后问题得到解决.
代码
| |
day2 2024-02-28
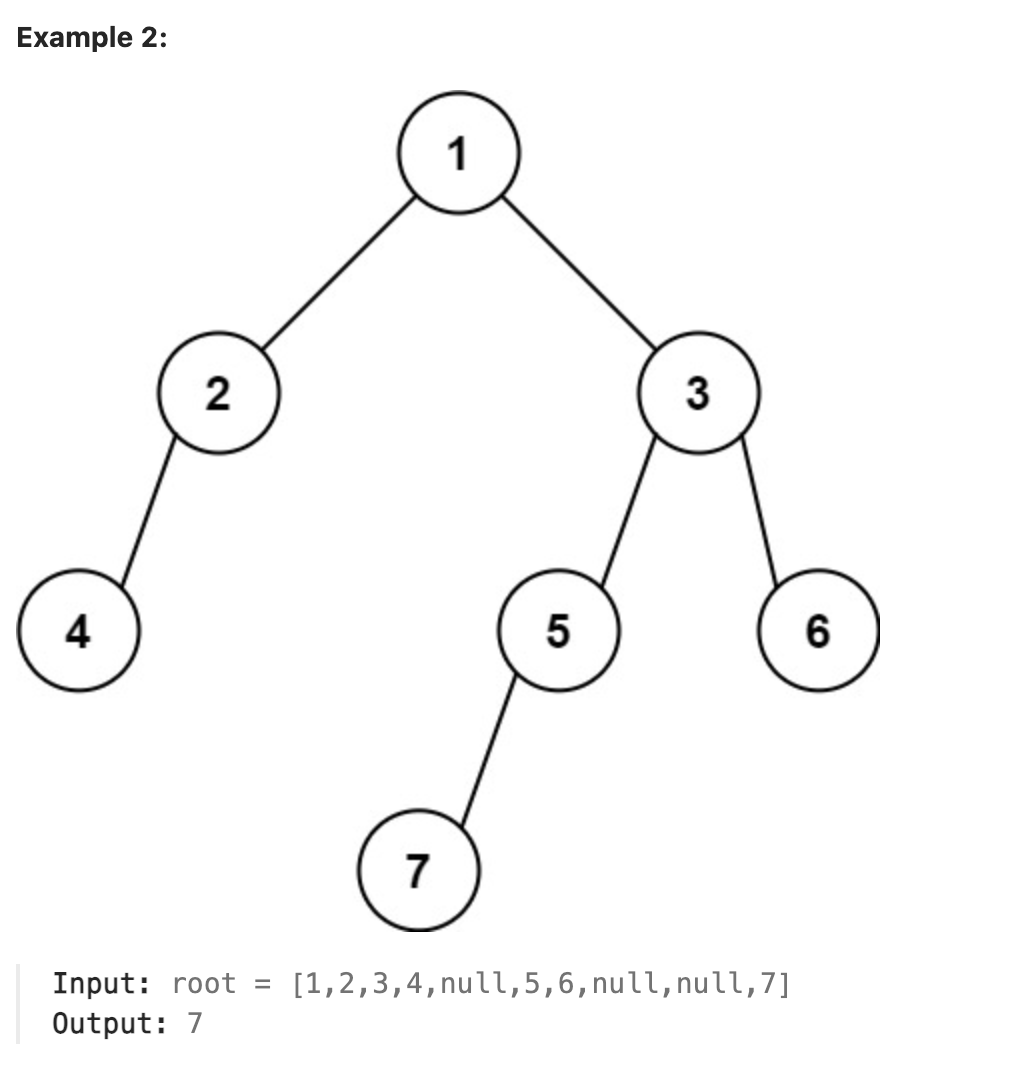
513. Find Bottom Left Tree Value
Given the root of a binary tree, return the leftmost value in the last row of the tree.
题解
找到二叉树最底层最左边的节点值, 用层序遍历遍历到最后一层找到最后一层最左边节点的值即可. 实现层序遍历可以使用一个队列, 将当前层节点的所有子节点入队后将当前层节点出队. 在go中可以使用切片实现一个队列. 使用一个标记变量记录当前层所有节点是否有子节点, 若无子节点则当前层为最低层, 返回当前层最左侧节点的值(此时队列中第一个节点的值).
代码
| |
总结
在题解中看到了一个使用深度优先搜索的方法, 记录当前搜索到的层级, 始终保存最大层级的第一个被搜索到的值, 因为使用的是后序遍历, 则每次遇到的当前层大于保存的最大层级时, 该节点就为新的最大层级的第一个节点, 即题目中要求的最左值(leftmost). 算法时间复杂度为O(n)——只遍历一次所有节点.
day3 2024-02-29
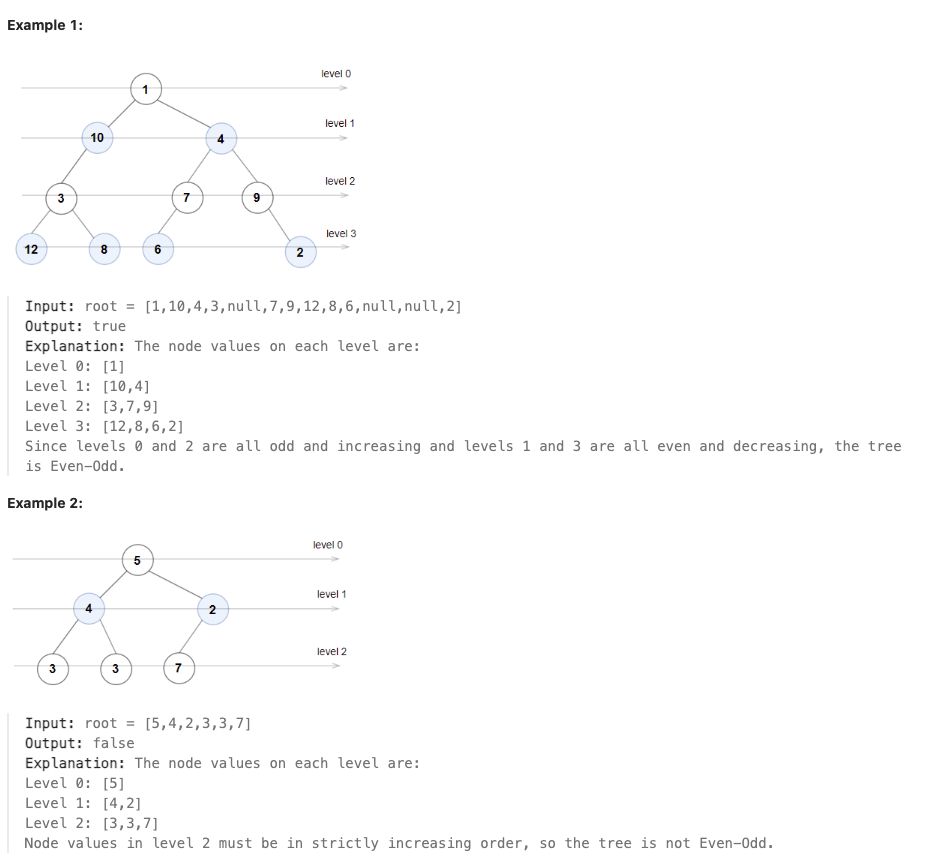
1609. Even Odd Tree
A binary tree is named Even-Odd if it meets the following conditions:
The root of the binary tree is at level index 0, its children are at level index 1, their children are at level index 2, etc. For every even-indexed level, all nodes at the level have odd integer values in strictly increasing order (from left to right). For every odd-indexed level, all nodes at the level have even integer values in strictly decreasing order (from left to right). Given the root of a binary tree, return true if the binary tree is Even-Odd, otherwise return false.
题解
对二叉树的奇数层, 其节点从左到右是严格递减的(意味着有两个节点的值相同是不允许的), 偶数层是严格递增的. 仍然可以使用昨天题目的层序遍历的方法, 增加一个level变量记录当前层数, 对该层内的节点值进行判断是否符合奇数层和偶数层对应的条件即可.
代码
| |
总结
go语言中的for range循环, 如果使用类似for key, value := range list 的形式, 那么key, value这两个变量都会在当前作用域下新建, 意味着即使在前面定义了key, key的值在循环结束后也不会被修改. 若想修改之前定义的key值, 需要将value也提前定义好并使用=而不是:=.
go语言中的for range循环时如果使用:=会新建两个变量, 然后将slice中的值复制给value变量, 将对应的index值赋值给key变量, 这意味着value变量不会指向数组中对应位置的地址, 而是一个不变的单独地址.
day4 2024-03-01
2864. Maximum Odd Binary number
You are given a binary string s that contains at least one ‘1’.
You have to rearrange the bits in such a way that the resulting binary number is the maximum odd binary number that can be created from this combination.
Return a string representing the maximum odd binary number that can be created from the given combination.
Note that the resulting string can have leading zeros.
Example 1:
Input: s = “010” Output: “001” Explanation: Because there is just one ‘1’, it must be in the last position. So the answer is “001”.
Example 2:
Input: s = “0101” Output: “1001” Explanation: One of the ‘1’s must be in the last position. The maximum number that can be made with the remaining digits is “100”. So the answer is “1001”.
题解
题目中说明了给出的字符串中至少有一个1, 因此可以复制一个字符串, 然后遍历原字符串, 遇到第一个1放在最后一位, 0永远插入到倒数第二位, 不是第一个1放在字符串最前面. 由此除保证字符串是奇数的最后一个1以外, 其余的1都在字符串最前面, 其余的0都插入在最前面的一串1和最后的1之间. 保证了字符串是最大的奇数字符串.
代码
| |
总结
在处理字符串的时候像中间某个位置插入字符也要使用双引号, 如插入字符0要用+"0"而不是+'0', 此外在截取切片的时候go的切片是左闭右开的. 如[0:3]截取的是0,1,2三个数
day5 2024-03-02
977. Squares of a Sorted Array
Given an integer array nums sorted in non-decreasing order, return an array of the squares of each number sorted in non-decreasing order.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [-4,-1,0,3,10] Output: [0,1,9,16,100] Explanation: After squaring, the array becomes [16,1,0,9,100]. After sorting, it becomes [0,1,9,16,100].
Example 2:
Input: nums = [-7,-3,2,3,11] Output: [4,9,9,49,121]
题解
考虑原数组已经按照非递减排序的情况下, 找到数组中正负交界处元素, 即数组中第一个正数, 以该位置作为起始位置, 使用双指针法, 分别向前和向后遍历数组, 遍历时不断比较两个指针指向的数字的绝对值大小, 将绝对值小的数字平方后追加到结果数组的尾部, 遍历完成即可完成平方值排序. 这样只需要遍历一遍数组即可完成排序.
代码
| |
总结
注意一个go的语法问题, 如果在for range循环中两个变量都使用匿名变量, 则应该使用赋值运算符而不是创建并赋值运算符, 即for _,_ = range slice 而不是for _,_ := range slice. 这很可能是因为匿名变量默认为已经创建好的变量, 不需要再创建匿名变量本身了.
day6 2024-03-03
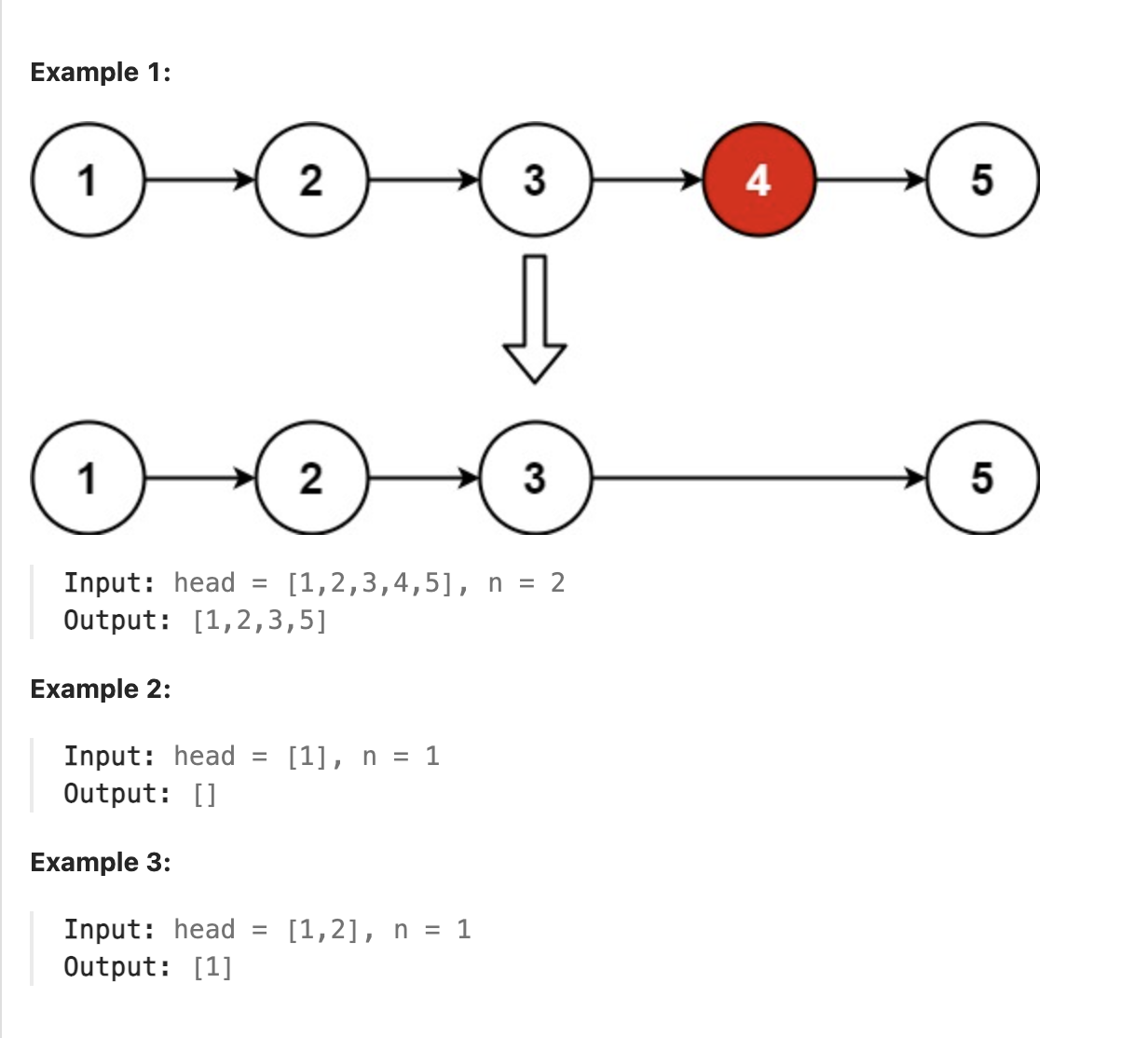
19. Remove Nth Node From End of List
Given the head of a linked list, remove the nth node from the end of the list and return its head.
题解
给出了链表头, 要求移除从后到前的第n个节点. 如果想一遍遍历就完成这个任务. 就使用空间换时间, 使用一个数组保存所有的Next指针的值. 然后让倒数第n+1个元素的Next指针指向n个元素的Next指针即可, 注意处理链表只有一个元素的特殊情况.
代码
| |
总结
在题解中看到大部分使用的是快慢指针的解法, 快慢指针应该是本题想要的解法, 下面贴一个快慢指针的解法示例
| |
day7 2024-03-04
948. Bag of Tokens
You start with an initial power of power, an initial score of 0, and a bag of tokens given as an integer array tokens, where each tokens[i] donates the value of tokeni.
Your goal is to maximize the total score by strategically playing these tokens. In one move, you can play an unplayed token in one of the two ways (but not both for the same token):
Face-up: If your current power is at least tokens[i], you may play tokeni, losing tokens[i] power and gaining 1 score. Face-down: If your current score is at least 1, you may play tokeni, gaining tokens[i] power and losing 1 score. Return the maximum possible score you can achieve after playing any number of tokens.
Example 1:
Input: tokens = [100], power = 50
Output: 0
Explanation: Since your score is 0 initially, you cannot play the token face-down. You also cannot play it face-up since your power (50) is less than tokens[0] (100).
Example 2:
Input: tokens = [200,100], power = 150
Output: 1
Explanation: Play token1 (100) face-up, reducing your power to 50 and increasing your score to 1.
There is no need to play token0, since you cannot play it face-up to add to your score. The maximum score achievable is 1.
Example 3:
Input: tokens = [100,200,300,400], power = 200
Output: 2
Explanation: Play the tokens in this order to get a score of 2:
Play token0 (100) face-up, reducing power to 100 and increasing score to 1. Play token3 (400) face-down, increasing power to 500 and reducing score to 0. Play token1 (200) face-up, reducing power to 300 and increasing score to 1. Play token2 (300) face-up, reducing power to 0 and increasing score to 2. The maximum score achievable is 2.
题解
本题的目的是最大化score. 一个基本的策略就是通过小的power换取score, 通过score换取大的power, 利用换到的大power赚取中间水平的token的score. 关键在于, 如何找到最大能换取的score. 首先考虑每次进行一次Face-up和Face-down, score没有变化, 只有power增大了, 那么每次都将score置0, 并判断当前能获得的最大score即可.
通过前面的分析可以得出, 算法分为以下几步
- 将tokens数组排序
- 判断power是否大于tokens[0], 即最小的token, 若大于, 则计算当前能获得的最大score
- 将power的值增加目前tokens数组中最大值和最小值(即排好序后的最后一项和第一项)的差值, 同时将tokens数组中第一项和最后一项移除. 重复2, 3步直到power小于tokens[0]或tokens数组长度为0中止.
- 返回最大的score
代码
| |
总结
在实现过程中, 起初使用一个数组来保存每次的score值, 这样空间复杂度略大, 后来查看他人代码, 发现只需要一个max变量来保存当前最大的score值, 并在每次循环计算当前轮次的score值时与当前的最大值比较并根据二者大小更新max变量的值即可, 这样只需要O(1)的空间复杂度.
day8 2024-03-05
1750. Minimum Length of String After Deleting Similar Ends
Given a string s consisting only of characters ‘a’, ‘b’, and ‘c’. You are asked to apply the following algorithm on the string any number of times:
- Pick a non-empty prefix from the string s where all the characters in the prefix are equal.
- Pick a non-empty suffix from the string s where all the characters in this suffix are equal.
- The prefix and the suffix should not intersect at any index.
- The characters from the prefix and suffix must be the same.
- Delete both the prefix and the suffix. Return the minimum length of s after performing the above operation any number of times (possibly zero times).

题解
本题的题目略显复杂, 读起来乍一看让人不明所以, 实际上题目的目标即为从字符串的前后同时删除相同的字符, 删除时只要是相同的就全部删除, 如最前面有一个a最后面有3个a则同时将这四个a删除. 删除的字符串下标不能相交. 思路比较简单, 判断字符串的前后字符是否相同, 然后删除前后的连续相同字符即可, 注意下标不要重叠. 同时注意边界情况, 字符串只有一个字符的情况单独处理一下(直接返回1).
代码
| |
总结
本题值得注意的地方在于for循环中条件的设置, 可能会忽略与运算符两侧条件表达式的前后顺序, 但由于短路机制的存在, 与运算符两侧表达式的前后顺序有时非常重要, 例如在本题中, 如果将forward<backward条件设置在前面, 则当forward到达数组的边界时会直接退出循环, 但若将相等判断放在前面, 会因为当forward到达数组边界时forward+1下标越界而出错.
day9 2024-03-06
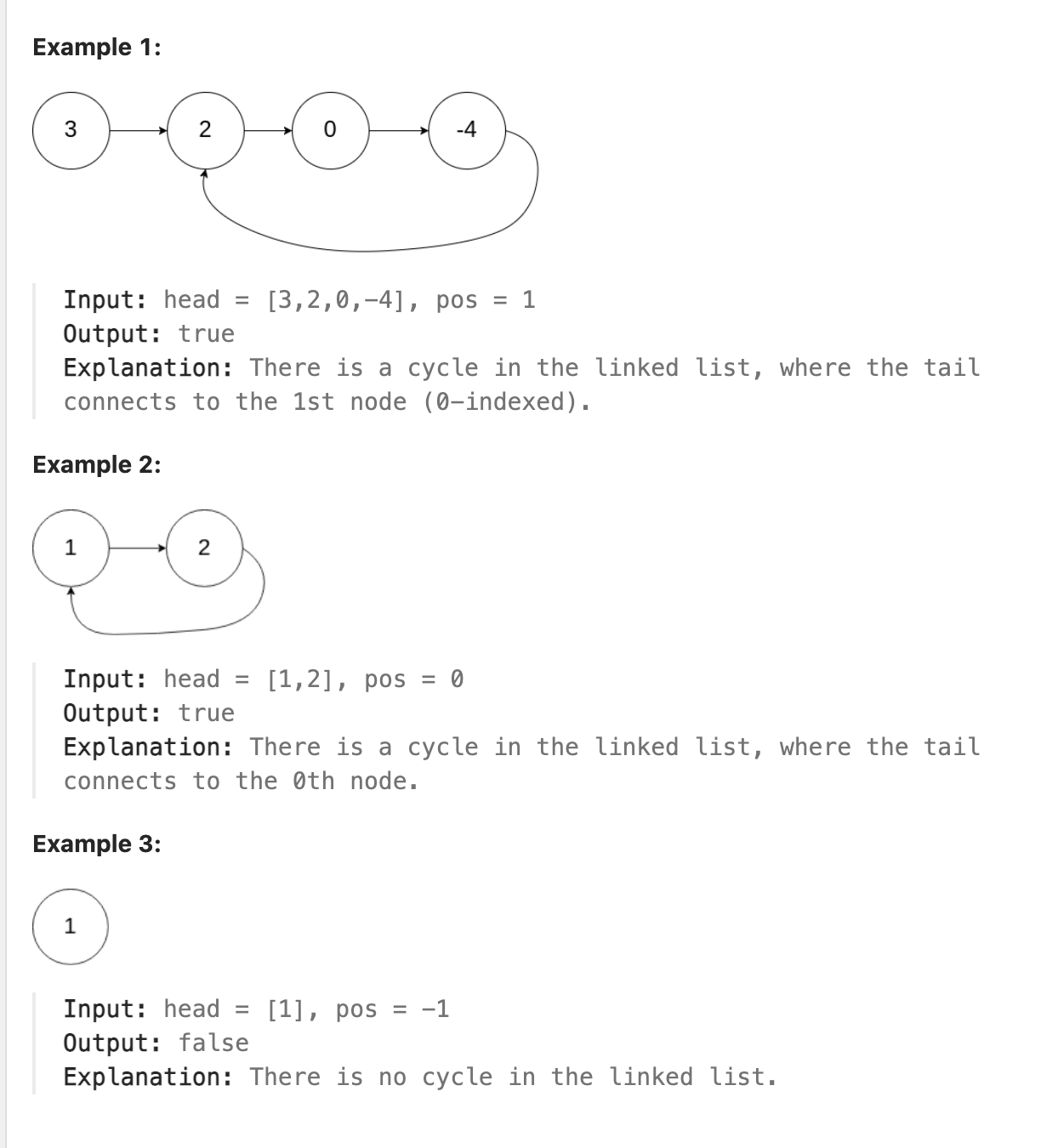
141. Linked List Cycle
Given head, the head of a linked list, determine if the linked list has a cycle in it.
There is a cycle in a linked list if there is some node in the list that can be reached again by continuously following the next pointer. Internally, pos is used to denote the index of the node that tail’s next pointer is connected to. Note that pos is not passed as a parameter.
Return true if there is a cycle in the linked list. Otherwise, return false.
题解
本题最简单的思路就是使用并查集, 因为go语言中的map类型在获取数据时会返回该键值在map中是否存在, 因此可以将map类型直接当作一个简单的并查集使用.
代码
| |
总结
题目中给出提示本题可以使用O(1)的空间复杂度解决, 即使用常数空间复杂度, 研究他人题解发现本题同样可以使用快慢指针,核心思想类似于加速度, 快指针的加速度比慢指针要快, 即快指针每次移动的步长比慢指针移动的步长多1. 这样若链表中有环则快指针最终总能比慢指针快整整一个环的长度从而追上慢指针. 若没有环则快指针永远不可能追上慢指针. 类似于跑步时如果一直跑, 跑得快的同学最终总能套跑得慢的同学一圈. 快慢指针在很多情景下都有很巧妙的应用. 后续可以在遇到多个相关题目后加以总结. 给出快慢指针解决本题的代码示例
| |
day10 2024-03-07
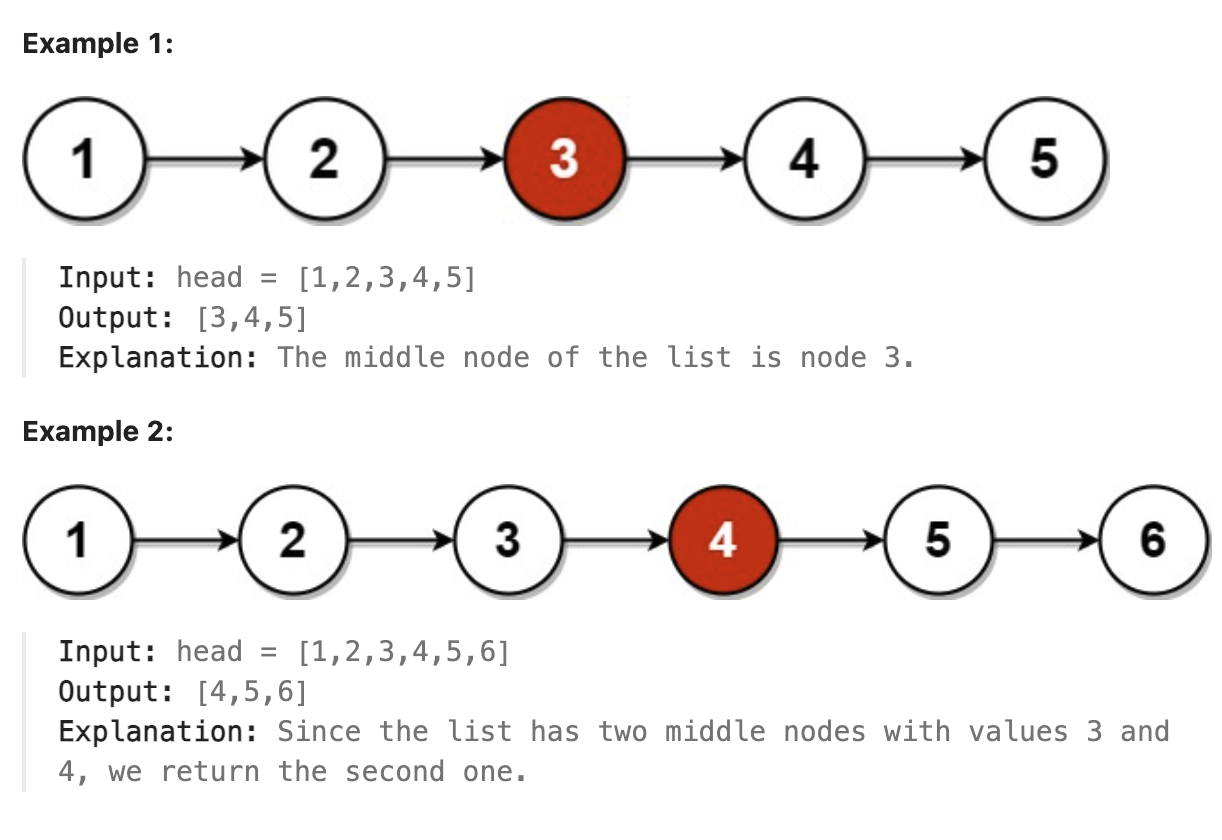
876. Middle of the Linked List
Given the head of a singly linked list, return the middle node of the linked list.
If there are two middle nodes, return the second middle node.
题解
本题寻找链表中间位置的元素, 是一个经典快慢指针的题目. 只需要让快指针前进的速度为2, 慢指针为1, 则快指针到达链表末尾时慢指针正好指向中间位置. 要注意链表元素个数为奇数和偶数时的处理方法的不同.
代码
| |
总结
本题是一道经典的快慢指针的简单题目, 进一步深化了快慢指针的应用.
day11 2024-03-08
3005. Count Elements With Maximum Frequency
You are given an array nums consisting of positive integers.
Return the total frequencies of elements in nums such that those elements all have the maximum frequency.
The frequency of an element is the number of occurrences of that element in the array.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,2,2,3,1,4] Output: 4 Explanation: The elements 1 and 2 have a frequency of 2 which is the maximum frequency in the array. So the number of elements in the array with maximum frequency is 4.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1,2,3,4,5] Output: 5 Explanation: All elements of the array have a frequency of 1 which is the maximum. So the number of elements in the array with maximum frequency is 5.
题解
因为题目给出了正整数的范围为1-100, 因此本题可以用简单的数组来解决, 数组下标表示对应的整数, 0不做任何表示. 然后遍历数组将频率最多的元素相加即可. 可以设置一个max标志位来表示当前的最大频率, 相等则增加和, 比max大则将和重置并设max为新的最大值.
代码
| |
总结
本题注意考查数据范围, 在数据范围有限的情况下直接使用数组要比哈希表快得多.
day12 2024-03-09
2540. Minimum Common Value
Given two integer arrays nums1 and nums2, sorted in non-decreasing order, return the minimum integer common to both arrays. If there is no common integer amongst nums1 and nums2, return -1.
Note that an integer is said to be common to nums1 and nums2 if both arrays have at least one occurrence of that integer.
Example 1:
Input: nums1 = [1,2,3], nums2 = [2,4] Output: 2 Explanation: The smallest element common to both arrays is 2, so we return 2.
Example 2:
Input: nums1 = [1,2,3,6], nums2 = [2,3,4,5] Output: 2 Explanation: There are two common elements in the array 2 and 3 out of which 2 is the smallest, so 2 is returned.
题解
本题使用两个指针分别指向两个数组, 然后依次移动两个指针比较大小即可, 位于数值更小的位置的数组指针向前移动直到相等或者到数组末尾为止.
代码
| |
总结
这是一道典型的双指针问题, 思路清晰就可以很快解决.
day13 2024-03-10
349. Intersection of Two arrays
Given two integer arrays nums1 and nums2, return an array of their intersection. Each element in the result must be unique and you may return the result in any order.
Example 1:
Input: nums1 = [1,2,2,1], nums2 = [2,2] Output: [2]
Example 2:
Input: nums1 = [4,9,5], nums2 = [9,4,9,8,4] Output: [9,4] Explanation: [4,9] is also accepted.
题解
因为数组是无序数组, 寻找二者的相同元素比较困难, 故可先对两数组排序, 然后双指针遍历两个数组找到数组中的相同值. 将值作为key, key对应的value为true放入map中. 这里不需要多余判断map中是否已经存在这个key了, 因为再次给相同的key赋值不会增加新的条目, 而只是覆盖之前的key的值, 我们只需要key来判断map中是否有相同值.
代码
| |
总结
在查看他人题解过程中, 发现排序其实是没有必要的, 可以直接将一个数组中的值全部作为key, 对应的value为true放入map中. 然后遍历另外一个数组, 同时判断当前遍历的元素在不在map中, 若存在则将其放入结果数组中, 同时将map中key对应的value置为false, 表示该key已经被访问过, 这样可以避免在结果数组中添加重复元素.
一个示例代码如下
| |
day14 2024-03-11
791. Custom Sort String
You are given two strings order and s. All the characters of order are unique and were sorted in some custom order previously.
Permute the characters of s so that they match the order that order was sorted. More specifically, if a character x occurs before a character y in order, then x should occur before y in the permuted string.
Return any permutation of s that satisfies this property.

题解
本题初始想先扫描s字符串, 使用一个map记录字符串中各个字符的数量, 再遍历order依次将字符按数量附加到末尾即可. 但考虑到字符只有26个小写英文字母, 使用一个长度为26的数组来保存对应位置的英文字母的数量. 再遍历要比map速度快.
代码
| |
总结
注意题中条件, 遍历的类型有限的情况下直接使用数组保存, 遍历起来速度要快得多.
day15 2024-03-12
1171. Remove Zero Sum Consecutive Nodes from Linked List
Given the head of a linked list, we repeatedly delete consecutive sequences of nodes that sum to 0 until there are no such sequences.
After doing so, return the head of the final linked list. You may return any such answer.
(Note that in the examples below, all sequences are serializations of ListNode objects.)

题解
本题有一定难度, 寻找连续的和为0的连续序列要使用前缀和, 若某两个元素的前缀和相同, 则位于二者之间的序列和即为0. 删除这部分序列. 先遍历链表, 找到所有前缀和相同的元素, 然后将其中间的部分全部删除即可. 使用一个map来保存前缀和对应的Node的指针, 当找到一个前缀和相同的Node时, 从map保存的指针开始删除到该Node的所有节点, 同时删除以中间部分节点的前缀和为key的map中对应的项防止后面有和中间部分项相同的前缀和的节点存在.
代码
| |
总结
删除中间部分节点的前缀和对应的key的项时, 考虑到中间部分的和一定为0, 因此用sum去累加中间部分节点的值并依次删除, 最后得到的sum就和删除节点开始前的sum相同. 本题一是要清楚通过前缀和来寻找连续的和为0的序列, 另一方面则是时刻记住这个序列的和为0的特性. 其实本题有一种代表元的抽象思想. 可以将一组和为0的序列看为一个, 其在加和过程中与不存在的节点具有等价性. 不影响和的变化.
day16 2024-03-13
2485. Find the Pivot Integer
Given a positive integer n, find the pivot integer x such that:
The sum of all elements between 1 and x inclusively equals the sum of all elements between x and n inclusively. Return the pivot integer x. If no such integer exists, return -1. It is guaranteed that there will be at most one pivot index for the given input.
Example 1:
Input: n = 8 Output: 6 Explanation: 6 is the pivot integer since: 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 + 6 = 6 + 7 + 8 = 21. Example 2:
Input: n = 1 Output: 1 Explanation: 1 is the pivot integer since: 1 = 1. Example 3:
Input: n = 4 Output: -1 Explanation: It can be proved that no such integer exist.
题解
本题使用数学方法进行计算
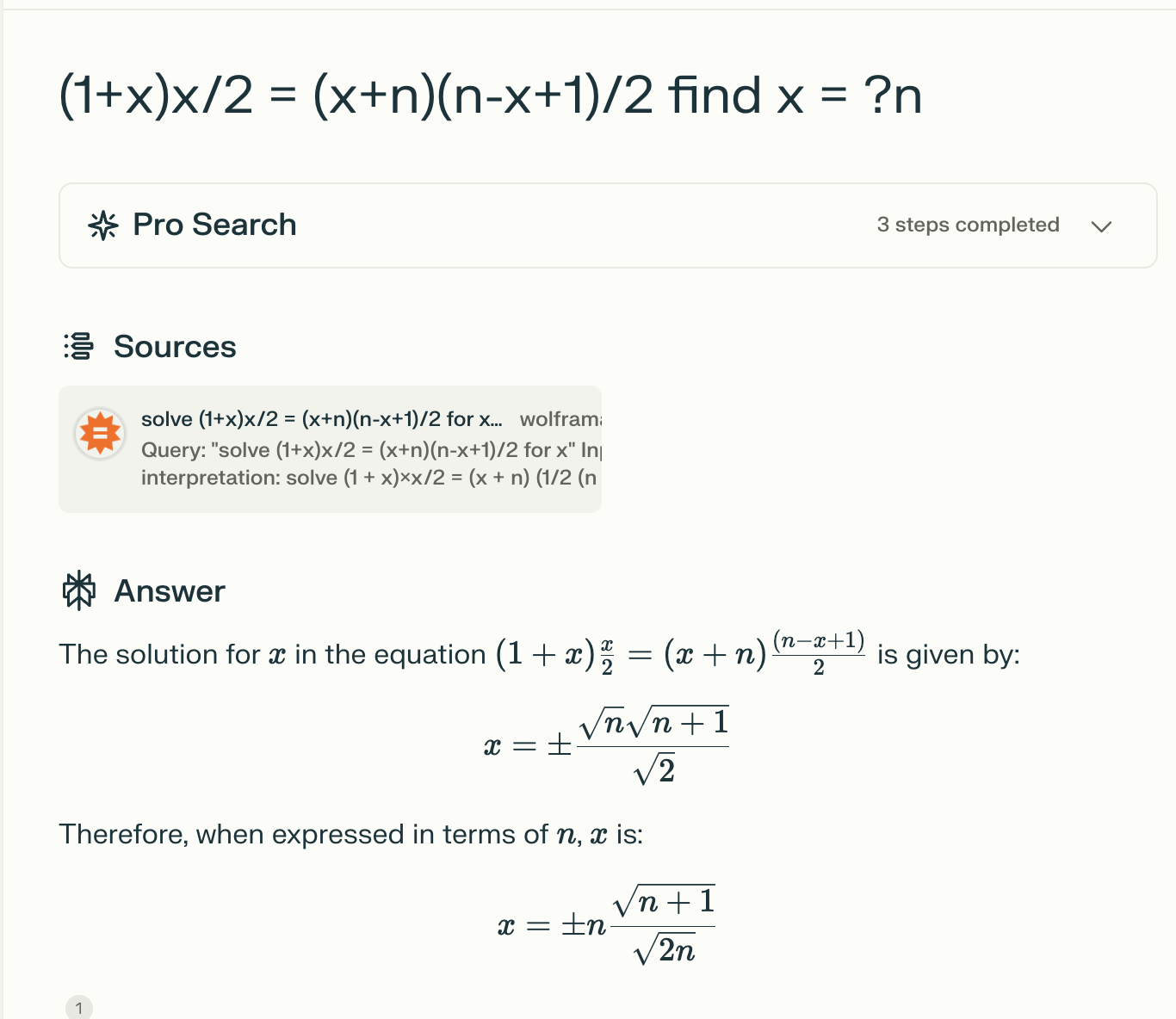 根据公式直接求出x的值即可, 注意考虑到精度问题, 要对最终得到的运算结果与取整后的数字的差的绝对值进行判断, 小于一定限度即可认为是整数值.
根据公式直接求出x的值即可, 注意考虑到精度问题, 要对最终得到的运算结果与取整后的数字的差的绝对值进行判断, 小于一定限度即可认为是整数值.
代码
| |
总结
查看他人解法发现本题其实也可以使用前缀和进行求解, 将每个下标位置处的前缀和求出并保存, 倒序遍历数组, 将后面的数的和与当前位置的前缀和比较即可, 示例代码
day17 2024-03-14
930. Binary Subarrays With Sum
Given a binary array nums and an integer goal, return the number of non-empty subarrays with a sum goal.
A subarray is a contiguous part of the array.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,0,1,0,1], goal = 2 Output: 4 Explanation: The 4 subarrays are bolded and underlined below: [1,0,1,0,1] [1,0,1,0,1] [1,0,1,0,1] [1,0,1,0,1] Example 2:
Input: nums = [0,0,0,0,0], goal = 0 Output: 15
题解
本题可以用前缀和求解, 类似这种求数组中连续和的问题都可以用前缀和求解, 首先计算出所有位置上的前缀和, 使用滑动窗口遍历前缀和数组, 根据goal的值调整窗口的左右边界, 注意0需要特殊处理, 0是否存在不影响整个序列的和, 0所在的位置处的前缀和和前面的元素相同.
代码
| |
总结
本题使用滑动窗口时间复杂度上比较高, 考虑在滑动窗口的过程中, 连续的0的部分被重复遍历, 大大增加了总体的运行时间. 其实本题只需要用当前的前缀和减去goal, 并寻找前面的前缀和中是否有符合差值的前缀和存在, 存在则从该前缀和位置到当前前缀和位置直接的序列满足和为goal的条件. 已经求出了前缀和就没必要再去一个个遍历并且滑动了, 如果使用滑动窗口则没必要计算前缀和. 我的解法实际上是对前缀和理解不深刻导致的. 巧用前缀和加哈希表(存储某个前缀和出现的次数)可以快速的解决这个问题. 示例代码如下
| |
还有一种极其巧妙的解法, 分别求得和小于等于goal的连续子序列的数量, 再减去和小于等于goal-1的连续子序列的数量即为最终结果. 本题中求子序列等于goal是比较困难的, 要考虑很多条件, 但是求小于等于goal的子序列却是比较简单的问题. 这种方法将一个困难问题转化为两个简单的子问题求解, 得到了更高效的方法. 充分利用整体性可使问题更简单. 代码如下
| |
day18 2024-03-15
238. Product of Array Except Self
Given an integer array nums, return an array answer such that answer[i] is equal to the product of all the elements of nums except nums[i].
The product of any prefix or suffix of nums is guaranteed to fit in a 32-bit integer.
You must write an algorithm that runs in O(n) time and without using the division operation.

题解
题目中明确要求本题不能使用分治法, 且算法复杂度在O(n). 本题要求的为数组中每个元素对应的除该元素之外的其他元素的乘积. 根据给出的例子可以发现当存在0的时候是一种特殊情况. 当存在0时除0以外的其他元素对应的结果均为0. 一般情况下可以使用先求出全部元素的乘积, 再遍历数据使用总乘积除以当前元素即可求得对应位置的结果. 因为这样只需要固定遍历两次数据, 故时间复杂度为O(n), 又只需要一个变量来保存总乘积, 一个变量指示是否存在0元素, 故空间复杂度为O(1). 因为题目中明确说明了乘积保证为整数, 故在使用除法的过程中不用考虑结果为小数的问题.
代码
| |
总结
查看更快的解法, 发现都使用了前缀积和后缀积, 即从前向后遍历, 计算出当前位置元素的前缀积, 然后反向遍历, 在计算出后缀积的同时就得到了最终的结果. 一个示例代码如下
| |
其实无论是前缀和还是前缀积, 都是一个对以往的计算状态的保留, 保存了更多的信息, 避免了重复的运算, 这种思想是值得细细品味的.
day19 525. Contiguous Array
Given a binary array nums, return the maximum length of a contiguous subarray with an equal number of 0 and 1.

题解
考虑本题若想找到到某一个位置处的0和1数量相同的最长子数组长度, 只需要根据到该下标处的0和1数量的差值, 找出符合这个差值的最小下标, 用当前下标减去这个差值下标, 得到的即为0和1数量相同的子数组的长度. 关键在于想要让0和1数量相同, 需要找出能消除当前0和1数量差值的位置. 0和1数量对于寻找相同数量子数组用处不大, 二者数量的差值对于构造一个数量相同的子数组至关重要. 通过加上或减去二者的数量差即可构造出二者数量相同的子数组. 考虑清楚这一点, 思路就很清晰了.
- 遍历数组, 保存到当前位置0和1的数量
- 计算二者的差值, 在一个哈希表中寻找以这个差值为key的项是否存在, 不存在则将差值为key, 当前下标作为该key对应的值插入哈希表. 若存在则用当前下标减去哈希表中以差值作为key的对应的下标值, 即得到到当前位置0和1数量相同的最长子数组的长度. 比较这个长度和保存的最长子数组长度, 更新最长子数组长度.
关键在与将差值作为key下标作为value插入哈希表后, 后续有相同的差值作为key时不在更新哈希表, 这样保存的就是符合这个差值的位置的最小值, 也就能构造出最长的0和1数量相同的子数组.
代码
| |
总结
本题和前几天的题目在思想上有异曲同工之妙, 也是前缀和的一种应用, 如果把0和1的数量差作为前缀和, 那么本题解题思路可简单概括为找到前缀和相等的位置的最远距离.
day20 2024-03-17
57. Insert Interval
You are given an array of non-overlapping intervals intervals where intervals[i] = [starti, endi] represent the start and the end of the ith interval and intervals is sorted in ascending order by starti. You are also given an interval newInterval = [start, end] that represents the start and end of another interval.
Insert newInterval into intervals such that intervals is still sorted in ascending order by starti and intervals still does not have any overlapping intervals (merge overlapping intervals if necessary).
Return intervals after the insertion.
Note that you don’t need to modify intervals in-place. You can make a new array and return it.

题解
遍历intervals, 将interval复制到结果数组中. 判断要插入的interval的start和end是否在当前interval中
- 在范围内则将新interval的start设置为当前interval的start. 使用相同的方式判断end的范围.
- 若start或end不在当前interval范围内且小于下一个interval的start, 则将start或者end设置为新interval的start或end. 此时新interval构造完成, 将后面的interval原样复制到result中即可.
代码
| |
总结
这种题思路上并没有特别之处, 但是判断逻辑比较繁琐, 需要耐心思考边界情况, 查看他人题解, 发现用原始数组与需要插入的interval做比较要比使用interval和原始数组的start和end做比较思路简单清晰得多, 这里还是对判断条件的变与不变理解的不够透彻, 需要插入的interval的start和end是不变的, 不断遍历原始数组与不变的start和end做比较要比使用不变的start和end去和不断变化的interval的start和end做比较判断起来容易得多. 找到不变的条件对于思路清楚的解决问题至关重要. 给出示例代码
| |
day21 2024-03-18
452. Minimum Number of Arrows to Burst Balloons
There are some spherical balloons taped onto a flat wall that represents the XY-plane. The balloons are represented as a 2D integer array points where points[i] = [xstart, xend] denotes a balloon whose horizontal diameter stretches between xstart and xend. You do not know the exact y-coordinates of the balloons.
Arrows can be shot up directly vertically (in the positive y-direction) from different points along the x-axis. A balloon with xstart and xend is burst by an arrow shot at x if xstart <= x <= xend. There is no limit to the number of arrows that can be shot. A shot arrow keeps traveling up infinitely, bursting any balloons in its path.
Given the array points, return the minimum number of arrows that must be shot to burst all balloons.

题解
本题描述的很复杂, 其实是寻找相互交错的数组有几组, 如果将数组的范围看作集合, 范围重叠的数组可以看作一个大集合, 那么就是寻找这样的集合的数目. 本题可用贪心算法, 先将这些数组按照x_start的大小从小到大排序, 然后遍历并寻找x_start在当前重合范围内的数组,并且将重合范围设置为当前重合范围和当前遍历的数组的x_end中的较小值以缩小重合范围. 直到当前数组不满足条件, 即可认为之前的数组需要一个arrow. 继续遍历, 重复该操作, 即可找到所有需要的arrow.
代码
| |
总结
本题的题目说明上有一些含糊, 根据题目说明, arrow只在竖直方向上移动, 也就是说, 必须要有重合的区间的数组才能用一个箭头, 假如有一个数组区间很大, 其和两个小区间重合但这两个小区间不重合, 按理来说应该使用两个arrow才能扎爆这三个气球, 但是看他人提交的代码中有如下一种代码, 似乎说明用一个arrow就可以. 究竟这种对不对有待进一步的思考. 代码如下
| |
day22 2024-03-19
621. Task Scheduler
You are given an array of CPU tasks, each represented by letters A to Z, and a cooling time, n. Each cycle or interval allows the completion of one task. Tasks can be completed in any order, but there’s a constraint: identical tasks must be separated by at least n intervals due to cooling time.
Return the minimum number of intervals required to complete all tasks.

题解
拿到本题, 最直接的想法就是将每种任务的数量统计出来, 从大到小排序, 然后按照冷却时间轮流按序执行不同的任务, 不能执行任务的时间片留空. 某种任务全部执行完后, 该任务占据的时间片也留空. 知道全部任务都执行完需要的时间就是最少时间. 这是一种贪心的思想, 简单思考其正确性, 因为即使调换顺序, 在执行到某个时间时也不会比这种贪心算法执行的任务更多.
代码
| |
总结
看了0ms的解法, 十分惊艳, 与其将任务一个一个的安放到插槽中, 不如直接按照频率最大的任务算出必须存在的空插槽的个数, 再用剩余的任务去填这些空插槽, 最后只需要将任务总数和剩余的空插槽个数相加即可得到最终的时长. 到这里我想到, 其实频率最高的任务留出的空插槽数目是固定的, 只要将除频率最高之外的任务总数和空插槽数目相比, 若小于空插槽数目, 则最后时长就是频率最高任务完成需要的时长. 这里需要将和频率最高的任务频率相同的任务数目先减一计算算到任务总数中, 最后再加到最终的时间总数上. 若大于空插槽数目, 最终结果就是任务数目.
| |
day23 2024-03-20
1669. Merge In Between Linked Lists
You are given two linked lists: list1 and list2 of sizes n and m respectively.
Remove list1’s nodes from the ath node to the bth node, and put list2 in their place.
The blue edges and nodes in the following figure indicate the result:
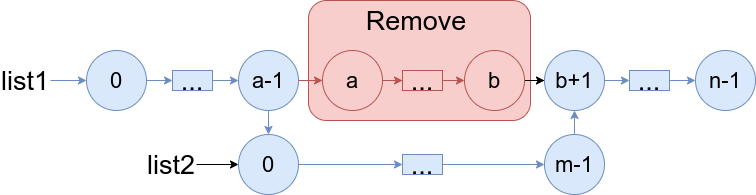
Build the result list and return its head.
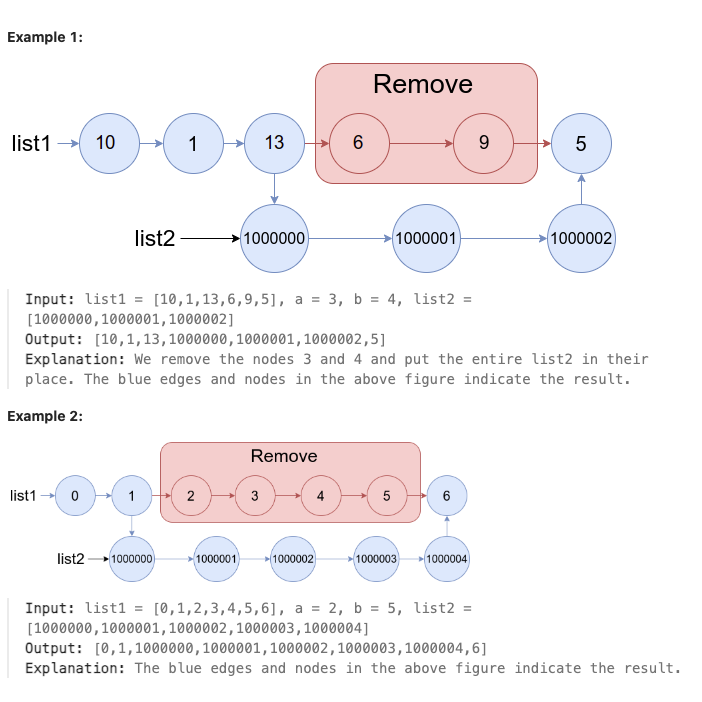
题解
本题为将链表中某段替换为指定的链表, 只需要遍历链表, 保存需要替换部分首尾两个节点的指针即可, 需要注意边界情况的处理, 即替换开头某段或者结尾某段链表时要处理空指针.
代码
| |
总结
本题保存了首尾两个指针的地址, 是典型的用空间换时间的思路, 不过实际应用过程中可能还要根据语言注意被动态分配出去的空间回收的问题.
day24 2024-03-21
206. Reverse Linked
Given the head of a singly linked list, reverse the list, and return the reversed list.
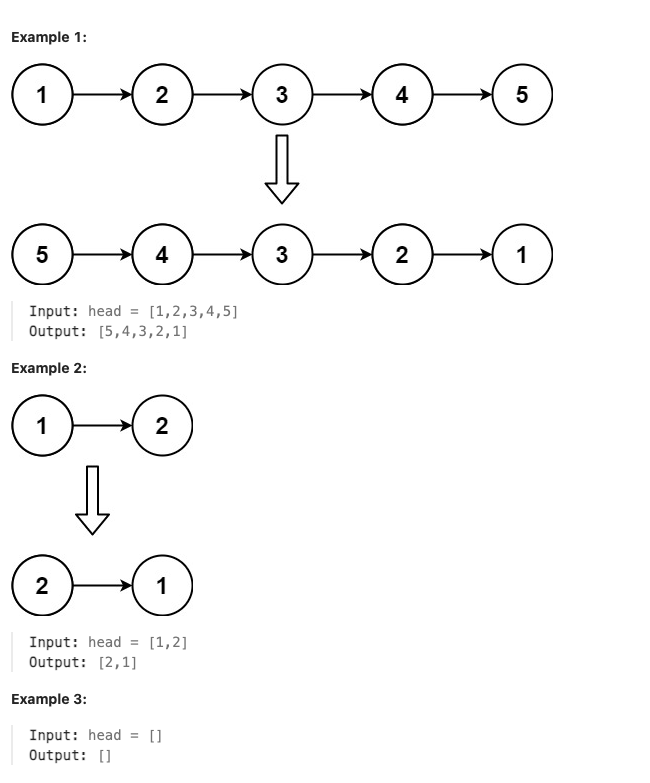
题解
本题相当基础, 是一道简单题, 只需要将链表整个反转过来即可. 用一个变量保存当前访问的节点的前一个节点的指针, 将当前节点的next修改为指向前一个节点的指针, 遍历整个链表即可. 注意处理边界情况(头指针为0).
代码
| |
总结
这两天都是链表相关的题目, 本题是一道基础题, 在查看他人解答的过程中发现本题也可以将链表数据全部复制出来, 再遍历链表逆序赋值即可. 示例代码如下
| |
day25 2024-03-22
234. Palindrome Linked
Given the head of a singly linked list, return true if it is a palindrome or false otherwise.
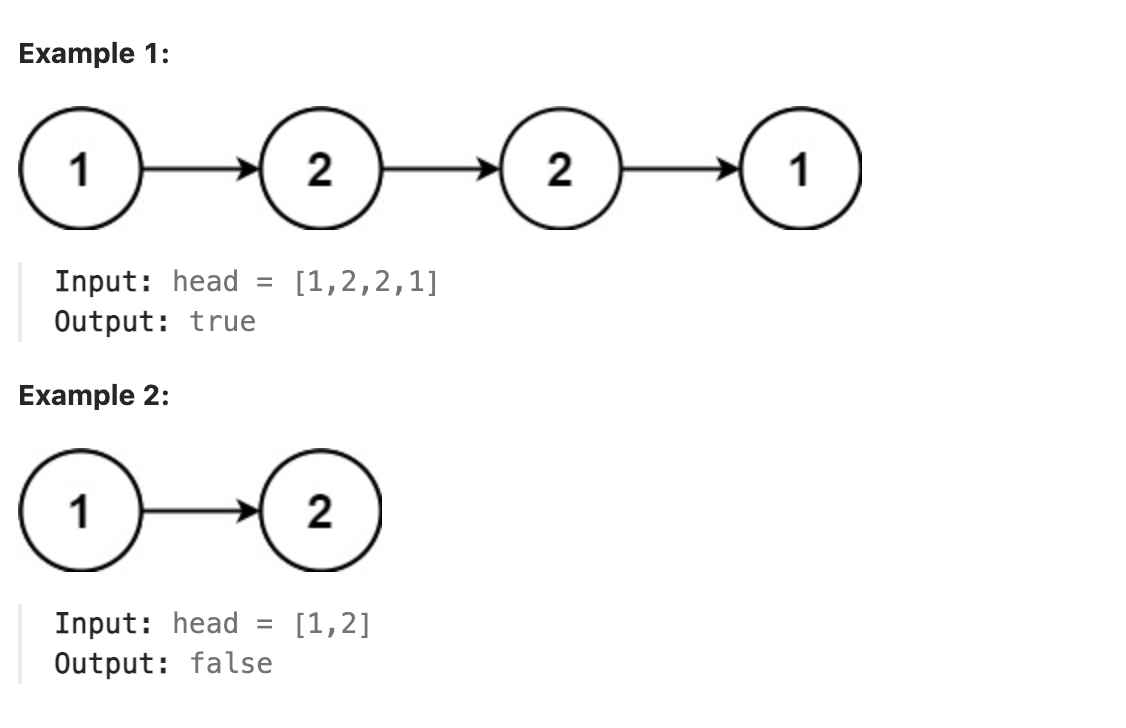
题解
本题也是一道基础题, 使用快慢指针的方法遍历到链表的中间, 在遍历的同时将链表的前半部分的值保存到数组中, 再从中间继续向后遍历, 遍历的同时反向遍历数组, 比较遍历的节点和遍历到的数组中元素的值. 若不同则不是回文, 直到全部遍历完成为止.
代码
| |
总结
查看用时较短的题解, 使用了快慢指针, 找到中间位置后将后半截链表反转, 然后从原始链表头部和反转的后半截链表头部开始依次遍历并比较即可. 这种方法时间复杂度为O(n), 空间复杂度为O(1), 代码如下
| |
day26 2024-03-23
143. Reorder
You are given the head of a singly linked-list. The list can be represented as:
L0 → L1 → … → Ln - 1 → Ln
Reorder the list to be on the following form:
L0 → Ln → L1 → Ln - 1 → L2 → Ln - 2 → …
You may not modify the values in the list’s nodes. Only nodes themselves may be changed.
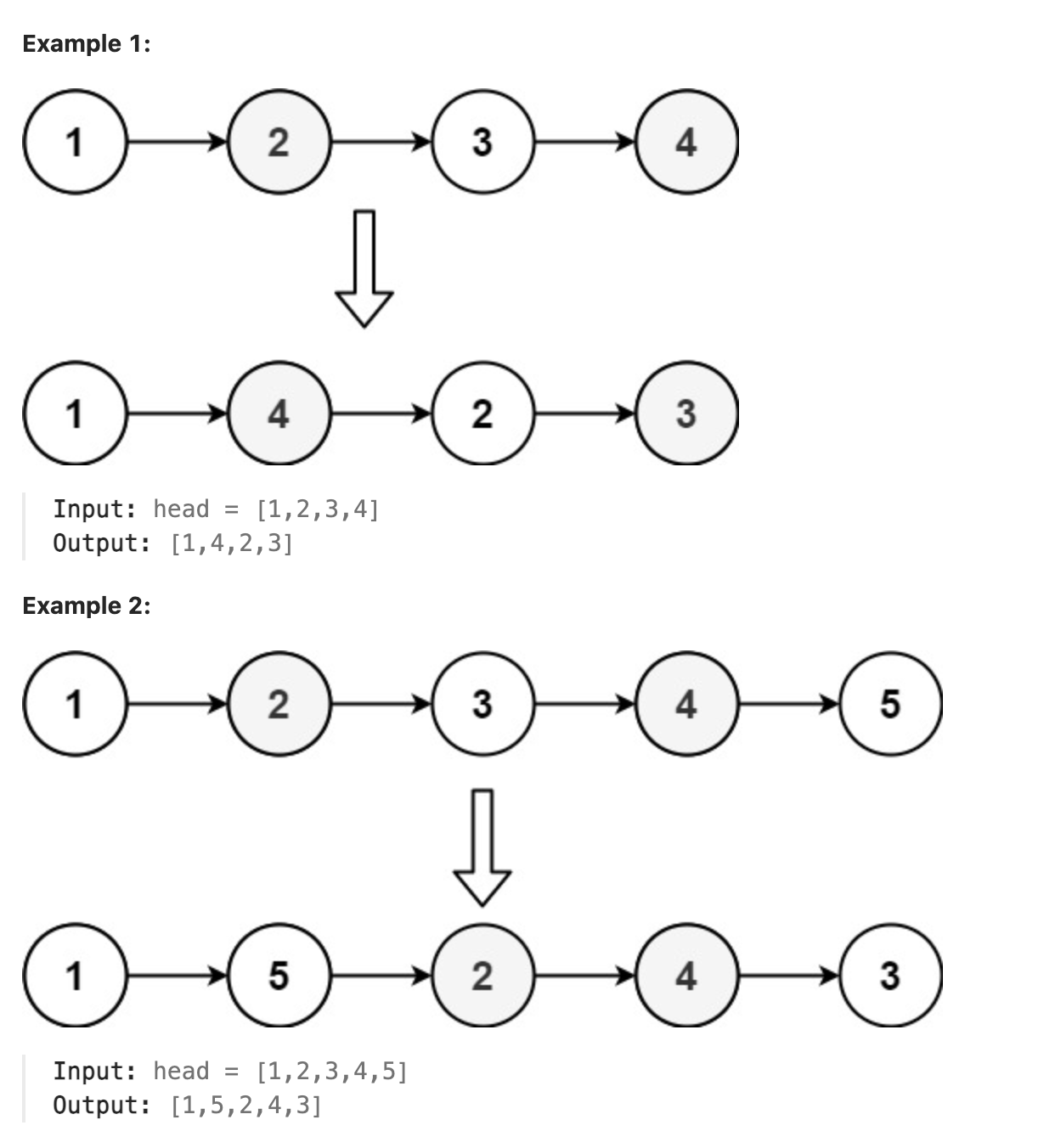
题解
拿到本题, 首先想到的是将链表中的全部数据保存到数组中, 然后通过同时从前后遍历数组并且给原来的链表赋值的方式, 即可快速解决本题, 如果不使用额外的空间, 可以使用快慢指针, 找到链表的中间节点, 从中间节点开始将链表的后半部分反向, 用两个指针分别从前半部分的开始和后半部分的末尾开始遍历, 并构造新链表即可. 也可以构造一个栈, 将链表的后半部分放入栈中, 然后从顶端一边出栈一边构造新链表即可. 题目中要求不能直接修改节点的值, 因此采用第三种思路.
代码
| |
总结
查看最快速度代码, 使用了一个数组先将链表的全部节点指针留一个间隔存放在数组中, 然后再逆序遍历数组将后半节点的指针逆序插入前面留出的空格中, 最后从头遍历数组, 连接整个链表即可. 这样写得出的代码比较简洁.
| |
day27 2024-03-24
287. Find the Duplicate Number
Given an array of integers nums containing n + 1 integers where each integer is in the range [1, n] inclusive.
There is only one repeated number in nums, return this repeated number.
You must solve the problem without modifying the array nums and uses only constant extra space.

题解
根据鸽笼原理, 显然必有一个数字有一个重复数字. 最简单的思路就是用每个数和数组其余数字比较, 直到找到相同的数为止, 显然这个方法的时间复杂度比较高, 要O(n^2). 最终并没有想出题目中要求的时间复杂度为O(n), 空间复杂度为O(1)的解法, 看题解得知使用的是Floyd 循环检测算法, 这个算法一般用于检测链表中是否存在环, 即使用快慢指针, 同时遍历链表, 如果存在环, 快指针最终会追上慢指针. 如果链表没有环, 则遍历链表最终会到达空指针自然停止, 这里的快慢指针是给了未知长度的链表一个停止条件, 可以避免若链表有环无限循环遍历下去. 这里将数组堪称链表是非常精妙的思路, 将数组中的值看作下一个节点在数组中的下标, 这样如果有两个节点相同, 则最终快指针和慢指针指向的下标会相同, 再从头遍历一次数组, 找到值为这个下标的数据, 即为重复的数.
代码
| |
day28 2024-03-25
442. Find All Duplicates in an Array
Given an integer array nums of length n where all the integers of nums are in the range [1, n] and each integer appears once or twice, return an array of all the integers that appears twice.
You must write an algorithm that runs in O(n) time and uses only constant extra space.

题解
本题若想在O(n)时间复杂度内求解, 必须在遍历数组的时候充分利用遍历过的数据提供的信息, 在后续充分利用已有信息, 在本题中, 遍历过程中的每个位置处的数本身就是信息. 若使用O(n)的空间复杂度, 可以创建一个和目标数组长度相同的空数组, 将遍历到的元素的数作为下标, 设定对应空数组中下标所在位置的值作为标记. 这样后续遍历时看到标记则知道这个数是重复的. 若想空间复杂度为O(1), 因为本题并没有要求不修改数组, 可以修改数组中以这个数为下标处的数据, 这里可以将其取相反数来表明这个下标已经出现过. 这也是因为体重明确说明数组中的数的范围在1-数组长度之间, 因此可以采用这种方法来标记数据是否已经出现, 如果有数大小超过数组长度, 这种方案就不适用了, 则必须使用O(n)的空间.
代码
| |
day28 2024-03-26
41. First Missing Positive
Given an unsorted integer array nums. Return the smallest positive integer that is not present in nums.
You must implement an algorithm that runs in O(n) time and uses O(1) auxiliary space.

题解
本题要求O(n)的时间复杂度和O(1)的空间复杂度, 解题思路上与昨天的题目相似, 考虑到数组长度为n, 即使是从1开始的连续正整数, 最大填充到n. 故用数组中的数作为下标修改对应位置的值来标记某个数是否存在是可行的. 但要注意, 当前数组中可能出负数和超过n的数字, 如果想使用将数作为下标将对应位置数设为负数的方式来提供信息, 则要先对负数和超过n的数字进行处理, 为了区分被标记的数和本身为负的数, 将负数和超过n的数修改为0. 再遍历数组按照昨天的思路将数作为下标, 将相应位置数设为负数标记已经访问. 这里可以将数全部设为-1. 最后再遍历一遍数组, 找到第一个数字大于等于0的数的下标, 即为丢失的最小正整数. 这样需要固定遍历三遍数组, 且空间复杂度为O(1).
代码
| |
总结
查看最快速代码, 其将负数直接修改为整数类型最大值, 对于超过数组长度的数直接忽略, 不作处理, 其余的当作下标取对应位置的相反数. 这样处理起来思路比较清晰.
day29 2024-03-27
713. Subarray Product Less Than K
Given an array of integers nums and an integer k, return the number of contiguous subarrays where the product of all the elements in the subarray is strictly less than k.

题解
本题要求返回的是连续的相邻子数组, 第一个想到的就是滑动窗口, 设置窗口的前后指针, 当窗口内的积<k时, 扩大窗口, 并增加计数, 当窗口内的积≥k时, 缩小窗口, 直到重新满足<k的条件为止. 这里增加计数的地方需要仔细考量, 并不是扩大窗口且积<k时, 就将计数加一, 因为该题是求积, 所以当两个数的积<k时, 其实已经包含了每个数都小于k在其中, 同理, 当三个数积<k时, 包含了任意两个的组合积都<k, 而本题只要求连续相邻的子序列. 故每次窗口扩大且符合条件时增加的计数应该为当前窗口的长度. (可以自己考虑一下从2个数扩大到3个数时默认新增了几种符合要求的子序列, 应该是包含新增加的数本身, 加上相邻一个数, 加上相邻两个数三种情况, 前面两个数的情况在之前已经计数过了)
代码
| |
总结
在查看速度更快的题解代码时, 发现可以通过内层循环一直缩小窗口到<k时, 才继续向下滑动窗口, 这样外层只需要不断向下遍历来扩大窗口即可. 这样写循环思路更清晰, 代码更简洁 如下
| |
想到这, 忽然明白, 其实核心在于只需要考虑以某个位置为结尾的向前连续符合要求的数组长度作为该位置处应该增加的计数数目即可. 这样就把整个问题拆分成了独立不关联的小问题. 将每个位置应该增加的计数数目累积, 就是最终的结果.
day30 2024-03-28
2958. Length of Longest Subarray With at Most K Frequency
You are given an integer array nums and an integer k.
The frequency of an element x is the number of times it occurs in an array.
An array is called good if the frequency of each element in this array is less than or equal to k.
Return the length of the longest good subarray of nums.
A subarray is a contiguous non-empty sequence of elements within an array.

题解
拿到本题, 直接思路就是使用滑动窗口, 使用一个哈希表来存储每个数字对应的个数, 在滑动的过程中, 扩大窗口时增加窗口新增数字的计数并不断更新最大长度, 直到当前数字的计数达到上限k开始缩小窗口, 缩小至当前数字计数小于k(缩小过程中的数都在哈希表中对应减掉频率)即可继续扩大窗口. 如此直到遍历完整个数组. 其实从解题思路上与昨天的题内核是十分相似的.
代码
| |
总结
查看前面10%更快的代码, 发现判断缩小窗口的结束可以用当前窗口前端达到上限的数在哈希表中对应的计数值来判断, 缩小窗口直到达到上限的数的计数值小于k即可结束, 这样整体代码更清晰, 更简洁, 如下
| |
day31 2024-03-29
2962. Count Subarrays Where Max Element Appears at Least K Times
You are given an integer array nums and a positive integer k.
Return the number of subarrays where the maximum element of nums appears at least k times in that subarray.
A subarray is a contiguous sequence of elements within an array.

题解
本题感觉就是昨天那道题的姊妹+升级版, 现在要求找到数组中包含的最大值, 其在这个子数组中的出现次数至少为k次. 这里明确题目中需要解决的两个问题. 1. 找到数组中的最大值 2. 对这个值在子序列中出现的次数进行计数. 无疑, 仍然可以使用滑动窗口来解决, 思路和昨天的题类似, 这里在扩大窗口时, 一直扩大到最大值数目为k, 继续向后遍历时要每次增加从头开始到包含k个最大值的窗口的最左端的元素个数. 核心思路在于让滑动窗口中只保留k个最大值, 这样所有包含前面数据的子数组和包含后面不为最大值的子数组的所有子数组都符合条件.
代码
| |
总结
查看他人的题解发现, 可以在保持窗口内最大值个数为k的思路下优化解题过程, 重复的加前面的元素是不必要的, 先将所有最大值的下标放入数组, 然后确定包含k个最大值的窗口的两端的下标, 将该窗口左侧前面的元素个数和窗口右侧后面的元素个数相乘即为该窗口对应的符合条件的解的个数, 切换到下一个包含k个最大值的窗口, 继续此操作, 直到窗口中最大值数目不足k为止.
| |
day32 2024-03-30
992. Subarrays with K Different Integers
Given an integer array nums and an integer k, return the number of good subarrays of nums.
A good array is an array where the number of different integers in that array is exactly k.
For example, [1,2,3,1,2] has 3 different integers: 1, 2, and 3.
A subarray is a contiguous part of an array.

题解
本题仍然使用滑动窗口, 这几天连续做滑动窗口的题, 总结了滑动窗口的"三要素": 1. 什么时候扩大窗口 2. 双么时候缩小窗口 3. 缩小和扩大窗口时执行哪些操作 对于本题, 题目中要求计数正好包含k个不同数的子数组的个数, 求精确包含k个这种问题往往比较困难, 可以转化为求解包含≤k个和≤k-1个不同数的子数组个数的差. 这种思路求解起来非常方便. 对于求解包含≤k个不同数的子数组的个数, 当数组中包含不同数个数不足k时, 扩大窗口同时将计数增加当前窗口的长度, 若为k+1, 则缩小窗口至正好完全去除了一个数(若某个数只出现了1次, 去掉后窗口内不同数个数就是k, 若不止一次, 则去掉了不同数个数也没有变化, 故要继续向下遍历). 最后求≤k和≤k-1情况的计数值做差即可.
代码
| |
总结
解题时没有注意题目限制, 后来查看最快解法发现忽略了题目中的数的范围, 题目中的数组中的数的大小不超过数组的长度, 数的范围已知, 因此可以使用数组代替哈希表来计数这样可以大大加快解题速度.
| |
day33 2024-03-31
2444. Count Subarrays With Fixed Bounds
You are given an integer array nums and two integers minK and maxK.
A fixed-bound subarray of nums is a subarray that satisfies the following conditions:
The minimum value in the subarray is equal to minK. The maximum value in the subarray is equal to maxK. Return the number of fixed-bound subarrays.
A subarray is a contiguous part of an array.

题解
本题先求出数组中包含上下界的所有可行子区域, 可行子区域指所有连续的符合上下界要求的最长区域. 将这些区域的头尾下标保存到一个二维数组中. 对于每个可行区域, 使用该区域包含的全部子数组的个数减去不满足上下界要求的子数组个数, 不满足上下界要求的子数组个数求解使用滑动窗口是比较容易的, 从头开始滑动, 窗口内只能包含上界或者下届或者都不包含. 若直接求解该区域中包含的满足上下界的子数组个数则比较困难. 用子数组总个数和不满足上下界要求的子数组个数做差即可得到想求的满足上下界的子数组个数. 对于每个子区域都执行这样的操作, 并将求得的满足条件的子数组个数加和即可得到最终的结果, 注意处理上下界都是同一个数的边界情况.
代码
| |
总结
本次解题代码的运行速度超过了100%的提交, 因此不再看他人的题解了, 同时庆祝一下自己拿到了3月份的奖章, 证明这个月每天都在坚持. 下个月希望能继续坚持下去.
day34 2024-04-01
58. Length of Last Word
Given a string s consisting of words and spaces, return the length of the last word in the string.
A word is a maximal substring consisting of non-space characters only.

题解
本题是一道简单题, 直接从头开始遍历, 遇到空格结束当前单词计数, 再遇到新字符时重新计数, 直到遍历完整个字符串即可.
代码
| |
总结
前面的题解大多用了go strings库中的函数来按空格分割字符串, 再返回最后一个分割出来的字符串长度. 一般实际应用中, 使用官方库是第一选择, 因为官方库大多对这些操作做了大量优化, 效率会高得多.
day35 2024-04-02
205. Isomorphic Strings
Given two strings s and t, determine if they are isomorphic.
Two strings s and t are isomorphic if the characters in s can be replaced to get t.
All occurrences of a character must be replaced with another character while preserving the order of characters. No two characters may map to the same character, but a character may map to itself.

题解
本题是一道简单题, 要求判定s和t是不是同构的, 即类似常说的ABB型这种结构. 本题使用一个哈希表记录字符与字符的映射即可, 如果出现了不同的映射则是不同构的.
代码
| |
总结
查看前面的题解, 发现了果然0ms用时的思路还是不同凡响, 用字符本身作为下标维护两个数组, 在遍历两个字符串的时候将两个字符串当前的字符作为下标, 将当前遍历的字符串的下标作为值放入两个数组中, 这样就记录了同时出现的两个字符最后的出现的下标, 如果这两个字符一直同时出现则二者下标一直是相同的, 若没有同时出现说明字符映射改变了, 没有继续之前的映射. 则两个字符串就是不同构的. 字符的本质是数, 那么字符可以表示更多的信息, 而不是字符本身, 将其作为数组下标就既使用了字符本身这个信息, 还使用了数组对应位置的元素这个信息, 能使用更多的信息就意味着更高的效率.
| |
day36 2024-04-03
79. Word Search
Given an m x n grid of characters board and a string word, return true if word exists in the grid.
The word can be constructed from letters of sequentially adjacent cells, where adjacent cells are horizontally or vertically neighboring. The same letter cell may not be used more than once.
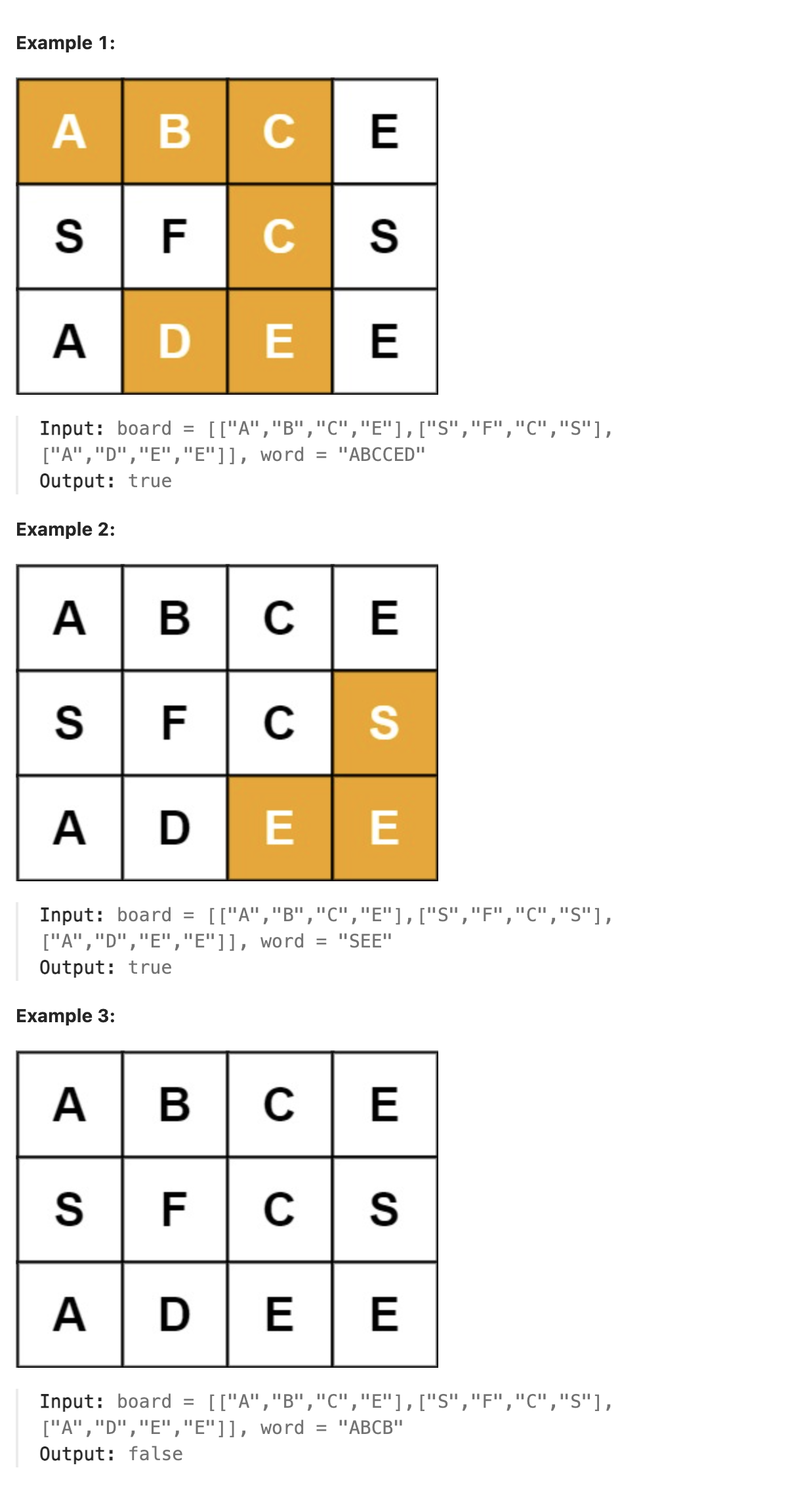
题解
本题可使用递归求解, 设置一个标记数组和board大小相同, 来标记已经访问过的元素, 遍历board数组, 找到目标字符串的起始字符, 对其调用explore函数求解, 若为true则直接返回true. 最后全部遍历完则返回false.
explore函数中, 传入了当前字符的行下标和列下标, 先判断可行的探索方向, 再在可行的探索方向上逐个判断其是否为目标字符串中的下一个字符以及是否已经被访问过, 若可以访问且为目标字符, 则对这个可行方向的字符调用explore函数继续后面的探索, 知道探索到目标字符串结尾则直接返回true. 若调用explore函数返回为true说明后面的字符串符合目标字符串且有可行路径, 则返回true. 若没有可探索方向或者所有可探索方向都不满足条件, 返回false.
使用递归要考虑的是在当前递归状态中应该完成什么任务以及递归的结束条件, 递归本质上是一种将全局问题化解为小的局部问题, 通过求解每个小的局部问题最终解决全局问题的解决问题的思路.
代码
| |
day37 2024-04-04
1614. Maximum Nesting Depth of the Parentheses
A string is a valid parentheses string (denoted VPS) if it meets one of the following:
It is an empty string “”, or a single character not equal to “(” or “)”, It can be written as AB (A concatenated with B), where A and B are VPS’s, or It can be written as (A), where A is a VPS. We can similarly define the nesting depth depth(S) of any VPS S as follows:
depth("") = 0
depth(C) = 0, where C is a string with a single character not equal to “(” or “)”.
depth(A + B) = max(depth(A), depth(B)), where A and B are VPS’s.
depth("(" + A + “)”) = 1 + depth(A), where A is a VPS.
For example, “”, “()()”, and “()(()())” are VPS’s (with nesting depths 0, 1, and 2), and “)(” and “(()” are not VPS’s.
Given a VPS represented as string s, return the nesting depth of s.

题解
本题是简单题, 因为题目说明了给定的括号一定是匹配的, 因此不用考虑括号匹配的问题. 只需设计一个值来保存当前还未匹配的左括号的个数, 这也是到当前这个字符的括号深度, 因此若出现了新的左括号, 就更新最大深度为当前的左括号个数和之前的最大深度中的较大值, 出现右括号则将未匹配的左括号个数减一, 最后返回最大深度即可.
代码
| |
day38 2024-04-05
1544. Make The String Great
Given a string s of lower and upper case English letters.
A good string is a string which doesn’t have two adjacent characters s[i] and s[i + 1] where:
0 <= i <= s.length - 2 s[i] is a lower-case letter and s[i + 1] is the same letter but in upper-case or vice-versa. To make the string good, you can choose two adjacent characters that make the string bad and remove them. You can keep doing this until the string becomes good.
Return the string after making it good. The answer is guaranteed to be unique under the given constraints.
Notice that an empty string is also good.

题解
本题可以使用类似简单回溯的方法, 遍历字符串并判断当前字符和下一个字符是否互为大小写, 若是则删掉两个字符同时将循环下标回退到当前字符的前一个, 继续遍历字符串, 如此反复直到到达字符串结尾即可, 注意处理字符位于字符串结尾和开始的边界情况.
代码
| |
总结
看到题解中有人使用栈, 通过额外的空间获得了更快的速度, 将前面的字符都入栈, 将栈顶和当前字符比较, 互为大小写则将栈顶出栈, 继续向下遍历并比较, 不互为大小写则将当前字符入栈. 这样不用回退下标, 可以充分利用go 中对for range循环优化带来的效率.
| |
day39 2024-04-06
1249. Minimum Remove to Make Valid parentheses
Given a string s of ‘(’ , ‘)’ and lowercase English characters.
Your task is to remove the minimum number of parentheses ( ‘(’ or ‘)’, in any positions ) so that the resulting parentheses string is valid and return any valid string.
Formally, a parentheses string is valid if and only if:
It is the empty string, contains only lowercase characters, or It can be written as AB (A concatenated with B), where A and B are valid strings, or It can be written as (A), where A is a valid string.

题解
本题实际上还是一个括号匹配的问题, 使用一个栈就可以解决问题, 与前一天题不同的是, 本题中的左括号不一定能完全被匹配, 所以栈中可以保存左括号的下标, 遍历到字符串末尾后, 将栈中仍然存在的未匹配的左括号全部删去即可.
代码
| |
day40 2024-04-07
678. Valid Parenthesis String
Given a string s containing only three types of characters: ‘(’, ‘)’ and ‘*’, return true if s is valid.
The following rules define a valid string:
Any left parenthesis ‘(’ must have a corresponding right parenthesis ‘)’.
Any right parenthesis ‘)’ must have a corresponding left parenthesis ‘(’.
Left parenthesis ‘(’ must go before the corresponding right parenthesis ‘)’.
‘*’ could be treated as a single right parenthesis ‘)’ or a single left parenthesis ‘(’ or an empty string “”.

题解
本题仍然是括号匹配问题, 只是这次加了一个万能字符’*’,相当于赖子,既可以当’(‘用也可以当’)‘用. 作为一个判定问题, 只需要判断字符串是否匹配即可. 因此使用一个变量记录当前未匹配的左括号个数和可以被匹配的星号个数, 当遇到未匹配的右括号时如果没有未匹配的左括号则使用星号匹配. 若遍历结束左括号没有剩余则匹配成功. 若星号个数比左括号少则直接匹配失败. 若左括号和星号仍有剩余, 且星号个数大于左括号时, 说明剩余的星号可能能完全匹配左括号,这时反向遍历,把’)‘作为之前的左括号看待,用同样的方法尝试匹配所有’(’. 最后只要’(‘能匹配成功即成功. p.s: 这里考虑的是正向遍历时若’)‘都匹配成功了, 那么只需要测试’(‘能否匹配就够了, 因为剩余的’)‘在正向遍历时已经确认可以通过多余的’*‘来完全匹配, 因此不用再考虑’)‘的匹配问题.
代码
| |
day41 2024-04-08
1700. Number of Students Unable to Eat Lunch
The school cafeteria offers circular and square sandwiches at lunch break, referred to by numbers 0 and 1 respectively. All students stand in a queue. Each student either prefers square or circular sandwiches.
The number of sandwiches in the cafeteria is equal to the number of students. The sandwiches are placed in a stack. At each step:
If the student at the front of the queue prefers the sandwich on the top of the stack, they will take it and leave the queue.
Otherwise, they will leave it and go to the queue’s end.
This continues until none of the queue students want to take the top sandwich and are thus unable to eat.
You are given two integer arrays students and sandwiches where sandwiches[i] is the type of the ith sandwich in the stack (i = 0 is the top of the stack) and students[j] is the preference of the jth student in the initial queue (j = 0 is the front of the queue). Return the number of students that are unable to eat.

题解
本题是一道简单题, 题干看似很长, 分析下来会发现, 若当前栈顶的三明治当前学生不喜欢, 就会向下轮换, 直到轮换到喜欢的学生, 因此栈顶三明治是否会被拿走取决于队伍中是否还有喜欢这种三明治的学生, 只要有这个学生总会被轮换到队伍的最前面. 则遍历学生数组, 统计两种三明治的喜欢的学生的数量. 遍历三明治数组, 遍历过程中减掉被拿走的三明治的类型喜欢的学生的数量, 直到三明治数组的当前元素没有学生喜欢, 则剩余的三明治就无法被拿到, 也就是无法吃到三明治的学生个数.
代码
| |
day42 2024-04-09
2073. Time Needed to Buy Tickets
There are n people in a line queuing to buy tickets, where the 0th person is at the front of the line and the (n - 1)th person is at the back of the line.
You are given a 0-indexed integer array tickets of length n where the number of tickets that the ith person would like to buy is tickets[i].
Each person takes exactly 1 second to buy a ticket. A person can only buy 1 ticket at a time and has to go back to the end of the line (which happens instantaneously) in order to buy more tickets. If a person does not have any tickets left to buy, the person will leave the line.
Return the time taken for the person at position k (0-indexed) to finish buying tickets.

题解
本题是一道简单题,并不需要去考虑模拟队列一轮一轮买票的过程, 而考虑队伍中的每个人在目标k买完票之前买了多少次票并将每个人中买的次数加和即可. 这里要将k之前和k之后的分开考虑, k之前的如果比k的需求大则在k买完之前都要买k需求的票的数量, 比k小则将自己的需求数量买完即可. 在k之后不同在于需求数大于等于k的人只会买k-1张票, 在k买完自己需要的票的时候这些人还在k的后面故当k买完时这些人最多买了k-1张. 遍历一遍数组按照这个规则将每个人的买票数加和即可得到最终结果.
代码
| |
day43 2024-04-10
950. Reveal Cards In Increasing Order
You are given an integer array deck. There is a deck of cards where every card has a unique integer. The integer on the ith card is deck[i].
You can order the deck in any order you want. Initially, all the cards start face down (unrevealed) in one deck.
You will do the following steps repeatedly until all cards are revealed:
Take the top card of the deck, reveal it, and take it out of the deck. If there are still cards in the deck then put the next top card of the deck at the bottom of the deck. If there are still unrevealed cards, go back to step 1. Otherwise, stop. Return an ordering of the deck that would reveal the cards in increasing order.
Note that the first entry in the answer is considered to be the top of the deck.

题解
本题为中等难度, 题目中的不变的为牌的数量, 目标即为将牌按照合适的顺序插入这个牌堆, 首先排序, 然后模拟取牌顺序将牌插入. 用一个数组保存当前牌堆中的可用位置. 设置可用位置为一个队列, 对于需要跳过的位置(即翻一张牌后下一张牌需要放到底部, 相当于跳过了这张牌)将其从队列头放到队列尾, 取出队列下一个位置并将当前牌插入, 再跳过一个位置, 插入一张牌, 如此重复直到清空队列.
代码
| |
总结
这样虽然写起来方便, 但实际上在不断append的过程中position会占用更多的空间, 使用循环队列可以避免空间的浪费.
day44 2024-04-11
402. Remove K Digits
Given string num representing a non-negative integer num, and an integer k, return the smallest possible integer after removing k digits from num.

题解
本题考虑数字中的某一位数字能产生的影响, 对应这个数字相邻的左右两个数字, 如果删掉了相邻的数字没有删掉当前这一位的数字, 在删除后的字符串中相当于用当前这一位数字代替了被删掉的相邻数字, 如果删掉了当前的数字没删掉相邻的数字, 同样相当于在这一位上用相邻的数字代替了被删掉的数字. 即在删除后的字符串中的这一位上用当前这一位的数字和相邻数字二选一, 前后的其余字符串不用考虑不影响这个局部变化. 仅考虑这个局部变化的过程, 最优解为在删除完毕的字符串中的当前位置应该放入较小的数字, 即相邻数字中较大的数应该被删去, 考虑左右相邻的对称性, 则可以得出, 删掉比左右相邻数字都大的数可以在删掉一个数后得到局部最优解, 删掉这个数后要回溯一位判断删除后之前的数是否符合条件. 重复此过程遍历数组, 删掉k个数后返回最终的字符串.
代码
| |
总结
本题自己想出的解法效率实在不太行, 思路上也不够简洁优美, 看了前面的题解, 发现从原来的思考的基础上应该进一步思考, 对于一串数字字符串来说, 可以删除的数字数量是有限的, 则要首先让数字的高位部分尽可能小, 删除的时候不能改变未删除的数字的相对位置, 根据之前的局部最优解的思考, 如果当前位置的数字比后一位大, 则应将这一位删掉, 让后一位占据当前位置, 这样保证了当前的数字一定比后一位数字小, 这样就做到了尽可能让小的数字位于前面, 使得每一步操作结束后的子数组具有单调性. 这也意味着之前考虑前后两个相邻数字的大小是多余的, 考虑后一位即可, 只需要使用一个单调栈来保证栈末尾的数比要入栈的数字小即可. 注意处理前导0和遍历一次字符串后没有删够元素的情况即可. 代码如下
| |
day45 2024-04-12
42. Trapping Rain Water
Given n non-negative integers representing an elevation map where the width of each bar is 1, compute how much water it can trap after raining.
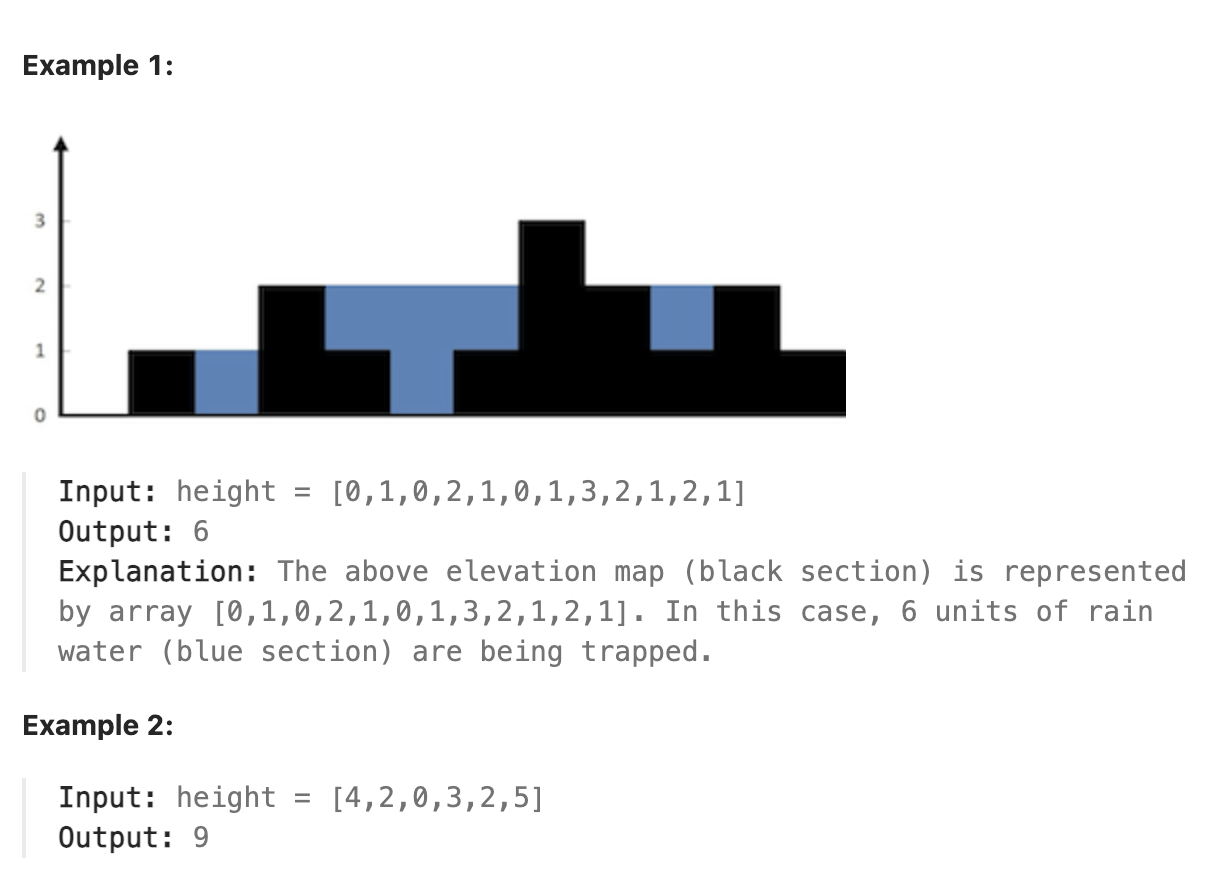
题解
本题是leetcode中一道经典难题, 思路上和昨天的题目有一些相似, 仍然思考局部的情况, 对于任一位置而言, 其在竖直方向上能接到的水的单位数与其自身的高度和其两侧的最高的"墙"的高度有关. 因此关键在于求出任一位置的两侧高度最高的"墙"的高度有多高. 可以使用两个数组来保存某一位置前面的最高的墙的高度和后面的最高墙的高度. 求最高墙的高度的过程可以通过动态规划解决, 用一个数记录当前位置左侧的最高墙高度是多少, 与自身比较, 如果该位置更高, 则更新最高高度, 否则将当前位置的左侧最高墙高度设置为之前的最高墙高度. 对于右侧同理.
代码
| |
总结
看题解时发现一种更巧妙高效的思路, 之前提到对每一个位置能接的雨水仅与其左右的最高墙高度有关, 那么可以把同时需要知道两个方向的信息固定为只需要考虑一个方向的信息即可. 如果当前位置右侧有墙比当前位置左侧所有墙都高, 那么只需要考虑当前位置左侧最高的墙有多高就可以计算出能接的雨水, 直到出现了墙比右侧的最高的墙还高, 此时就移动尾部的指向右侧最高墙的指针, 向左移动, 此时已知左侧的最高墙比目前尾部指针右侧的所有墙都高, 因此同样只需考虑右侧最高的墙有多高即可, 直到出现墙比左侧的最高墙高, 则再次交换主导权, 移动头部方向的指针. 如此轮换移动指针, 将需要同时比较两个方向的问题简化成了只需要比较一个方向的问题, 保留了更多的信息, 只需要遍历一遍数组即可求得结果.
| |
day46 2024-04-13
85. Maximal Rectangle
Given a rows x cols binary matrix filled with 0’s and 1’s, find the largest rectangle containing only 1’s and return its area.

题解
本题可以在一层层遍历矩阵的过程中, 将每一行中每个位置的元素按照如下规则进行操作加入到当前的列状态数组中. 若值为1且之前的列状态值大于0, 则增加对应的列状态值. 若值为0则用0替换对应的列状态值, 这样相当于在列状态中保存了从以该行为底该列中向上连续为1的值的个数. 根据当前的列状态即可求得到当前行为止以当前行为底的全为1的矩形区域中1的数量(仅包含1的矩形区域的面积). 如此不断遍历每一行并执行操作, 计算以该行为底的区域面积, 并更新面积最大值. 最后返回结果即可. 要解决的第二个问题就是如何求得以该行为底的最大矩形区域面积, 可以使用单调栈来保存之前的列的值, 如果遇到了比栈顶值小的列, 则将之前的最大列占据的面积求出来, 直到当前列值比栈顶大为止. 这里关键在于若后面的列值比前面某一个都大, 则前面的那一列的值可以一直扩展到后面, 在求面积时即用前面某一列的值乘以所有大于等于其值的连续的列的数量(即矩形的宽度)即可得到该列对应的得到的矩形面积. 而遇到更小的列时说明前面的某些列不能继续扩展了, 就要求出之前得到的面积是多少. 这里想起来有一些复杂, 可以细细思考一下.
代码
| |
day47 2024-04-14
404. Sum of Left Leaves
Given the root of a binary tree, return the sum of all left leaves.
A leaf is a node with no children. A left leaf is a leaf that is the left child of another node.
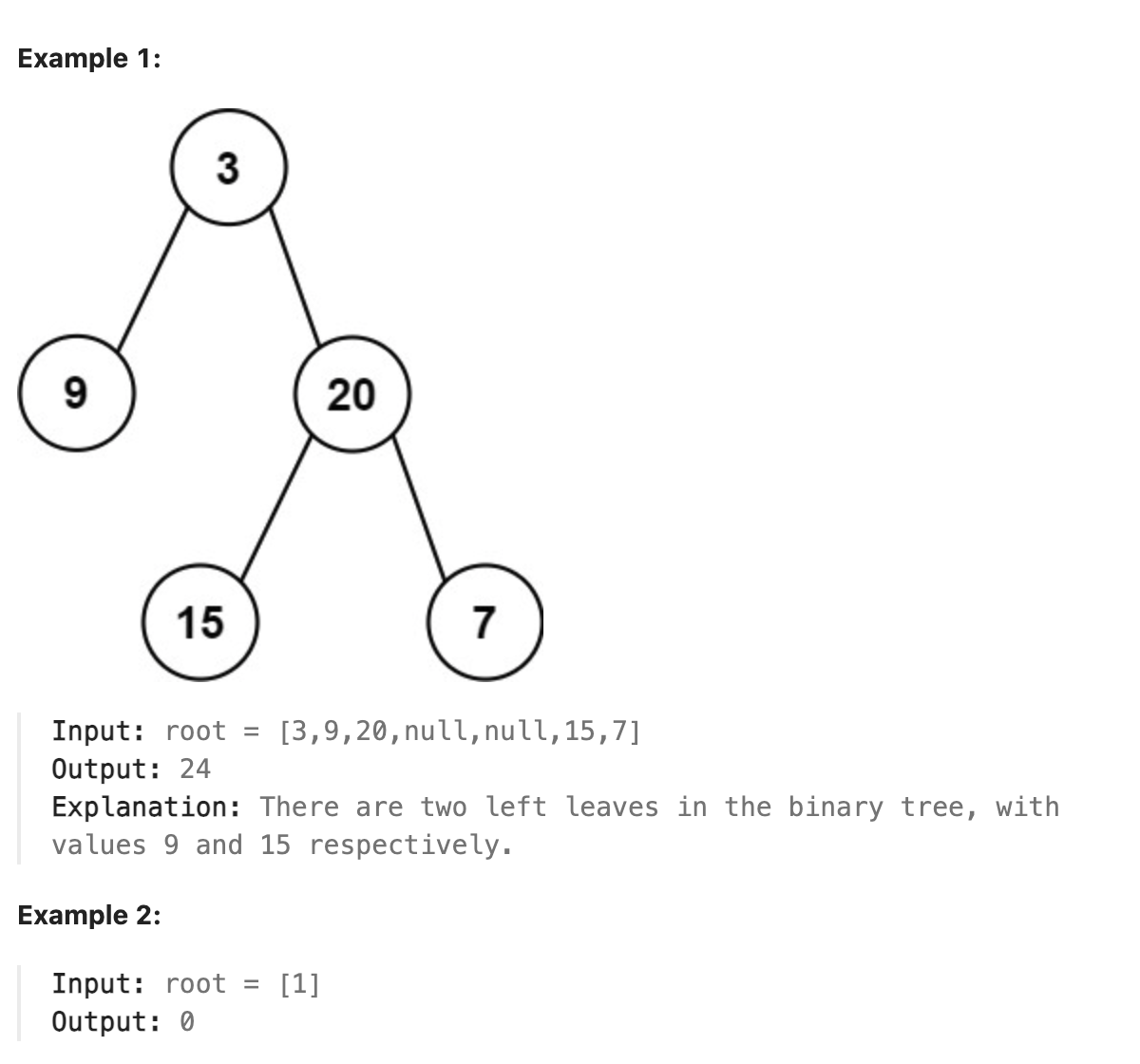
题解
本题是一道简单题, 使用深度优先搜索, 尾序遍历. 遍历的实现可以使用简单的递归函数, 注意对左右两个节点的处理方式不同, 对左节点如果其没有子节点则将值加到结果中, 对右节点则直接继续遍历即可.
代码
| |
day48 2024-04-15
129. Sum Root to Leaf Numbers
You are given the root of a binary tree containing digits from 0 to 9 only.
Each root-to-leaf path in the tree represents a number.
For example, the root-to-leaf path 1 -> 2 -> 3 represents the number 123. Return the total sum of all root-to-leaf numbers. Test cases are generated so that the answer will fit in a 32-bit integer.
A leaf node is a node with no children.
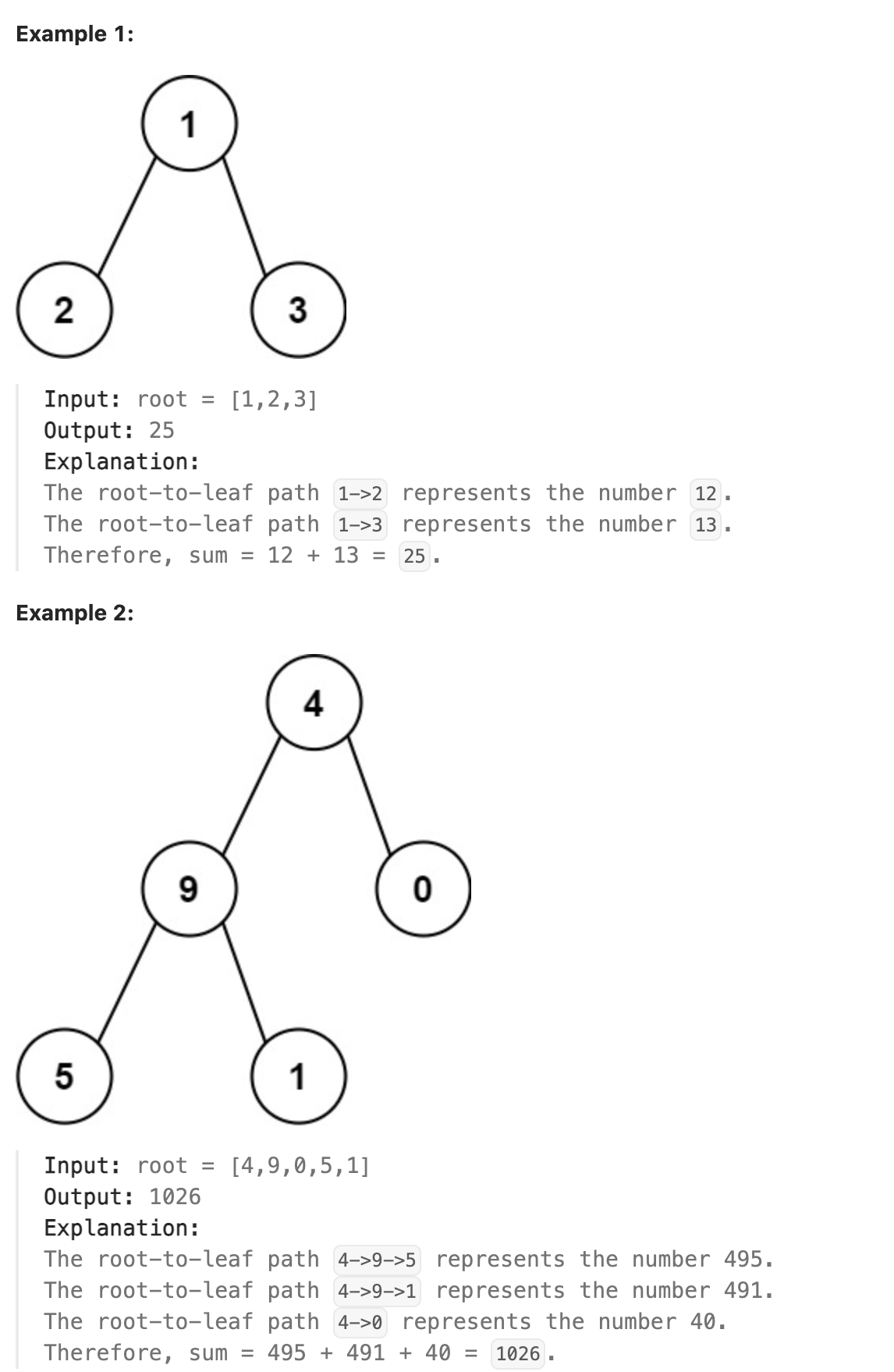
题解
仍然使用递归求解, 对树执行后序遍历, 在对子节点调用递归函数时将当前路径到该子节点的父节点组成的数字作为递归函数的参数, 子节点将该参数乘10后传给子节点的子节点, 并将子节点的两个子节点的返回值加和作为路径和返回给父节点. 若该子节点为叶子节点, 则加上叶子节点的值并返回. 最终在根节点将左右两子节点的返回值加和即可得到最终解.
代码
| |
总结
运行时间2ms本以为算法效率不够高, 结果看了看运行时间0ms的代码, 代码逻辑和我一模一样, 可能被优化的点在于递归函数中可以先判断是否为叶子节点, 再去创建sum变量. 其实这种将属性传递给子节点的方法在编译原理中的语义分析阶段很常用, 也就是属性文法, 可以看作一种继承属性, 更加详细的内容可以查阅编译原理相关的书籍.
day49 2024-04-16
623. Add One Row to Tree
Given the root of a binary tree and two integers val and depth, add a row of nodes with value val at the given depth depth.
Note that the root node is at depth 1.
The adding rule is:
Given the integer depth, for each not null tree node cur at the depth depth - 1, create two tree nodes with value val as cur’s left subtree root and right subtree root.
cur’s original left subtree should be the left subtree of the new left subtree root.
cur’s original right subtree should be the right subtree of the new right subtree root.
If depth == 1 that means there is no depth depth - 1 at all, then create a tree node with value val as the new root of the whole original tree, and the original tree is the new root’s left subtree.
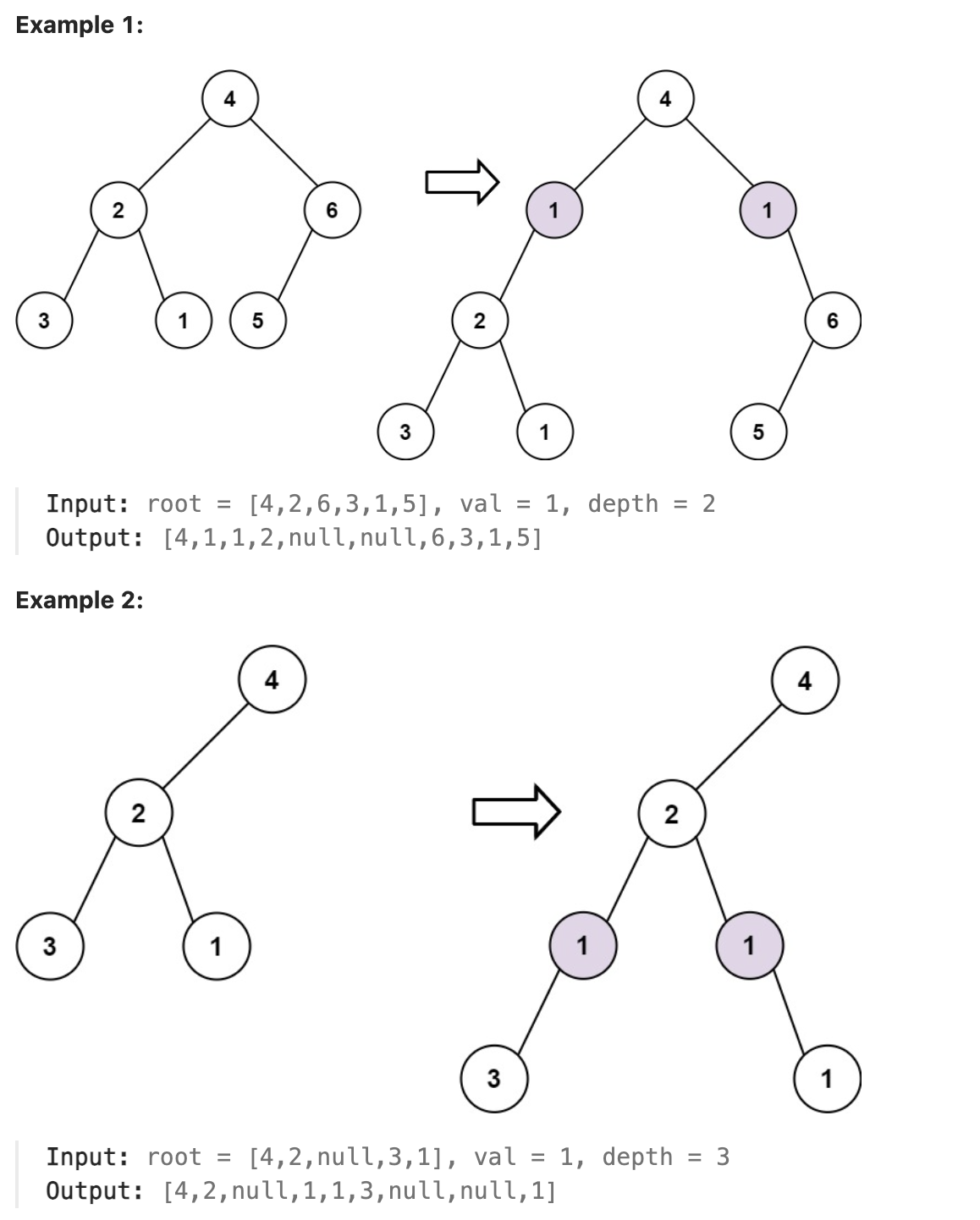
题解
本题使用层序遍历, 遍历到对应深度减一的节点时按规则插入节点, 注意处理只有一个节点的特殊情况即可.
代码
| |
总结
本题也可使用dfs结合变量记录当前深度来解决.
day50 2024-04-17
988. Smallest String Starting From Leaf
You are given the root of a binary tree where each node has a value in the range [0, 25] representing the letters ‘a’ to ‘z’.
Return the lexicographically smallest string that starts at a leaf of this tree and ends at the root.
As a reminder, any shorter prefix of a string is lexicographically smaller.
For example, “ab” is lexicographically smaller than “aba”.
A leaf of a node is a node that has no children.
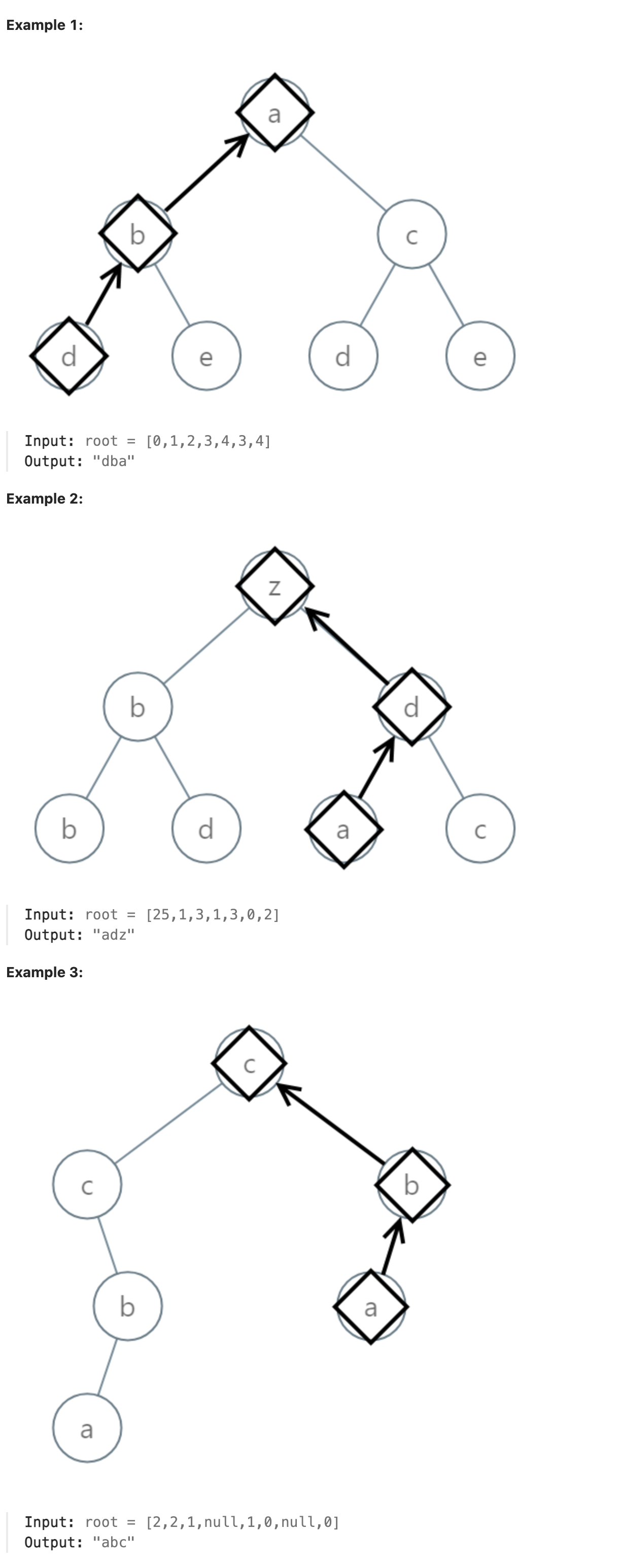
题解
使用递归实现dfs, 在dfs的过程中将路径上经过的节点数组作为参数传递给子节点, 对子节点执行dfs. dfs中将父路径的数组和左右两个子树返回的数组分别拼接, 对拼接后的数组进行比较, 将较小的作为返回值返回. 最终在根节点即可返回全局最小字典序字符串.
代码
| |
总结
本题看似简单, 实则有一些陷阱, 如果只考虑子树的字典序大小, 只比较子树的字典序大小并返回, 在比较过程中不考虑经过的父路径的话, 对于下面这种情况就会产生错误.
感兴趣的可以自行尝试只考虑子树的字典序, 对于这个例子会产生问题.
另外一方面, 看0ms的解答代码, 其不在dfs过程中比较, 而是直接通过dfs将这棵树能产生的全部字符串保存起来, 最后再对所有的字符串进行排序, 使用了go内置的sort排序, 返回排好序后的第一个字符串即最小的字符串. 这种方法减少了递归过程中的处理逻辑, 运行起来开销小得多, 所以速度比较快.
day51 2024-04-18
463. Island Perimeter
You are given row x col grid representing a map where grid[i][j] = 1 represents land and grid[i][j] = 0 represents water.
Grid cells are connected horizontally/vertically (not diagonally). The grid is completely surrounded by water, and there is exactly one island (i.e., one or more connected land cells).
The island doesn’t have “lakes”, meaning the water inside isn’t connected to the water around the island. One cell is a square with side length 1. The grid is rectangular, width and height don’t exceed 100. Determine the perimeter of the island.
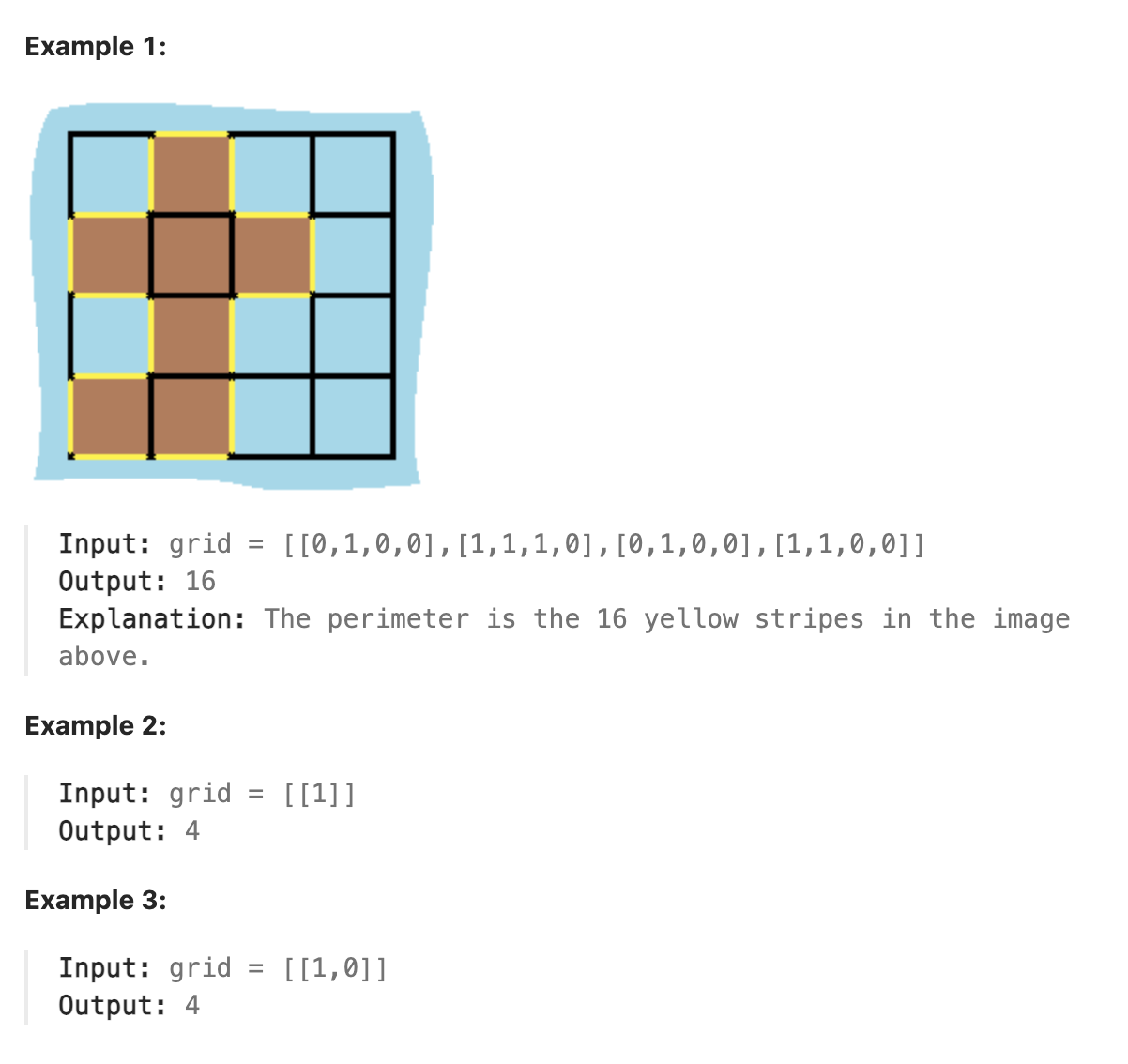
题解
本题直接遍历二维数组, 当遇到值为1即陆地时对四个方向进行判断并对与水面相邻的陆地的边界进行累加即可.
代码
| |
总结
在查看题解的过程中, 发现尽管算法思路相同, 但实现起来有一种比较巧妙的方法, 如下
| |
day52 2024-04-19
200. Number of Islands
Given an m x n 2D binary grid grid which represents a map of ‘1’s (land) and ‘0’s (water), return the number of islands.
An island is surrounded by water and is formed by connecting adjacent lands horizontally or vertically. You may assume all four edges of the grid are all surrounded by water.

题解
本题遍历矩阵, 遇到1时对该元素执行bfs, 并将搜索过程中遇到的所有1置为0. 搜索结束后将最终结果加一. 继续遍历, 重复此过程即可.
代码
| |
总结
本题我的解法中使用队列来执行bfs, 使用数组来模拟队列的过程中出队入队都会消耗资源, 增加执行时间. 实际上本题无需额外空间, 因为数组是可以修改的, 只需要找到1并将与该1连接的岛屿的所有1置为0即可, 这个过程可以使用dfs来实现,在dfs的过程中目标仅为将所有相连岛屿的1置为0, 因此返回值并不重要. 这种方法省去了队列操作的开销, 下面这种总体比较简洁, 值得学习.
| |
day53 2024-04-20
1992. Find All Groups of Farmland
You are given a 0-indexed m x n binary matrix land where a 0 represents a hectare of forested land and a 1 represents a hectare of farmland.
To keep the land organized, there are designated rectangular areas of hectares that consist entirely of farmland. These rectangular areas are called groups. No two groups are adjacent, meaning farmland in one group is not four-directionally adjacent to another farmland in a different group.
land can be represented by a coordinate system where the top left corner of land is (0, 0) and the bottom right corner of land is (m-1, n-1). Find the coordinates of the top left and bottom right corner of each group of farmland. A group of farmland with a top left corner at (r1, c1) and a bottom right corner at (r2, c2) is represented by the 4-length array [r1, c1, r2, c2].
Return a 2D array containing the 4-length arrays described above for each group of farmland in land. If there are no groups of farmland, return an empty array. You may return the answer in any order.
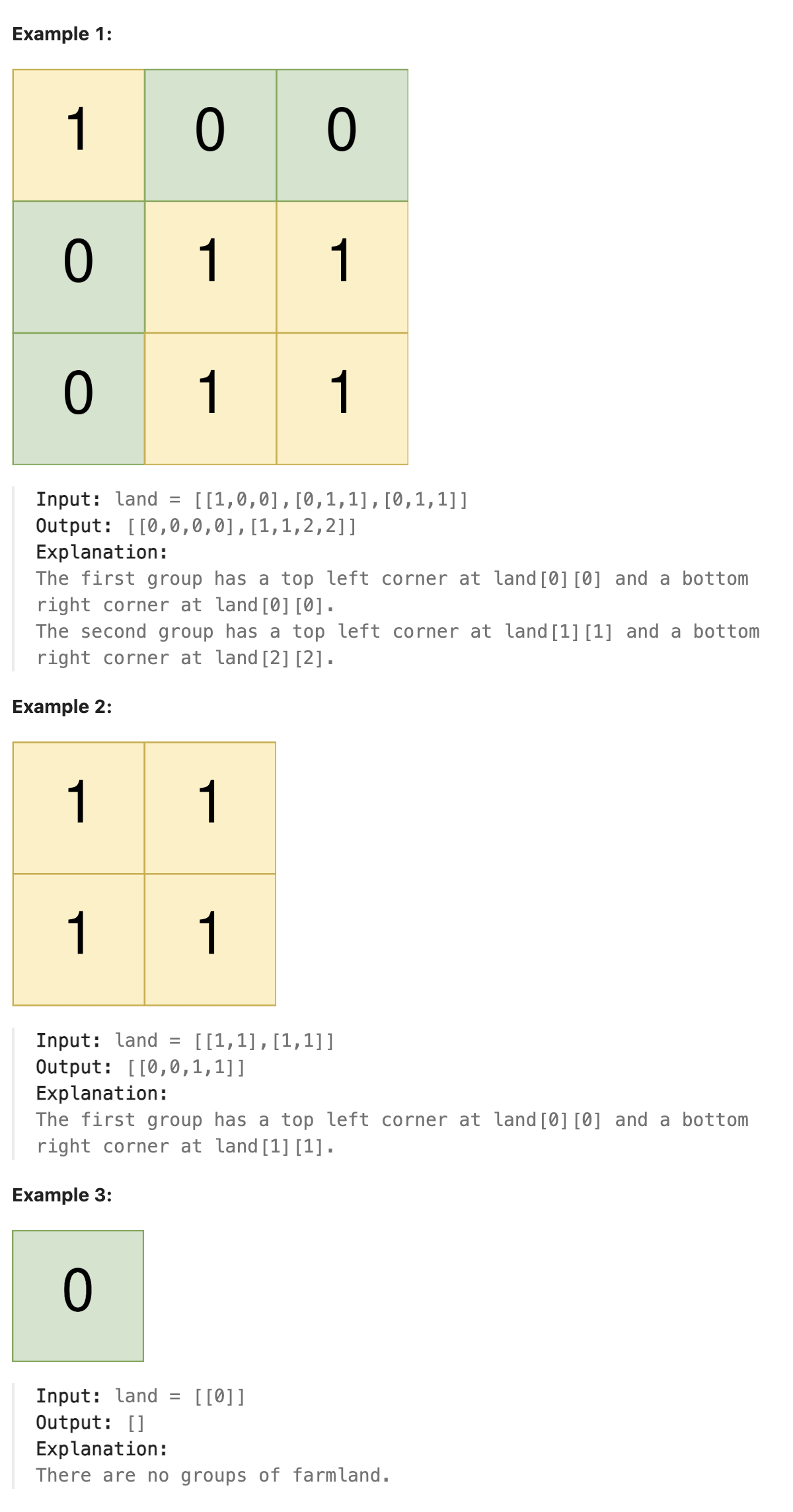
题解
本题限定了农田只会是一个矩形, 因此遍历数组,遇到1时向右向下遍历, 即可知道这个矩形的长和宽. 将左上和右下坐标插入矩形坐标数组中, 并将该片矩形全部置零. 如此反复即可. 在全部置零后将右下角坐标插入矩形坐标数组中, 并将坐标数组放入结果数组.
代码
| |
day54 2024-04-21
1971. Find if Path Exists in Graph
There is a bi-directional graph with n vertices, where each vertex is labeled from 0 to n - 1 (inclusive). The edges in the graph are represented as a 2D integer array edges, where each edges[i] = [ui, vi] denotes a bi-directional edge between vertex ui and vertex vi. Every vertex pair is connected by at most one edge, and no vertex has an edge to itself.
You want to determine if there is a valid path that exists from vertex source to vertex destination.
Given edges and the integers n, source, and destination, return true if there is a valid path from source to destination, or false otherwise.
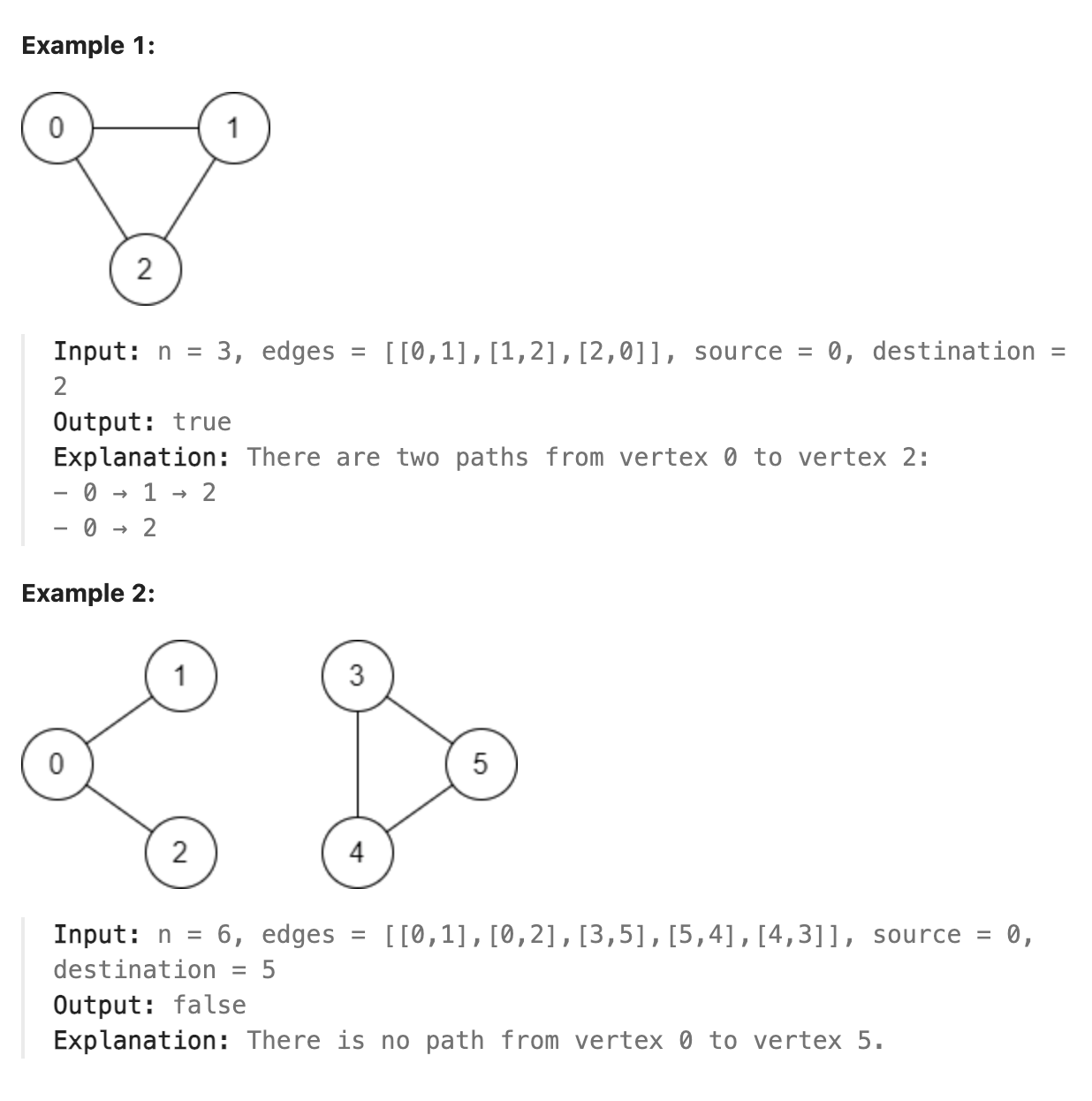
题解
本题使用并查集即可快速解决, 因为若两个节点连通, 两个节点必定位于同一个连通图中, 而每个连通图可以通过并查集使用一个节点的值来表示, 因此遍历所有边并构造并查集, 最终比较源点和目标点所在的并查集的代表元(即用来代表一个连通图的节点的值)是否相同即可确定是否有通路.
代码
| |
总结
最快的解法同样使用了并查集, 不过将并查集的操作都单独写成了对应的函数. 同时使用了数组来保存集合中某个元素的父元素是什么, 数组下标表示某个节点, 对应的值表示其父节点的值. 这样查询速度更快, 不过浪费了一些空间.
| |
day55 2024-04-22
752. Open the Lock
You have a lock in front of you with 4 circular wheels. Each wheel has 10 slots: ‘0’, ‘1’, ‘2’, ‘3’, ‘4’, ‘5’, ‘6’, ‘7’, ‘8’, ‘9’. The wheels can rotate freely and wrap around: for example we can turn ‘9’ to be ‘0’, or ‘0’ to be ‘9’. Each move consists of turning one wheel one slot.
The lock initially starts at ‘0000’, a string representing the state of the 4 wheels.
You are given a list of deadends dead ends, meaning if the lock displays any of these codes, the wheels of the lock will stop turning and you will be unable to open it.
Given a target representing the value of the wheels that will unlock the lock, return the minimum total number of turns required to open the lock, or -1 if it is impossible.

题解
本题题面非常有意思, 关键是怎么转化这道题. 首先思考如果只有两个转盘, 那么问题可以转化成在一个二维平面上从点(0,0)走到目标点的有障碍物最短路问题, 即在二维数组中, 从(0,0)走到目标点,每次只能向相邻方向移动一位, 同时有一些坐标是不能走得(可以理解为有障碍物). 对于这个问题, 无疑首先想到的就可以通过BFS求解. 将这个问题从二维扩展到四维, 因为每个转盘只有0-9 共10个数字, 所以每一维只需要10个数表示即可, 这样问题就变成了在一个10*10*10*10的四维数组中, 从(0,0,0,0)走到目标点的最短路问题, 其中数组中有些位置是不可达的. 同样使用和二维数组中类似的BFS求解即可.
代码
| |
总结
遇到题面看上去复杂的题目需要将题目的核心问题抽离出来. 若题目本身解决起来比较困难, 可以先尝试思考解决题目的一个子问题, 如降低维度, 减少数量, 再尝试推广到题目本身. 另外在数学中往往从一维到二维有很多不同点, 可能需要全新的工具和解决方式. 但从二维到更高维往往只是简单推广, 这也是为什么很多数学问题只证明二维的情况即可代表全部高维情况的原因.
day56 2024-04-23
310. Minimum Height Trees
A tree is an undirected graph in which any two vertices are connected by exactly one path. In other words, any connected graph without simple cycles is a tree.
Given a tree of n nodes labelled from 0 to n - 1, and an array of n - 1 edges where edges[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that there is an undirected edge between the two nodes ai and bi in the tree, you can choose any node of the tree as the root. When you select a node x as the root, the result tree has height h. Among all possible rooted trees, those with minimum height (i.e. min(h)) are called minimum height trees (MHTs).
Return a list of all MHTs’ root labels. You can return the answer in any order.
The height of a rooted tree is the number of edges on the longest downward path between the root and a leaf.
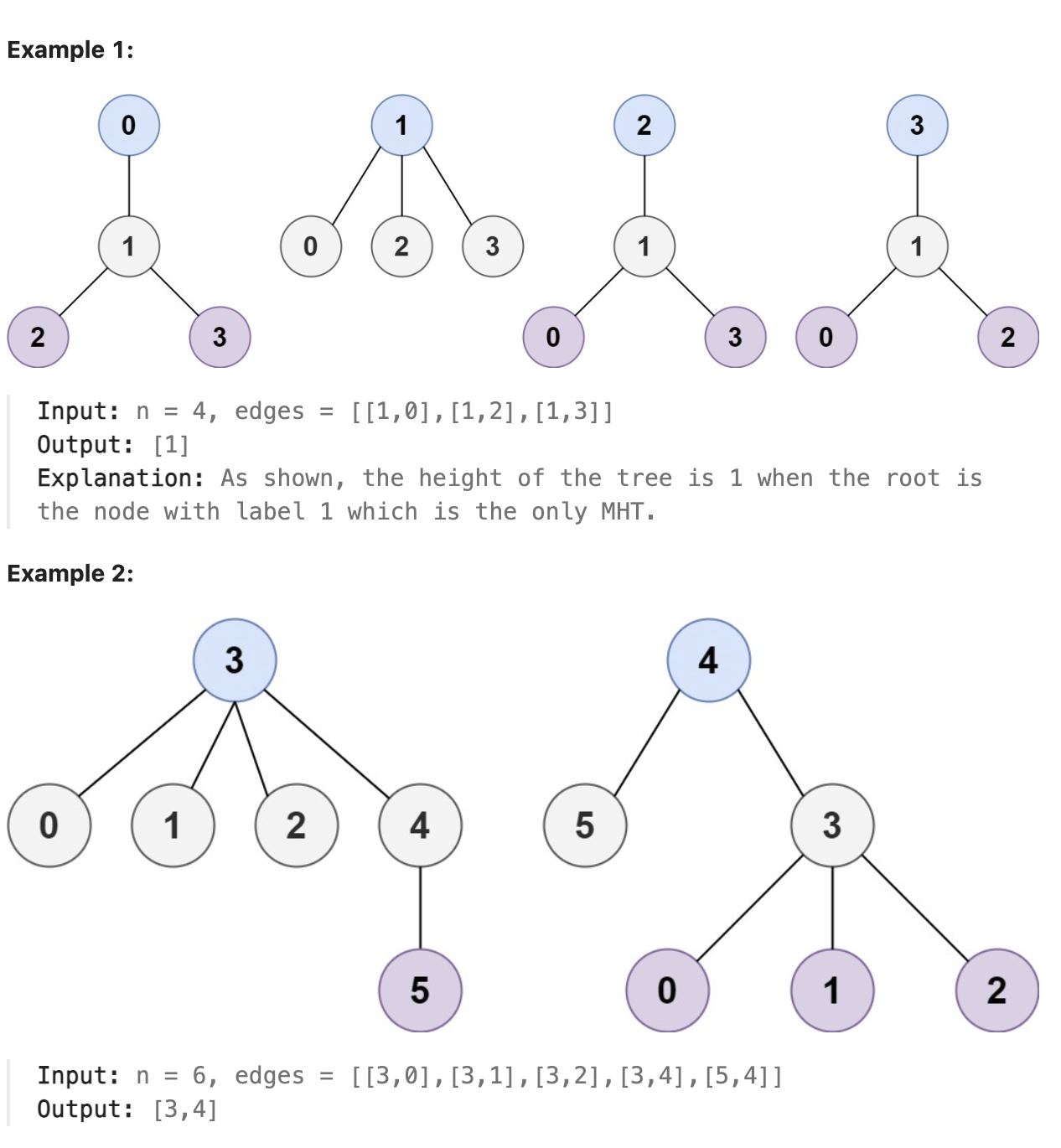
题解
本题乍一看让人摸不着头脑, 细细想想最远的距离肯定是从一个叶子节点到另一个叶子节点, 那么最小高度的子树就是位于这个最远路径上中间位置的一个或者两个节点(取决于路径的长度是奇数还是偶数). 则本题的关键在于求出该无向图中的最长路径, 求出无向图中最长路径可以选择任一叶子节点, 对其进行dfs, 再将得到的当前最长路径的终点作为起点, 进行dfs即可得到全图的最长路径.
代码
| |
总结
显然, 这种解法是相当慢的, 执行两次dfs也有大量的重复计算. 这里解决本题可以使用对无向图的拓扑排序. 排序操作为设定一个队列, 找到当前图中所有度为1的点, 将其删去(从队列中弹出)并删去其邻接的边, 将与其相邻的点中度为1 的点放入队列. 如此重复, 直到队列中只有一个或者两个点, 即为整个图中的最长路径的中间点. 这里要理解拓扑排序其实是对图的从边缘到中心的一种刻画. 也就是对依赖关系的刻画. 越靠近"中心"的点依赖越多. 排序过程中越靠前的点离图的"中心"越远. 依赖越少. 代码如下, 很简洁
| |
day57 2024-04-24
1137. N-th Tribonacci Number
The Tribonacci sequence Tn is defined as follows:
T0 = 0, T1 = 1, T2 = 1, and Tn+3 = Tn + Tn+1 + Tn+2 for n >= 0.
Given n, return the value of Tn.

题解
一个简单的动态规划即可.
代码
| |
今天题目有些过于简单了,遂再补一道题
2385. Amount of Time for Binary Tree to Be Infected
You are given the root of a binary tree with unique values, and an integer start. At minute 0, an infection starts from the node with value start.
Each minute, a node becomes infected if:
The node is currently uninfected. The node is adjacent to an infected node. Return the number of minutes needed for the entire tree to be infected.
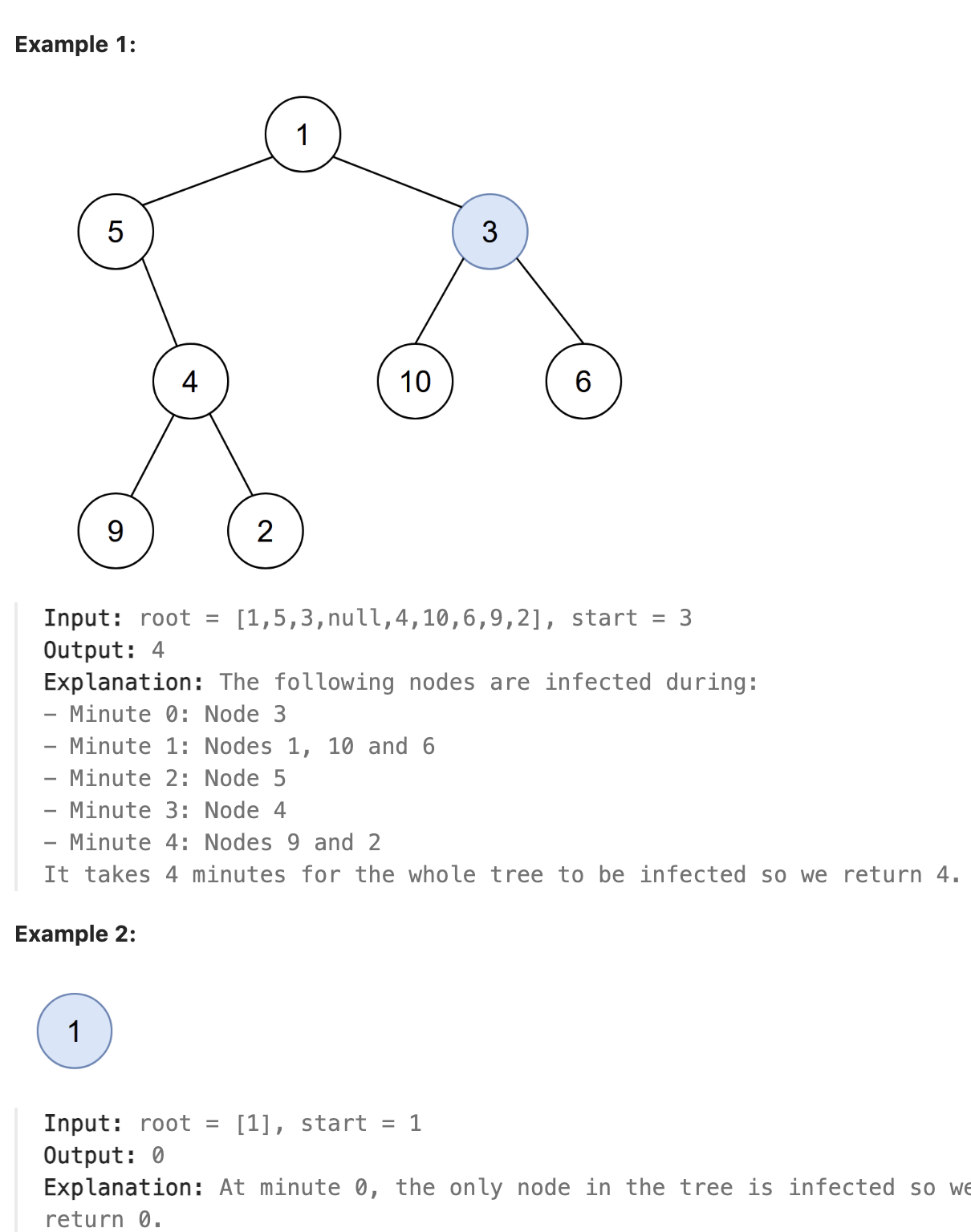
题解
这道题第一眼看上去就像在一个图中给定一个节点,寻找这个图中与这个节点距离最远的节点的距离.然而题面条件是二叉树,因此最直观的方法就是将二叉树转换为无向图, 再使用BFS找到最远的距离, 这样需要将所有节点遍历两遍.
代码
| |
总结
显然这种方法略慢, 要是可以在一次遍历的时候保存一定的信息, 减少重复的节点访问就好了, 思考这棵二叉树, 如果我们知道了从根节点到开始节点的距离, 并且保存了从根节点到开始节点的路径, 那么最远距离分为两种情况, 要么是以开始节点为根节点的子树足够深, 要么是开始节点的祖先节点的另外一棵子树足够深, 二者哪个更大就取哪个的最远距离. 尽管思路如此, 但当时我的想法是这样在寻找从根节点到开始节点时也要使用DFS, 这样在最差情况也要访问整棵树, 但实际上平均情况下会少访问大概以开始节点为根节点的子树的节点. 这样当节点数很多的时候也有一定的复杂度优势. 但是事实证明, 我想的还是不够全面, 实际上我们在递归调用的时候可以通过返回更多信息(一个布尔值)来标记该节点的某个子树上含有开始节点, 同时返回当前节点距离开始节点的距离. 这样通过一个非常巧妙的信息流动, 在开始节点处判断了以开始节点为根节点的子树的最大深度, 从开始节点处递归返回时向祖先节点传递该子树包含开始节点和距离开始节点的距离信息. 这样充分利用了在递归遍历过程中的全部信息. 只需要一次遍历即可解决. 充分的利用和整合信息是提高算法效率的关键, 示例代码如下
| |
day58 2024-04-25
2370. Longest Ideal Subsequence
You are given a string s consisting of lowercase letters and an integer k. We call a string t ideal if the following conditions are satisfied:
t is a subsequence of the string s. The absolute difference in the alphabet order of every two adjacent letters in t is less than or equal to k. Return the length of the longest ideal string.
A subsequence is a string that can be derived from another string by deleting some or no characters without changing the order of the remaining characters.
Note that the alphabet order is not cyclic. For example, the absolute difference in the alphabet order of ‘a’ and ‘z’ is 25, not 1.

题解
字符串子序列问题是一类很经典的递推计数问题. 一般可以用动态规划来解决. 问题的关键在于如何找到问题的子问题. 对于本题, 思考通过贪心等方式直接找到最长的子序列显然是不可行的, 因为一个字符在当前串中作为结尾可以使该串长度增大, 但后续可能有更长的串与没有这个字符的串可以连接, 但加上这个字符使得这个更长的串不能连接了. 显然考虑的不够周全. 那么现在还是要紧紧围绕我们在解题时多次提到过的思想: 能更有效的利用更多的信息, 算法的效率就越高. 对于一个字符来说, 哪些信息是有用的, 与之相差k个距离以内的字符是有用的, 因为这些字符可以与当前字符连接. 用贪心难以解决的原因在于, 只考虑了和当前字符相邻的k以内这一群邻居中的一个, 自然不能高效求解. 那么我们只要一直保存着所有以字符结尾的子序列的长度, 在遇到新字符时只需要对k个距离内的字符子序列进行比较, 找出最长的并将其加1作为当前字符的最长子序列长度. 这样充分利用了以前遍历过的可行字符组合的信息. 并将所有邻居都考虑进来, 最终就能得到可行解.
代码
| |
day59 2024-04-26
1289. Minimum Falling Path Sum II
Given an n x n integer matrix grid, return the minimum sum of a falling path with non-zero shifts.
A falling path with non-zero shifts is a choice of exactly one element from each row of grid such that no two elements chosen in adjacent rows are in the same column.

题解
本题为一道难题, 拿到题目首先观察, 可以想到的比较直接的点是如果从第一行直接向下一行行遍历并选择的话, 那么以3*3的矩阵为例, 第一行的第一二列同时选择第二行的第三列, 则对二者来说, 第三行的可选项是相同的. 即除一二列以外的列二者可以选择来累加的元素是相同的. 如第一个示例中的1-6-7,1-6-8,2-6-7,2-6-8. 显然这里对于1,2来说二三列的选择完全相同, 在这种情况下无疑选择1可以得到更小的和. 问题就变成了, 如何把这种已知的对以前的行中的元素的相对大小这一信息保留下来, 很简单, 让每一行的各个元素都保存在其上面行的最小元素和即可. 这样就保证了在能选择该元素的情况下, 以前的路径是从每行中挑出来的可选元素中的最小元素组成的路径. 也就保留了之前各行的元素之间已经判断过的相对大小. 这是一种动态规划的思想, 这里还要解决另外一个问题, 已知n-1行中保留了之前行的最小路径和, 对于第n行的各个元素, 如何高效的从n-1行中的可选元素中选出最小的(同一列的不可选). 显然每个都对n-1行整行做比较是$n^2$的复杂度, 应该高效利用保留信息. 仔细思考一下可以发现, 其实只需要知道最小的和第二小两个值就够了, 因为对于任意一个元素其同一列要么是最小的那个, 那就应该选第二小的, 要么不是最小的, 那就选最小的, 对于求最小值来说, 只需考虑这两种情况就够了(求最小和第二小的值本身也是一个很有趣的小问题, 不用排序, 一次遍历即可, 读者可先自行思考, 然后参考代码中的实现). 思路清晰后, 实现代码即可.
代码
| |
总结
Beats 100%
day60 2024-04-27
514. Freedom Trail
In the video game Fallout 4, the quest “Road to Freedom” requires players to reach a metal dial called the “Freedom Trail Ring” and use the dial to spell a specific keyword to open the door.
Given a string ring that represents the code engraved on the outer ring and another string key that represents the keyword that needs to be spelled, return the minimum number of steps to spell all the characters in the keyword.
Initially, the first character of the ring is aligned at the “12:00” direction. You should spell all the characters in key one by one by rotating ring clockwise or anticlockwise to make each character of the string key aligned at the “12:00” direction and then by pressing the center button.
At the stage of rotating the ring to spell the key character key[i]:
You can rotate the ring clockwise or anticlockwise by one place, which counts as one step. The final purpose of the rotation is to align one of ring’s characters at the “12:00” direction, where this character must equal key[i].
If the character key[i] has been aligned at the “12:00” direction, press the center button to spell, which also counts as one step. After the pressing, you could begin to spell the next character in the key (next stage). Otherwise, you have finished all the spelling.
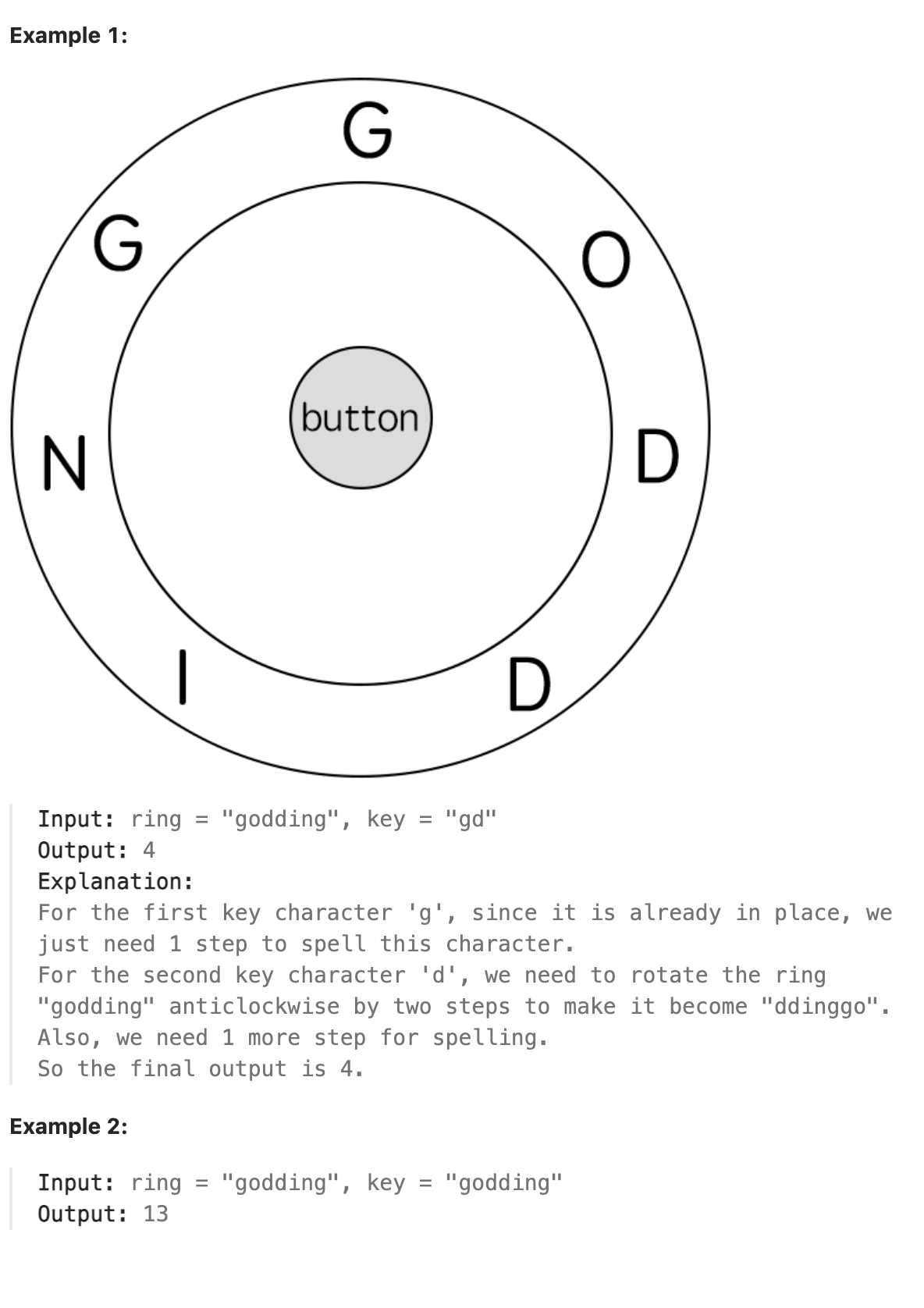
题解
本题是一道难题, 花了很长时间, 但理解的还是不够透彻, 关键在于保存什么样的状态是可以避免不必要的运算的. 保存的状态必须是在运算过程中必要的且若之前计算过则避免重复运算. 考虑本题中的关键, key中下一个字符要转动到12点方向只于当前12点方向的字符有关, 也就是只与当前12点方向的ring字符串中对应位置上的字符有关, 因此我们想要知道的是在ring字符串的该位置上的字符转动到key的下一个字符的最短距离是多少, ring中可能有多个key的下一个字符, 转动到这些字符中的哪个能获得全局最短距离在当前场景下是未知的, 因此最好的方法就是延迟决定, 递归的对所有可行位置执行搜索, 这样从上到下一层层深入直到key中最后一个字符, 再将各个路径上得到的距离做比较, 取最小的那个作为下一个转动到12点方向的字符位置, 这里在递归过程中要保存子递归中已经计算过的后面的ring对后面的key的字符的最短距离. 这里要理解保存的状态是在子递归过程中运算出来的一系列子结果, 这些子结果后面可能有用, 也可能没用, 但是算过了就要保存下来, 有没有用在比较高的递归层级是未知因素.
这里还有一些比较抽象的思考, 该题的解法中使用动态规划思想最小的子问题是什么, 其实是key中从任一个字符到下一个字符移动的最短距离, 可以将寻找路径的过程想象成一棵树, 每一层代表key中以层数为下标对应字符在ring串中的所有可行位置, 这样一棵非常庞大的演化树, 递归的过程就是遍历这棵树的所有到叶子节点的路径并保存该过程中的状态最终找到最短路. 理解这个状态空间是什么以及为什么保存这个状态是很高效的十分重要, 值得细细品味
代码
| |
day61 2024-04-28
834. Sum of Distances in Tree
There is an undirected connected tree with n nodes labeled from 0 to n - 1 and n - 1 edges.
You are given the integer n and the array edges where edges[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that there is an edge between nodes ai and bi in the tree.
Return an array answer of length n where answer[i] is the sum of the distances between the ith node in the tree and all other nodes.
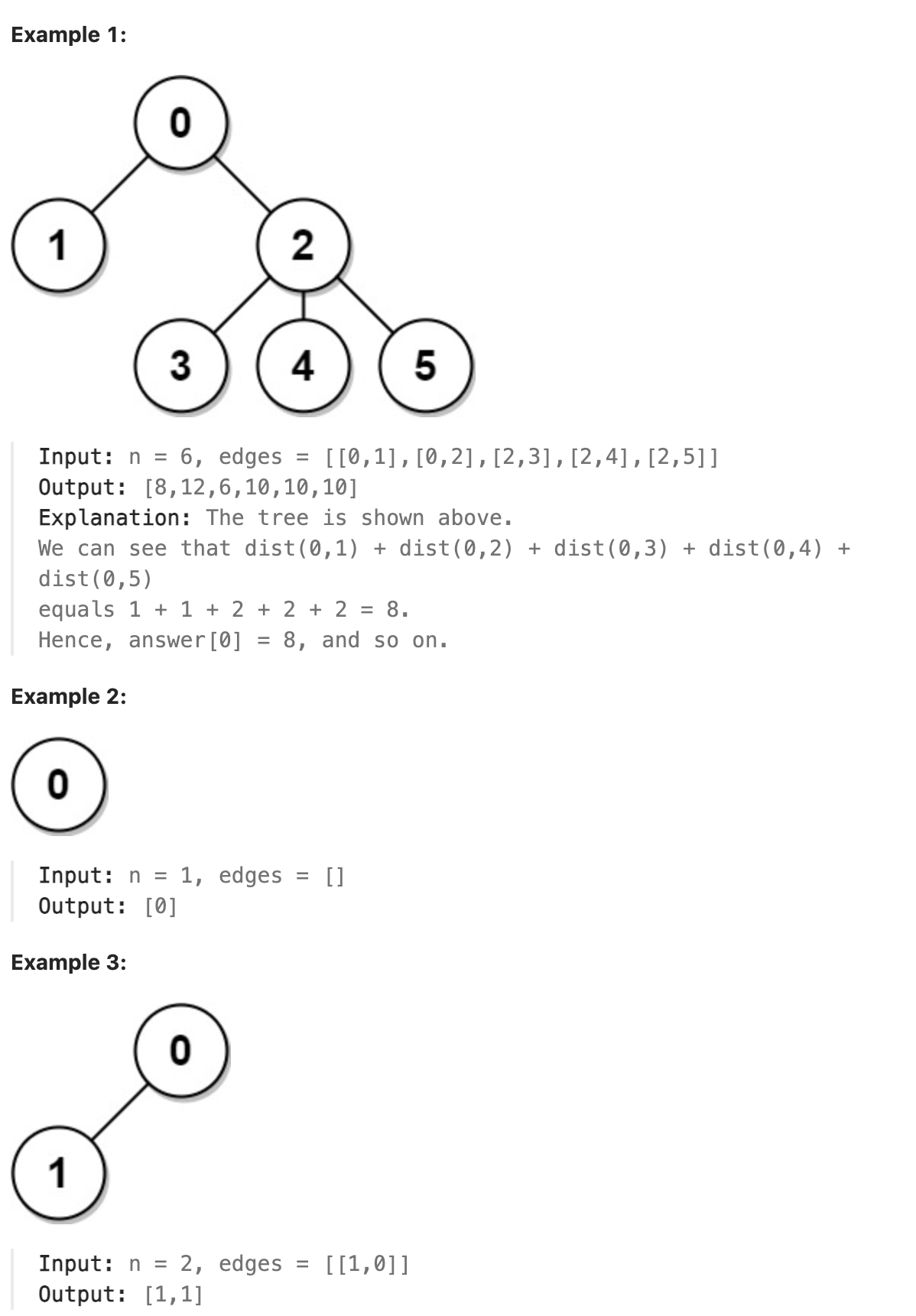
题解
考虑这棵树,其实将任意一个节点作为树的根节点都不影响结果, 这也意味着这个树中各个元素地位相同, 更像是一张无向图. 对于树中任意一个节点而言, 若将其看作根节点, 只要知道了其所有连通节点到连通节点的的"子树"的距离和和这个"子树"中包含的节点数量, 就能算出根节点到其他所有节点的距离和. 而求其连通节点到连通节点的子树的距离和可以继续采用这种思路, 显然可以通过递归的方式求解, 思想是动态规划的思想. 最直接的解法就是将这个递归式写出来, 同时保存在求解过程中解出的某节点对应的一个连通节点的"子树"的距离和. 但这种方法会超时, 因此需要思考哪里还有重复计算的部分, 考虑一个极端例子, 一共有30000个节点, 其中29999个节点都和节点0相连. 这种情况下, 如果依次遍历各个节点并计算其相邻节点的"子树"距离和, 会发现尽管已经保存了节点0到其余节点的距离和, 但还是要将0到剩余29998个节点都遍历一遍(不用计算,只直接拿结果), 这样显然是$n^2$的复杂度, 显然这里可以简化, 对于节点0, 已经计算得到了它到其余所有节点的距离和, 只需要使用这个距离和减掉从0到当前节点的"子树"包含的距离和再加上0剩余的连通节点的"子树"包含的节点数目(原本的距离是到节点0, 从节点0到当前节点要将每个节点距离加1)就得到了当前节点到其余各节点的距离和.
想到这会发现, 其实只要任选一个节点计算其到其他节点的距离和, 若将这个节点作为根节点, 那么在计算过程中就已经将全部节点的"子树"距离和计算出来, 与真正的节点距离和相比, 只缺少了一个分支的距离和. 则在算出当前节点的距离和后, 可直接继续计算相邻节点的距离和, 计算方式为当前节点距离和减掉当前节点到相邻节点这一分支的距离和加上剩余的节点数, 再加上这个相邻节点到它的其余相邻节点的距离和, 这在之前的递归计算过程中已经保存了. 本题想高效求解, 不但要保存求解过程中的的中间结果, 还要充分利用已经求解出来的结果.
代码
初始版本:
| |
优化版本:
| |
总结
看讨论区时发现, 这类题目叫作Tree rerooting DP, 的确在本题中计算距离和的过程相当于不断更换树的根节点. 下面这个视频中对这一问题有比较系统的讲解
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7_huTWwl5jM
了解下系统性的思路是好的, 但我向来不支持"套用", 要理解其内在的本质并根据实际问题灵活运用才是真正掌握. 就好像动态规划的"状态转移公式", 核心思想在于将大问题分解成小的子问题以及保存解决子问题过程中的信息(中间结果)用于后续处理, 正如我不断强调的核心观点, 利用的有效信息越多, 算法效率就越高.
day62 2024-04-29
2997. Minimum Number of Operations to Make Array XOR Equal to K
You are given a 0-indexed integer array nums and a positive integer k.
You can apply the following operation on the array any number of times:
Choose any element of the array and flip a bit in its binary representation. Flipping a bit means changing a 0 to 1 or vice versa. Return the minimum number of operations required to make the bitwise XOR of all elements of the final array equal to k.
Note that you can flip leading zero bits in the binary representation of elements. For example, for the number (101)2 you can flip the fourth bit and obtain (1101)2.

题解
本题最终对数组中所有的数进行异或运算, 得到目标k. 考虑到对k中的每一位而言, 数组中的数只需要在该位上做异或运算最终与k的该位相等. 对数组中的数, 对除最后一个数以外的所有数异或, 得到的结果再与最后一个数异或, 只需调整最后一个数的各个位使得最终结果与k相同. 因为调整任意一个数的某个位都是等价的, 而先将前面的数异或相当于保存了前面所有数中各个位异或后的信息. 将结果和最后一个数按位与k比较并调整即可. 只需注意如果一个数的后面的位比较完成前面全是0, 对对应的也要做相应调整.
代码
| |
总结
其实将所有数异或后直接和k进行异或, 得到的结果中如果某位为1则说明和k的这一位不同, 为0则相同, 将结果不断右移并判断最后一位是否为1即可得到需要翻转的次数.
day63 2024-04-30
1915. Number of Wonderful Substrings
A wonderful string is a string where at most one letter appears an odd number of times.
For example, “ccjjc” and “abab” are wonderful, but “ab” is not. Given a string word that consists of the first ten lowercase English letters (‘a’ through ‘j’), return the number of wonderful non-empty substrings in word. If the same substring appears multiple times in word, then count each occurrence separately.
A substring is a contiguous sequence of characters in a string.

题解
这种子字符串的问题大概要保存一些状态以供后续的判断, 关键在于保存什么状态是有用的, 这里可以保存到某个下标为止的前缀字符串中各个字符的数量, 但是注意本题只要求判断字符串中出现了奇数次的字符的数量, 因此关键在于字符串中的某个字符的数量是否为奇数. 考虑这样的情况, 如果以下标3为结尾的字符串中字符’a’出现了奇数次, 以下标5为结尾的字符串中字符’a’也出现了奇数次, 那么这两个下标之间的字符串中’a’必定出现了偶数次(两奇数做差, 必定为偶数). 同样两偶数做差也必定为偶数, 只有偶数和奇数做差时才会出现奇数. 因此只需要保存到某个下标结尾处字符串中各个字符出现次数的奇偶性再与其他下标做比较, 字符奇偶性不同的字符小于2则二者之间的字符串是可行的, 否则不可行.
保存各个字符的奇偶性可以使用位标记, 从a到z每个字母用一个二进制位表示, 用一个十维数组也可行, 但在只需要保存一个二值状态时用位更节省空间. 求出到各个下标的各个字符的奇偶串后, 依次遍历每个位置, 分别与后面的所有位置做异或, 再判断异或后的数字的二进制表示中1的个数是否大于1个, 大于则这两个下标之间的字符串奇数个字符大于1, 判断是否大于一个可以使用n&(n-1)来消掉最低的1, 再判断剩余的数字是否为0, 不为0说明大于1个.
但使用这种方法, 每次都要将当前下标与后面的所有下标都比较一遍, 显然是$n^2$的复杂度. 这里可以发现, 使用这种方法遍历没有考虑到这种字符串差出现的先后位置与结果无关, 即差值的具体数量与结果无关. 例如, 在下标为1处的位串为0101, 在3和5处的位串都为0111, 实际上这两个位置与下标1做异或后的结果相同, 即1-3和1-5之间都只有1个位置是奇数个, 至于这个位置是3个或是5个, 或者3-5之间这个位置没发生变化其他位置多了两个, 都不影响区间字符串的奇偶性质. 这里的思想和用位来表示字符的奇偶性有异曲同工之妙, 即无需考虑具体数量, 只需考虑其拥有的性质即可.
有了这种想法, 那么只需要保存所有的位串, 并统计所有位串的数量, 如0101的位串有五个, 说明这五个位串代表的下标之间的四个间隙的所有字符都是偶数个那么这四个显然是符合要求的结果. 再计算有一个奇数位的情况, 只需要将每个串中的各个位依次翻转并查询翻转后的位串的数量即可. 每个串最多翻转10次(a-j 10个字符), 10位二进制串最多有1024种组合, 意味着最多翻转1024*10=10240次. 降为常数复杂度.
在翻转的过程中, 两种字符串之间翻转后的组合会被计数两次(0101翻转得到0111,0111翻转得到0101), 将最终结果除以2即可.
代码
| |
总结
本题是一道比较综合的题目, 找到关键状态是解决问题的核心.
day64 2024-05-01
2000. Reverse Prefix of word
Given a 0-indexed string word and a character ch, reverse the segment of word that starts at index 0 and ends at the index of the first occurrence of ch (inclusive). If the character ch does not exist in word, do nothing.
For example, if word = “abcdefd” and ch = “d”, then you should reverse the segment that starts at 0 and ends at 3 (inclusive). The resulting string will be “dcbaefd”. Return the resulting string.

题解
本题是一道简单题, 显然找到第一个ch的位置翻转字符串即可, 若想在找到后快速翻转字符串, 可以在找到对应字符的下标后除以2找到中间位置字符, 分别从子字符串开头和结尾开始向中间遍历并不断交换首尾字符即可实现翻转,
代码
| |
day65 2024-05-02
2441. Largest Positive Integer That Exists With Its Negative
Given an integer array nums that does not contain any zeros, find the largest positive integer k such that -k also exists in the array.
Return the positive integer k. If there is no such integer, return -1.

题解
本题是一道简单题, 题目中给出数字的范围为-1000到1000, 因此可以使用一个1001长度的数组来保存每个数字的状态, 状态分为未出现, 出现了一个负数, 出现了一个正数和出现过了这个数的正负两个数四种情况. 因此使用四个数字来表示这四种情况即可, 0表示未出现, -1表示只出现过负数, 1表示只出现过正数, 2表示一正一负, 遍历数组并改变相应状态, 当状态变为2时与当前的最大结果比较并更新最大值即可.
代码
| |
day 66 2024-05-03
165. Compare Version Numbers
Given two version numbers, version1 and version2, compare them.
Version numbers consist of one or more revisions joined by a dot ‘.’. Each revision consists of digits and may contain leading zeros. Every revision contains at least one character. Revisions are 0-indexed from left to right, with the leftmost revision being revision 0, the next revision being revision 1, and so on. For example 2.5.33 and 0.1 are valid version numbers.
To compare version numbers, compare their revisions in left-to-right order. Revisions are compared using their integer value ignoring any leading zeros. This means that revisions 1 and 001 are considered equal. If a version number does not specify a revision at an index, then treat the revision as 0. For example, version 1.0 is less than version 1.1 because their revision 0s are the same, but their revision 1s are 0 and 1 respectively, and 0 < 1.
Return the following:
If version1 < version2, return -1. If version1 > version2, return 1. Otherwise, return 0.

题解
本题将字符串根据.号分割成字符数组, 再将两个字符数组转换成整数并比较大小.
代码
| |
day67 2024-05-04
881. Boats to Save People
You are given an array people where people[i] is the weight of the ith person, and an infinite number of boats where each boat can carry a maximum weight of limit. Each boat carries at most two people at the same time, provided the sum of the weight of those people is at most limit.
Return the minimum number of boats to carry every given person.

题解
本题中每艘船只能乘坐两个人, 则两个人的重量和应小于船的限制limit, 因此重量较小的人可以和重量较大的人乘同一艘船, 但重量大于limit/2的人只能独自乘船, 不能与他人共乘. 则先统计各个重量的人数, 放在数组中, 数组下标表示对应的重量. 值为对应的人数. 从头遍历数组, 对于重量小于limit/2的人, 可以和与其重量和为limit及以下的人共同乘船, 从能与其共同乘船的最大重量开始向前遍历, 直到遍历过的重量的人数和与当前重量人数相同为止. 这些人每两两一组可以共乘同一艘船. 如果还有剩余, 说明后面已经全部遍历完, 考虑当前重量小于等于limit/2, 故两个人可以共同乘船, 将结果加上剩余人数的1/2, 奇数再加上一即可. 对于遍历到重量大于limit/2的情况, 因为不能和他人共同乘船, 直接将结果加上当前重量人数即可.
代码
| |
总结
本题关键在于船的人数有限制, 只能两个人, 如果船的人数无限而重量有限的话, 要尽可能将船装满, 从后向前遍历时要根据当前遍历到的重量减去对应的比较轻的重量的人数直到将船装满为止.
day68 2024-05-05
237. Delete Node in a Linked List
There is a singly-linked list head and we want to delete a node node in it.
You are given the node to be deleted node. You will not be given access to the first node of head.
All the values of the linked list are unique, and it is guaranteed that the given node node is not the last node in the linked list.
Delete the given node. Note that by deleting the node, we do not mean removing it from memory. We mean:
The value of the given node should not exist in the linked list. The number of nodes in the linked list should decrease by one. All the values before node should be in the same order. All the values after node should be in the same order. Custom testing:
For the input, you should provide the entire linked list head and the node to be given node. node should not be the last node of the list and should be an actual node in the list. We will build the linked list and pass the node to your function. The output will be the entire list after calling your function.
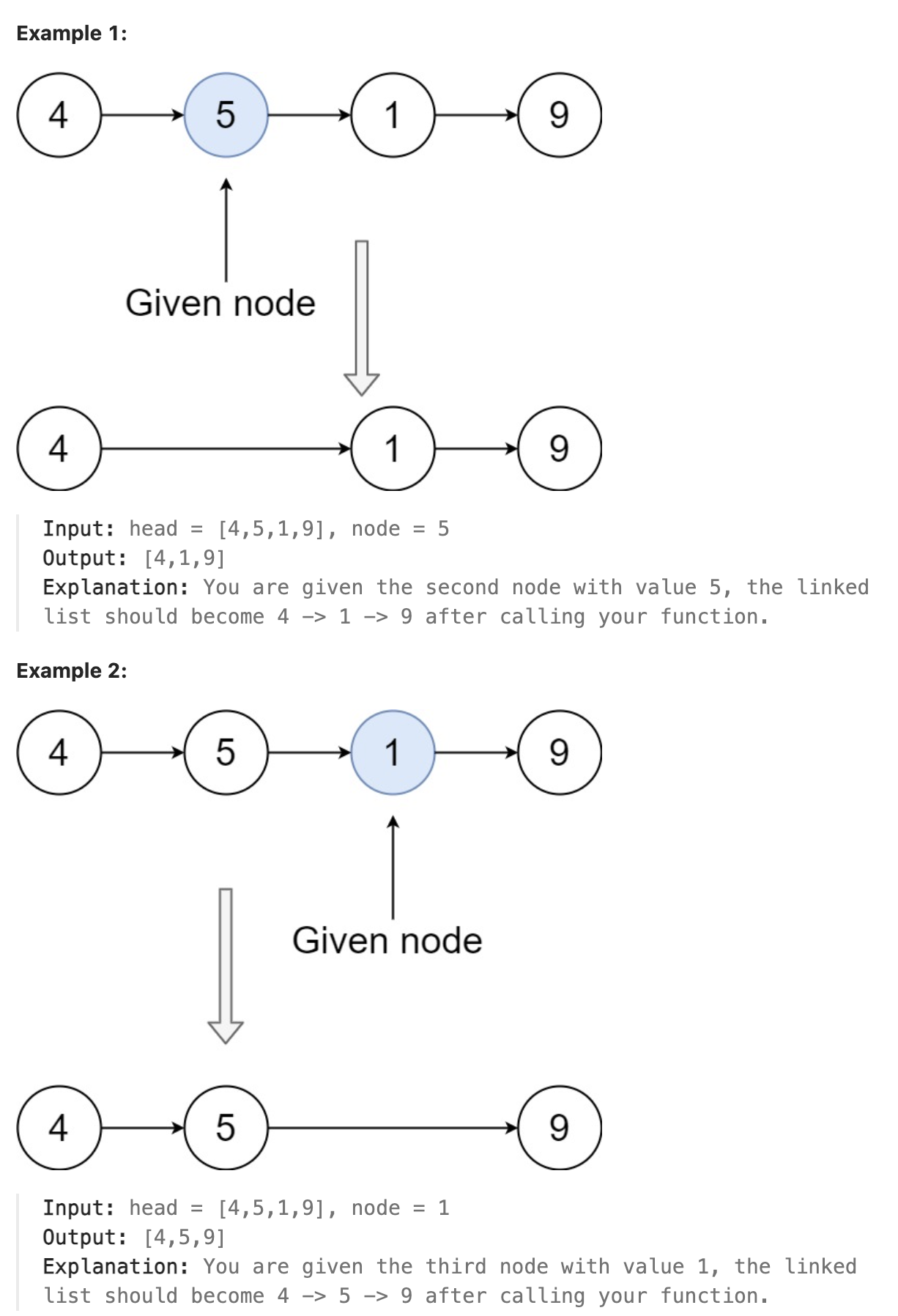
题解
本题是一道基本的链表操作问题, 给定要删除的节点指针, 则不知道节点的前置节点指针, 只能通过遍历链表并将将后一个节点的值赋给前一个节点的方式来删除掉(覆盖)当前节点的值. 注意对倒数第二个节点, 当将最后一个节点的值赋给它后将其Next指针置为nil从而删掉原来的最后一个节点.
代码
| |
day69 2024-05-06
2487. Remove Nodes From Linked List
You are given the head of a linked list.
Remove every node which has a node with a greater value anywhere to the right side of it.
Return the head of the modified linked list.
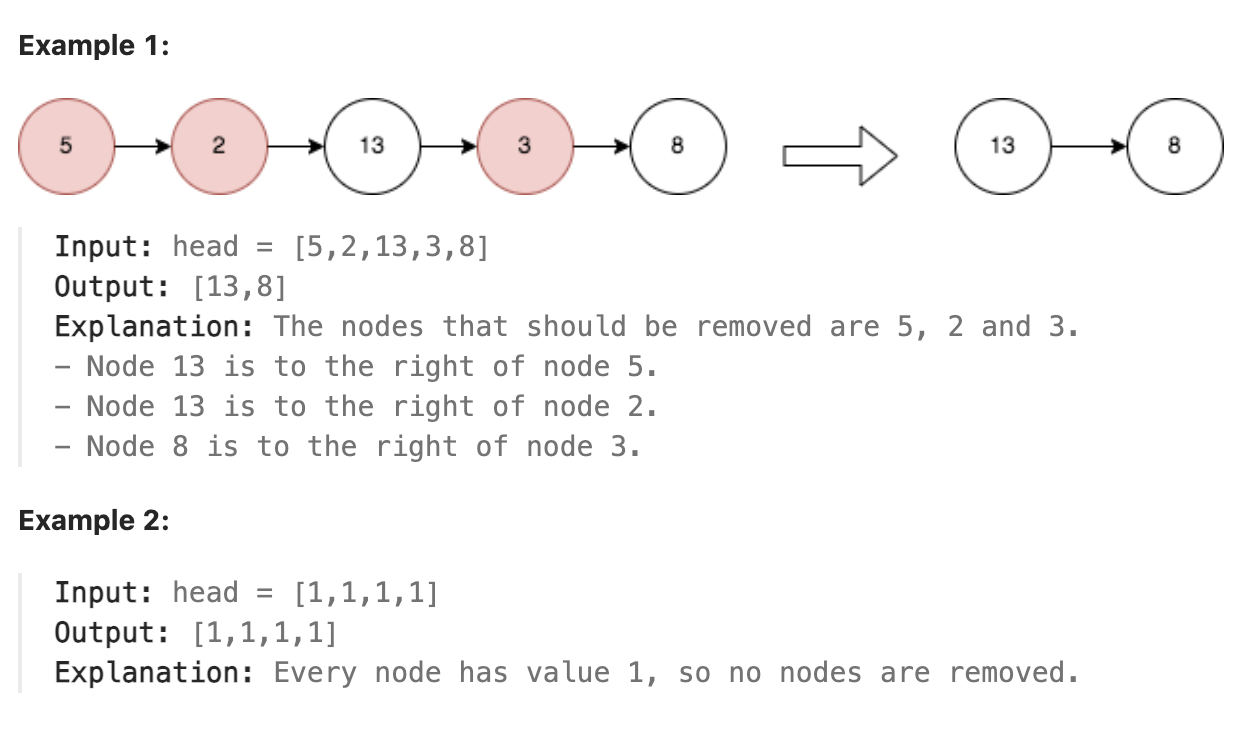
题解
本题要删除的是链表右边存在比它值大的节点的节点. 最直接的思路就是将链表反向, 从头遍历, 保存当前遍历过的最大值, 小于该值的都删除, 大于则更新当前最大值, 删除完毕后再将链表反向, 就得到了删除后的结果.
代码
| |
day70 2024-05-07
2816. Double a Number Represented as a Linked List
You are given the head of a non-empty linked list representing a non-negative integer without leading zeroes.
Return the head of the linked list after doubling it
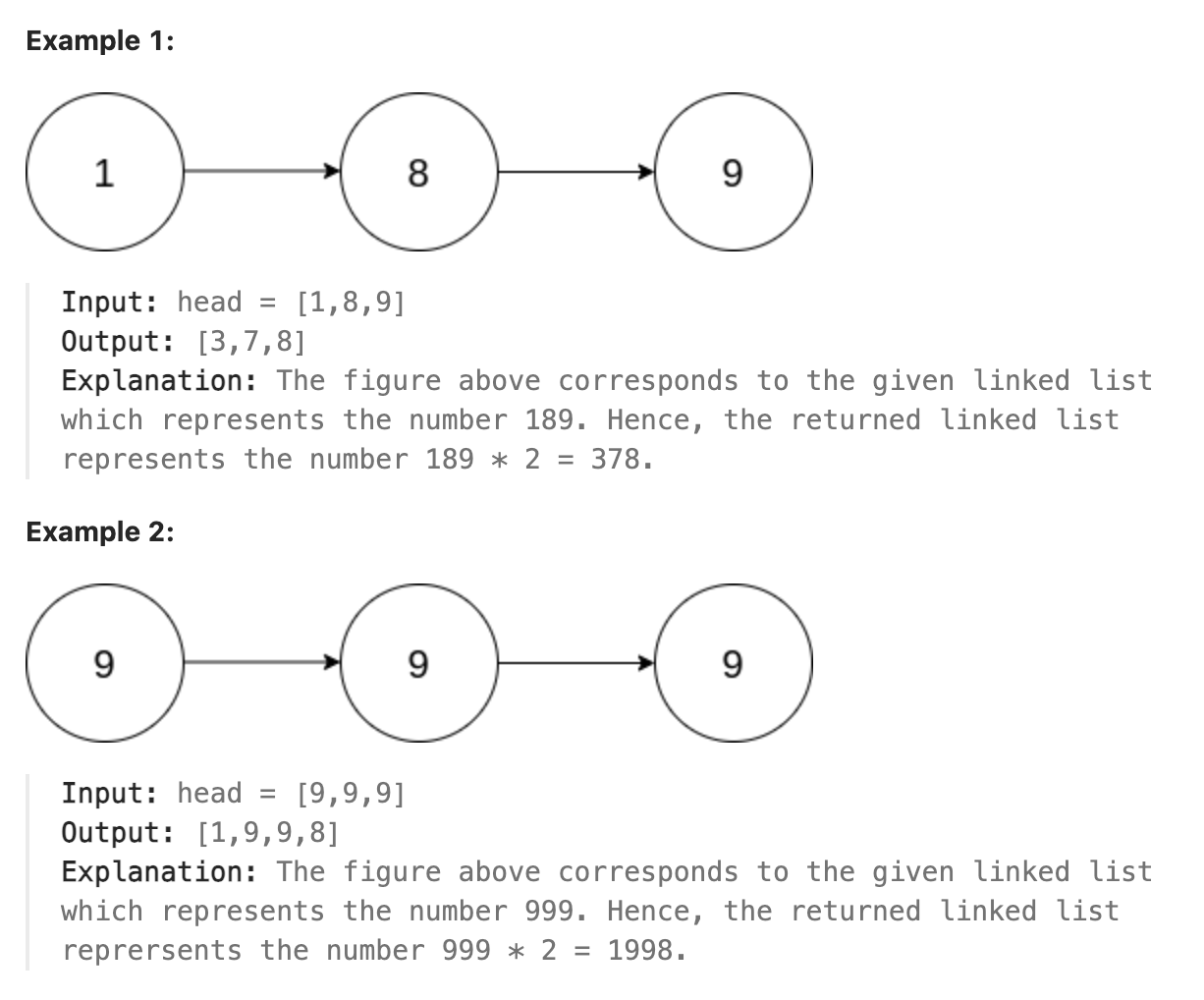
题解
和昨天类似的解题思路, 将链表逆转, 依次计算各位并保存进位, 修改值最后一个节点有进位增加一个新的值为1的节点即可.再将链表逆转回来.
代码
| |
总结
逆转其实是多余的, 每一位数仅取决于当前位的值和后一位是否有进位, 因此用两个指针分别指向当前位和下一位, 计算下一位的值若进位将进位加到当前位即可, 这里的核心思路在于将当前位的倍乘和进位的加两个操作分离了, 在当前位的上一位时执行当前位的倍乘操作, 在当前位下一位执行当前位的进位加. 因为进位不受后面的位的影响, 因此使用双指针即可快速解决.
| |
day71 2024-05-08
506. Relative Ranks
You are given an integer array score of size n, where score[i] is the score of the ith athlete in a competition. All the scores are guaranteed to be unique.
The athletes are placed based on their scores, where the 1st place athlete has the highest score, the 2nd place athlete has the 2nd highest score, and so on. The placement of each athlete determines their rank:
The 1st place athlete’s rank is “Gold Medal”. The 2nd place athlete’s rank is “Silver Medal”. The 3rd place athlete’s rank is “Bronze Medal”. For the 4th place to the nth place athlete, their rank is their placement number (i.e., the xth place athlete’s rank is “x”). Return an array answer of size n where answer[i] is the rank of the ith athlete.

题解
本题为简单题, 思路上比较清晰, 先排序, 然后保存对应score的排名, 再遍历一次数组, 根据score的排名赋予对应的rank即可, 特殊处理前三个即可.
代码
| |
day72 2024-05-09
3075. Maximize Happiness of Selected Children
You are given an array happiness of length n, and a positive integer k.
There are n children standing in a queue, where the ith child has happiness value happiness[i]. You want to select k children from these n children in k turns.
In each turn, when you select a child, the happiness value of all the children that have not been selected till now decreases by 1. Note that the happiness value cannot become negative and gets decremented only if it is positive.
Return the maximum sum of the happiness values of the selected children you can achieve by selecting k children.

题解
本题思路上比较简单, 要求最大和, 将数组从大到小排序, 排序后依次取前k个元素加和即可, 注意处理每加一个元素, 下一个元素就要减掉目前已经加过的元素数量的值, 这可以通过数组下标来天然实现. 这类题目关键在于排序算法, 使用库中实现的排序算法一般都比较快. 但我们仍然要对常用的排序算法心中有数.
代码
| |
day73 2024-05-10
786. K-th Smallest Prime Fraction
You are given a sorted integer array arr containing 1 and prime numbers, where all the integers of arr are unique. You are also given an integer k.
For every i and j where 0 <= i < j < arr.length, we consider the fraction arr[i] / arr[j].
Return the kth smallest fraction considered. Return your answer as an array of integers of size 2, where answer[0] == arr[i] and answer[1] == arr[j].

题解
保存每个分数的值, 和对应的分子分母, 对对应的分数值排序, 取第k小的即可
代码
| |
总结
看到了一种很有趣的解法, 使用二分法, 每次计算出中间值右侧的分数的个数, 根据与k的相对大小更新中间值. 代码如下, 这种方法比其他许多解法快的多得多, 在最快的平均时长为694ms的情况下竟然只需用时4ms. 这种解法关键在于其通过一开始取中间值为0.5的方式大大减少了需要遍历的分数的数目. 而且没有遍历的分数在后续因为中间值的调整也不会再遍历了, 也就是说每一次遍历的数目都是原本遍历的分数个数的一小部分, 如果数量特别多的情况下可以近似的认为分数的值分布在0-0.5和0.5-1之间的分数个数大致相同. 这样从期望角度讲每次都只需要遍历一般个数的分数, 这样遍历过程总体的时间复杂度为O(nlogn), 并且不需要排序, 最终可以直接返回结果, 因此能有很高的效率.
| |
day74 2024-05-11
857. Minimum Cost to Hire K Workers
There are n workers. You are given two integer arrays quality and wage where quality[i] is the quality of the ith worker and wage[i] is the minimum wage expectation for the ith worker.
We want to hire exactly k workers to form a paid group. To hire a group of k workers, we must pay them according to the following rules:
Every worker in the paid group must be paid at least their minimum wage expectation. In the group, each worker’s pay must be directly proportional to their quality. This means if a worker’s quality is double that of another worker in the group, then they must be paid twice as much as the other worker. Given the integer k, return the least amount of money needed to form a paid group satisfying the above conditions. Answers within 10-5 of the actual answer will be accepted.

题解
本题是一道难题, 说实话, 本题只想到了可以用工资和工作量的比值来衡量员工这一步, 因为这种使用比值来决定如何选择的方式在这种同时有某个对象的价值和成本的场景下非常常见. 也就是常说的性价比. 但并没有想出来可以使用优先级队列来一直保存当前k个quality的最小和以及如何更新结果的步骤, 我陷入了一个误区即工资和工作量比值特别高的员工一定不会被选择, 实则不然, 考虑极端情况, 一个平均工作价值为7但工作量为200的员工, 我需要付给他1400, 而一个平均工作价值为200但工作量为1的员工我只需付给他200, 如果之前的员工工作量只有3那我总共需要付800, 显然小于另一个平均工作价值为7的员工. 以及对go优先级队列的实现不是很娴熟.
本题我查看了他人的题解, 🔗:https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-cost-to-hire-k-workers/solutions/1815856/yi-bu-bu-ti-shi-ru-he-si-kao-ci-ti-by-en-1p00/
代码
| |
day75 2024-05-12
2373. Largest Local Values in a Matrix
You are given an n x n integer matrix grid.
Generate an integer matrix maxLocal of size (n - 2) x (n - 2) such that:
maxLocal[i][j] is equal to the largest value of the 3 x 3 matrix in grid centered around row i + 1 and column j + 1. In other words, we want to find the largest value in every contiguous 3 x 3 matrix in grid.
Return the generated matrix.
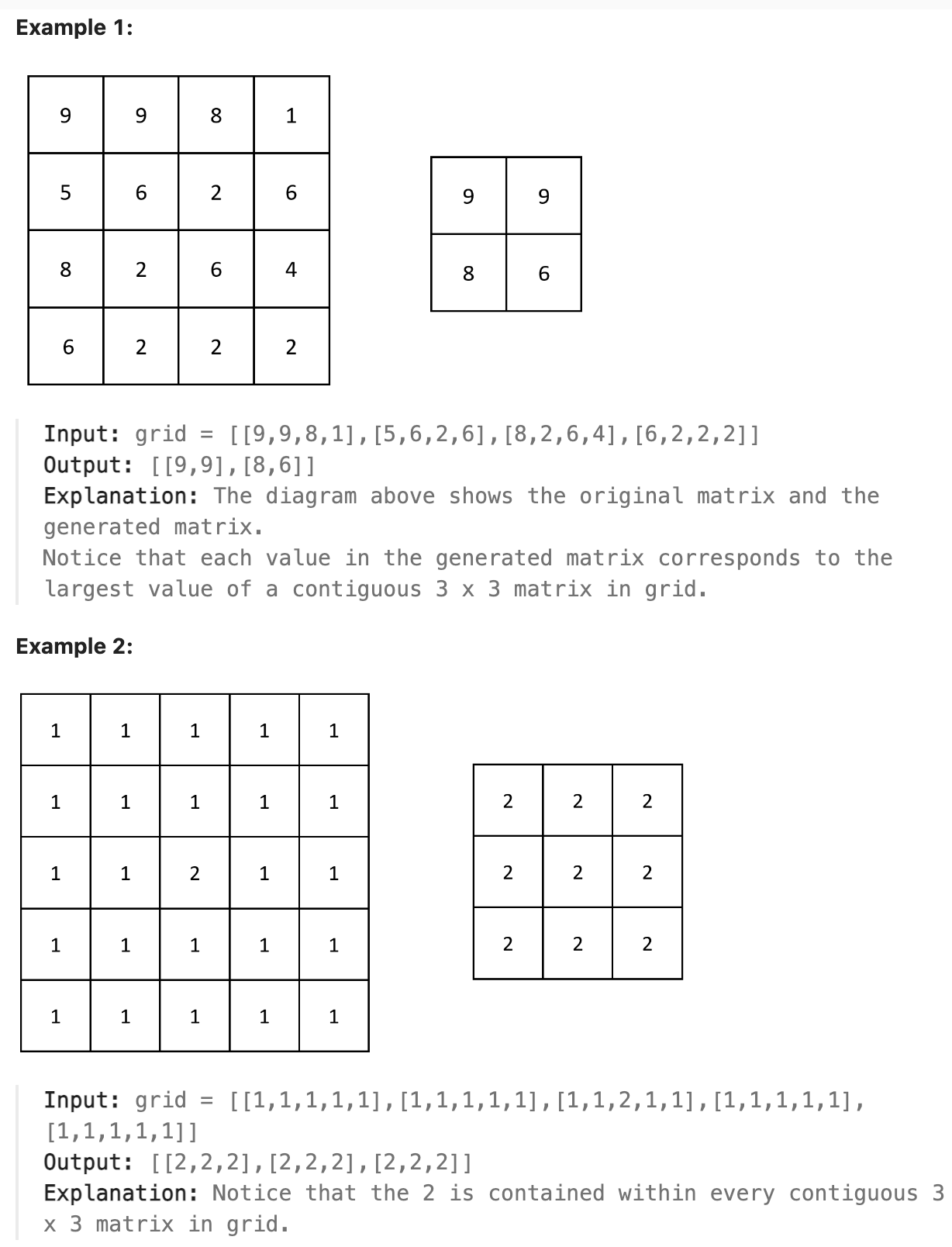
题解
本题是深度学习中经典的最大池化操作, 用四层循环来完成即可.
代码
| |
day76 2024-05-13
861. Score After Flipping Matrix
You are given an m x n binary matrix grid.
A move consists of choosing any row or column and toggling each value in that row or column (i.e., changing all 0’s to 1’s, and all 1’s to 0’s).
Every row of the matrix is interpreted as a binary number, and the score of the matrix is the sum of these numbers.
Return the highest possible score after making any number of moves (including zero moves).
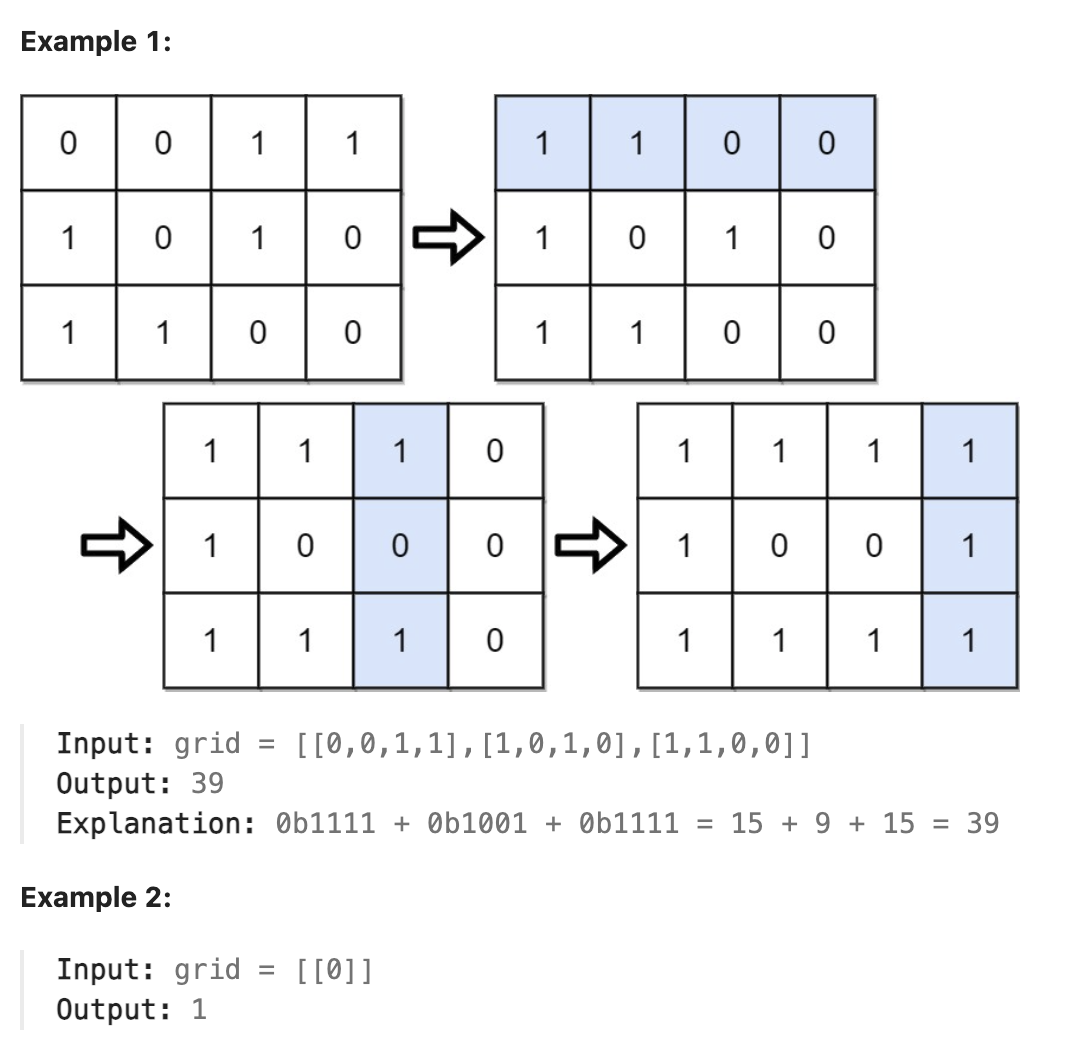
题解
考虑本题要求的是所有行的数的和. 因此某一行的值中某一位是0或者1对于和来说并不重要, 同一位上所有数中1的个数对和来说才比较重要. 只要某个位上的1的数量最多, 那么无论这些1分布在哪个数中, 最终的和都是最大的. 但每一行中的第一个1是比较特殊的, 考虑无论后面的位数怎么变动都不会超过最高位为1的数的大小, 因此最高位必须为1才能保证最大值.其余位按照列来翻转使得每一列的1的个数最多即可. 注意在遍历数组并执行首位为0的行进行行翻转的过程中可以记录每一列的1的个数, 行翻转后不需要再遍历数组, 只需根据每一列1的个数和列长判断列翻转后1的个数是否更多即可, 取列翻转和不翻转二者中的1的个数最多的数量与对应的位代表的数(可通过移位实现)相乘并累加即可.
代码
| |
day77 2024-05-14
1219. Path with Maximum Gold
In a gold mine grid of size m x n, each cell in this mine has an integer representing the amount of gold in that cell, 0 if it is empty.
Return the maximum amount of gold you can collect under the conditions:
Every time you are located in a cell you will collect all the gold in that cell. From your position, you can walk one step to the left, right, up, or down. You can’t visit the same cell more than once. Never visit a cell with 0 gold. You can start and stop collecting gold from any position in the grid that has some gold.

题解
本题需要找到所有的可行路径并比较每条路径上的金币和来求得最大值. 使用dfs结合回溯即可解决, 注意在数组上进行dfs时探索四个方向可以使用一个方向数组来表示方向, 每次将当前位置的坐标加上方向数组中的某一个方向并判断其是否超过边界及该方向是否有效(值大于0)即可. 注意对当前遍历的路径要先将当前坐标处的值置为0在dfs结束后要将值恢复便于后续回溯.
代码
| |
总结
其实上面代码还有优化的空间, 在遍历数组并走所有路径的过程中, 显然有些路径是重复的, 可以再使用一个三维数组保存二维数组中某一位向四个方向走的路径得到的四个方向的最大值. 这样在遇到重复路径时直接返回值即可. 不用再次递归遍历.
day78 2024-05-15
2812. Find the Safest Path in a Grid
You are given a 0-indexed 2D matrix grid of size n x n, where (r, c) represents:
A cell containing a thief if grid[r][c] = 1 An empty cell if grid[r][c] = 0 You are initially positioned at cell (0, 0). In one move, you can move to any adjacent cell in the grid, including cells containing thieves.
The safeness factor of a path on the grid is defined as the minimum manhattan distance from any cell in the path to any thief in the grid.
Return the maximum safeness factor of all paths leading to cell (n - 1, n - 1).
An adjacent cell of cell (r, c), is one of the cells (r, c + 1), (r, c - 1), (r + 1, c) and (r - 1, c) if it exists.
The Manhattan distance between two cells (a, b) and (x, y) is equal to |a - x| + |b - y|, where |val| denotes the absolute value of val.
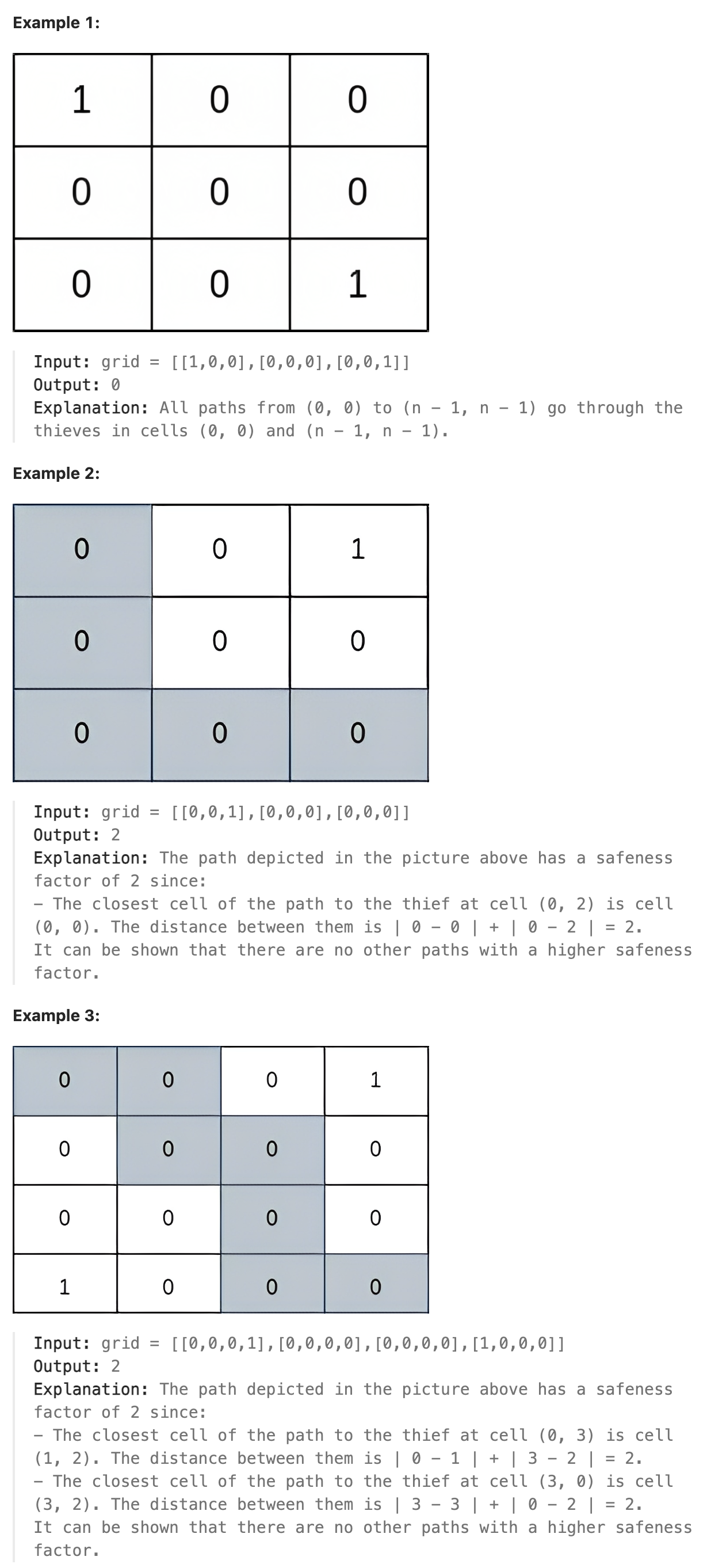
题解
本题的安全因子定义为路径上的任一坐标到任何贼节点的最小曼哈顿距离. 因此应该从贼的节点出发, 通过BFS向外计算出每个节点到这个贼节点的距离, 通过对所有的贼节点进行BFS, 即可得到全部节点到任一贼节点的最小距离. 问题变为, 有了最小距离如何找到一条满足最小距离的可行路径. 可知我们要寻找的路径其路径上的所有点到贼的最小距离都应该大于或等于假设的最小距离, 否则这条路径的安全因子应该更小. 如何找到所有最小距离中可行的最大值? 可以通过从起点出发执行bfs寻找从(0,0)到(n-1,n-1)之间的可行路径, 在bfs过程中相邻节点的距离大于等于当前假设的最小距离节点才可达, 否则不可达, 如果相邻节点找不到可行路径则减小假设的最小值, 这里减小可以采用二分法进行增减. 如果找到了一条可行路径则增大假设的最小值再次判断是否有路径可达. 相当于在所有可行最小距离中二分查找到可行的最大值. 这样要比从最大的可行距离开始每次减少1直到找到最终的可行距离快得多.
代码
| |
day 79 2024-05-16
2331. Evaluate Boolean Binary Tree
You are given the root of a full binary tree with the following properties:
Leaf nodes have either the value 0 or 1, where 0 represents False and 1 represents True. Non-leaf nodes have either the value 2 or 3, where 2 represents the boolean OR and 3 represents the boolean AND. The evaluation of a node is as follows:
If the node is a leaf node, the evaluation is the value of the node, i.e. True or False. Otherwise, evaluate the node’s two children and apply the boolean operation of its value with the children’s evaluations. Return the boolean result of evaluating the root node.
A full binary tree is a binary tree where each node has either 0 or 2 children.
A leaf node is a node that has zero children.
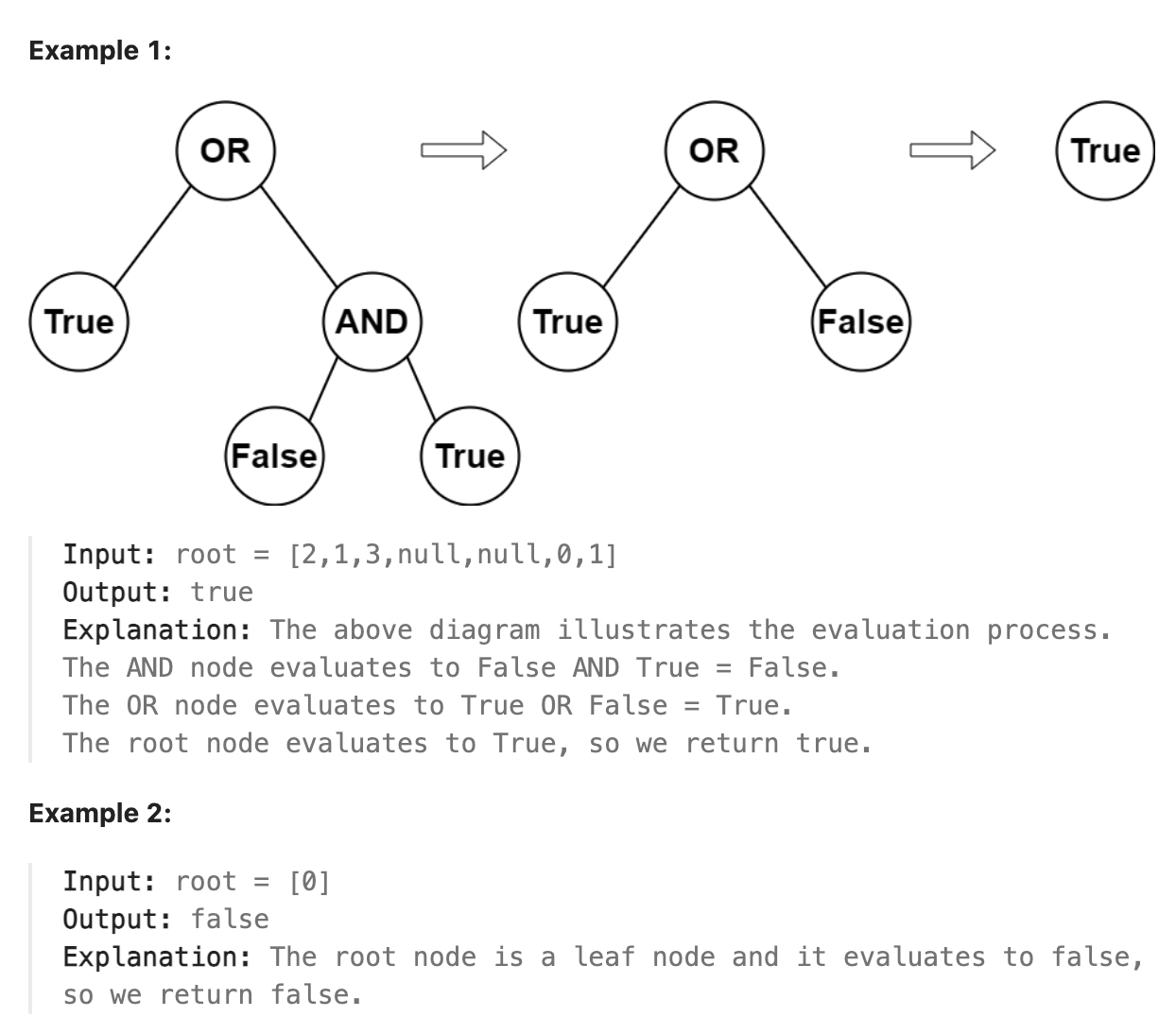
题解
后续遍历计算各个节点的布尔值最终得到根节点的布尔值即可, 考查二叉树的后序遍历, 可以使用递归实现.
代码
| |
day80 2024-05-17
1325. Delete Leaves With a Given Value
Given a binary tree root and an integer target, delete all the leaf nodes with value target.
Note that once you delete a leaf node with value target, if its parent node becomes a leaf node and has the value target, it should also be deleted (you need to continue doing that until you cannot).
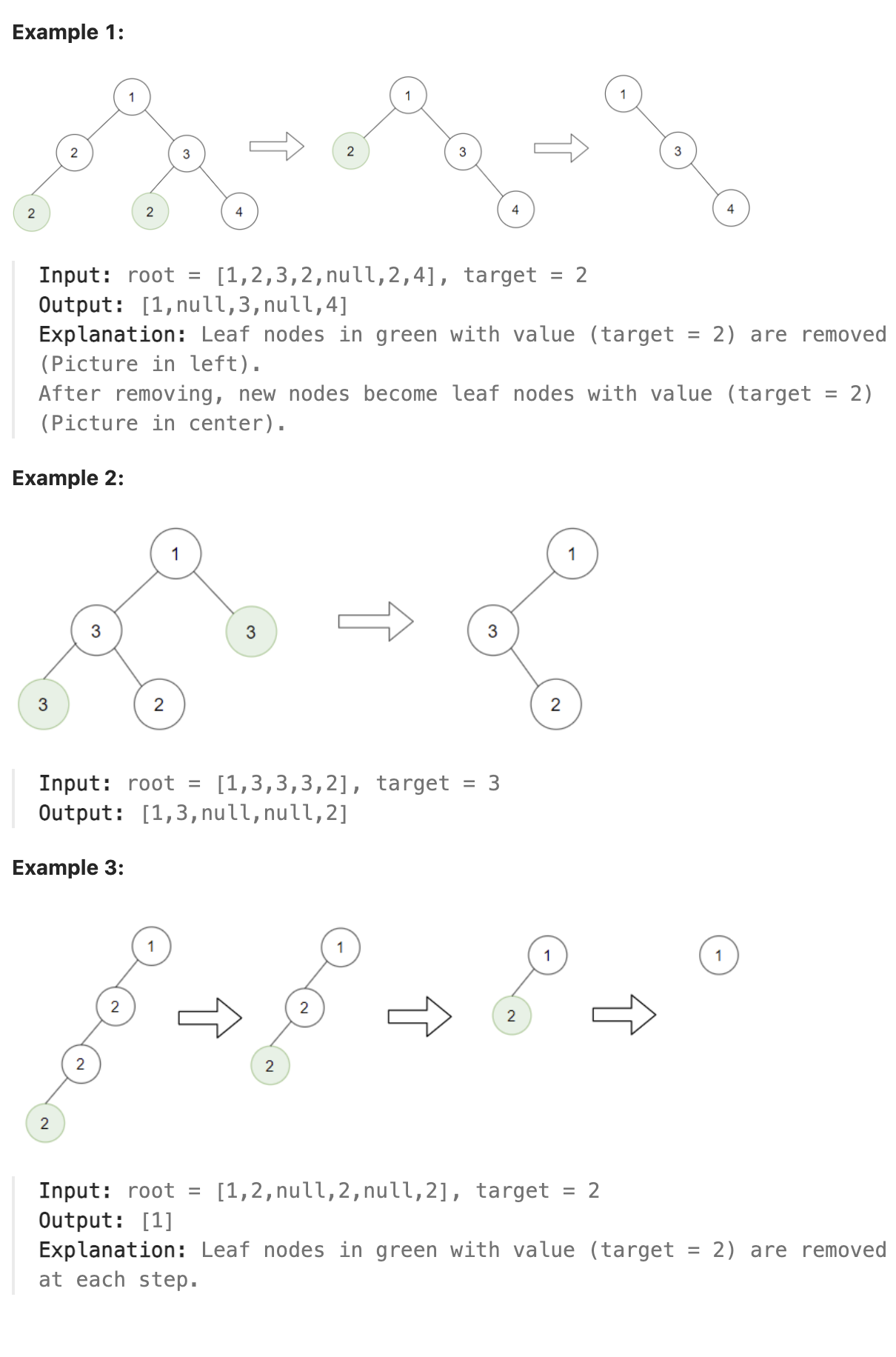
题解
后序遍历即可, 使用递归遍历过程中返回当前节点是否被删除, 需要被删除返回true, 否则返回false. 父节点对子节点进行函数调用, 根据子节点的情况决定是否判断父节点是否要被删除. 这里相当于将子节点及子节点以下的信息向上传递.
代码
| |
总结
直接返回节点会更简洁一些, 对于值符合的叶子节点, 递归时返回nil即可.
day81 2024-05-18
979. Distribute Coins in Binary Tree
You are given the root of a binary tree with n nodes where each node in the tree has node.val coins. There are n coins in total throughout the whole tree.
In one move, we may choose two adjacent nodes and move one coin from one node to another. A move may be from parent to child, or from child to parent.
Return the minimum number of moves required to make every node have exactly one coin.
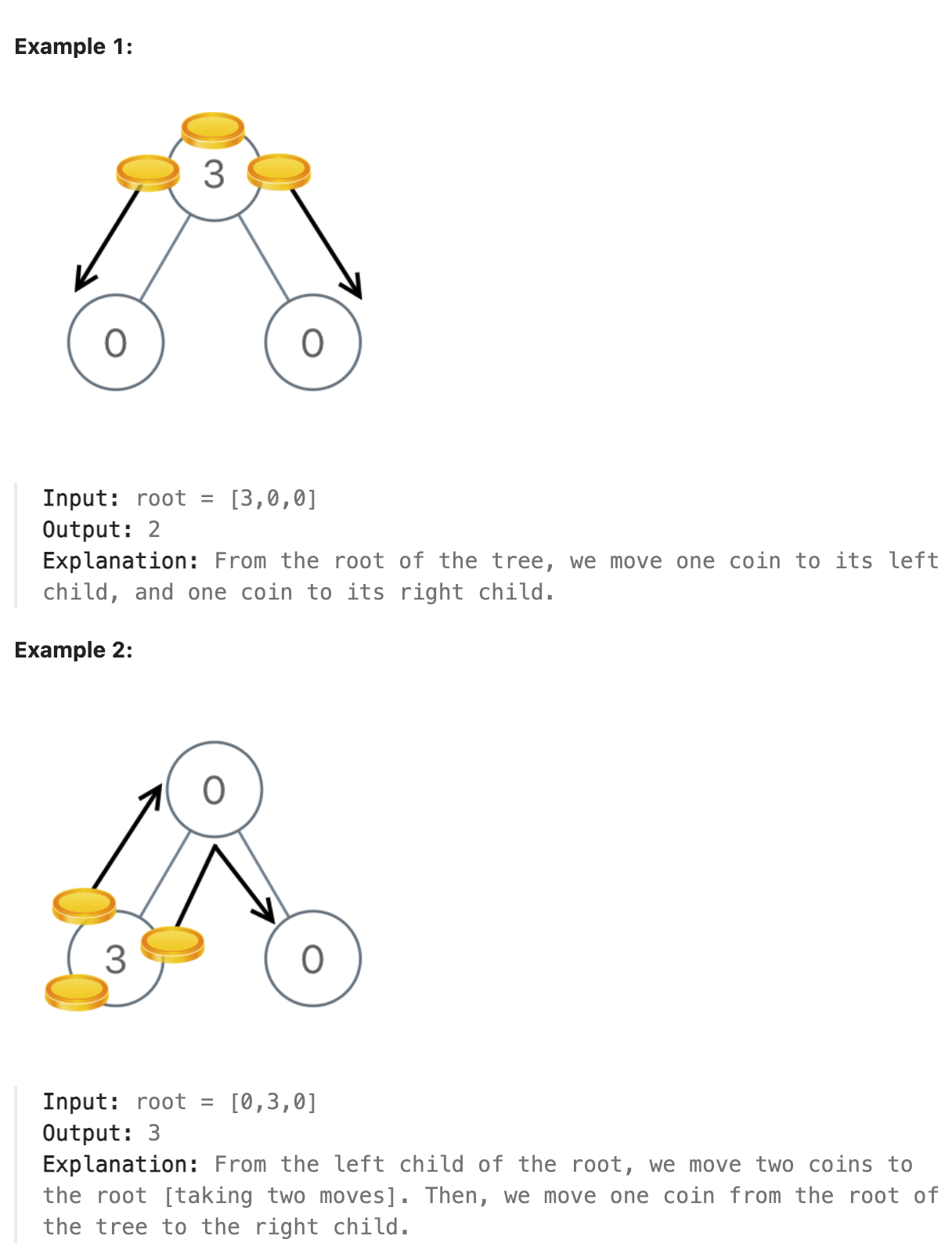
题解
考虑仅有一个根节点和两个叶子节点的情况. 因为最终要得到每个节点仅有一个硬币, 因此叶子节点多余的硬币一定会被传递上去, 没有硬币的节点一定能从父节点获得一个硬币. 将硬币传递上去和从父节点获得硬币都需要与硬币数相等的步数. 因此对于每个父节点, 分别递归计算两个子树能给父节点的硬币数, 需要硬币用负数表示, 同时计算两个子树将每个节点都变为1个硬币到父节点时总共需要的步数. 对于叶子节点来说, 这样的操作即为, 若需要硬币则硬币数设为-1, 同时步数为1. 对于有多余硬币的叶子节点, 将多余的硬币设为硬币数, 同时步数设为多余的硬币数量. 进行后序遍历计算最终需要的步数即可.
代码
| |
总结
本题的关键之一在于理解把多余的硬币传上去和从父节点拿硬币从从步数上来说是等价的. 另一重要的等价性就是父节点和一个子节点都有多余硬币, 另一个子节点需要硬币时, 无论是把父节点的硬币分配给子节点还是把另一个子节点多余的硬币分配给子节点, 最终对步数的贡献都是相同的. 因为若把父节点的硬币给子节点(1步), 另一个子节点的硬币要向上传递(2步), 总共要3步. 而将另一个子节点的硬币分给这个子节点(2步), 父节点硬币向上传递(1步)也需要3步. 所以对于每个子树来说, 重要的是其能传递或者需要多少硬币, 至于内部分配情况对于总步数没有影响.
day82 2024-05-19
3068. Find the Maximum Sum of Node Values
There exists an undirected tree with n nodes numbered 0 to n - 1. You are given a 0-indexed 2D integer array edges of length n - 1, where edges[i] = [ui, vi] indicates that there is an edge between nodes ui and vi in the tree. You are also given a positive integer k, and a 0-indexed array of non-negative integers nums of length n, where nums[i] represents the value of the node numbered i.
Alice wants the sum of values of tree nodes to be maximum, for which Alice can perform the following operation any number of times (including zero) on the tree:
Choose any edge [u, v] connecting the nodes u and v, and update their values as follows: nums[u] = nums[u] XOR k nums[v] = nums[v] XOR k Return the maximum possible sum of the values Alice can achieve by performing the operation any number of times.
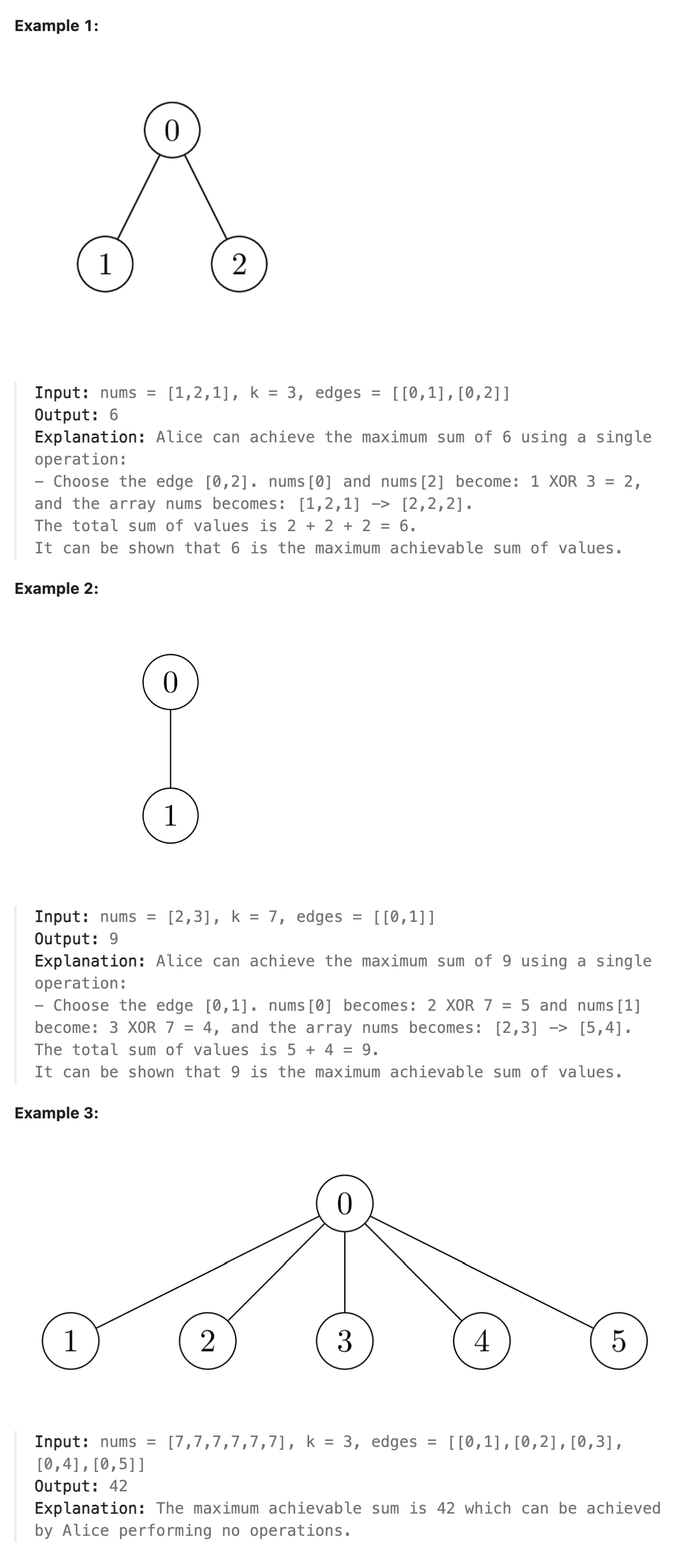
题解
本题为一道难题, 一个关键点在于意识到其实任意两个相邻节点可以同时与k进行异或运算等价于该树中任意两个节点可以同时与k进行异或运算而不影响其他节点的值, 原因在于对任一节点与k异或两次后会恢复原来节点的值, 因此这种与k进行异或的操作相当于具有传递性. 如a,b,c三个节点, a,b连通, b,c连通, a,b与k进行异或操作后, b,c再进行异或操作,此时b的值恢复为原来的值, 相当于a,c与k进行异或操作. 考虑这是一个连通图, 所有节点之间都有路径相连, 因此遍历所有节点将所有与k异或后值会变大的节点异或后的值保存下来, 如果有奇数个则找到与k异或后值变小的节点中减少的值最小的节点, 比较变大节点的增量和减少节点的减量, 根据值较大的节点进行操作. 在本图一定为连通图的情况下, 其实具体的边已经不重要了. 这种"操作"的传递性与昨天的题目在思路上有几分相似之处. 通过传递性去掉了相邻节点的限制, 进而可以直接通过全局的计算直接得到最终结果而不需要诸如动态规划等比较费时费空间的操作.
代码
| |
day83 2024-05-20
1863. Sum of All Subset XOR Totals
The XOR total of an array is defined as the bitwise XOR of all its elements, or 0 if the array is empty.
For example, the XOR total of the array [2,5,6] is 2 XOR 5 XOR 6 = 1. Given an array nums, return the sum of all XOR totals for every subset of nums.
Note: Subsets with the same elements should be counted multiple times.
An array a is a subset of an array b if a can be obtained from b by deleting some (possibly zero) elements of b.

题解
本题如何求出所有组合并且保存以前计算过的组合的状态是关键, 考虑只有两个数的情况, 一共有三个组合, 1,2,1-2. 在此基础上考虑三个数的情况,会发现共有7种组合, 1,2,1-2,3,1-3,2-3,1-2-3. 可以注意到, 除了3自己这种情况外, 其余包含3的情况是将3和只有两个数的所有情况组合. 因此可以得出规律, 对于前n+1个数, 可以将包含前n个数的所有组合与第n+1个数组合, 再加上第n+1个数自身即为前n+1个数的所有组合. 用数组保存到当前位置的所有已经计算过的组合即可.
代码
| |
day84 2024-05-21
78. Subsets
Given an integer array nums of unique elements, return all possible subsets (the power set).
The solution set must not contain duplicate subsets. Return the solution in any order.

题解
本题在寻找全部的子数组的方法上和昨天题目的方法一致, 都是保存前n个数能构成的所有组合的集合,再与第n+1个数依次组合(空也算单独一个组合), 就得到了前n个数能构成的所有组合.
代码
| |
总结
还有一种通过dfs递归实现的方法也很有趣, 核心在于把握所有组合中原来数组中的数要么出现要么不出现, 那么就可以递归调用每次选择包含或者不包含下一个数, 通过将所有的包含与不包含组合, 就得到了所有的组合.
| |
day85 2024-05-22
131. Palindrome Partitioning
Given a string s, partition s such that every substring of the partition is a palindrome . Return all possible palindrome partitioning of s.

题解
本题需要枚举所有的子集分割并判断分割后的这些子集是否均为回文串. 这里可以使用回溯算法. 可以进行一些剪枝, 因为题目限制了所有字串都必须为回文串, 因此若产生的某个子串已经不是回文串则可以直接停止遍历其之后的串. 回溯算法可以使用递归实现. 本质上是一种深度优先搜索.
代码
| |
day86 2024-05-23
2597. The Number of Beautiful Subsets
You are given an array nums of positive integers and a positive integer k.
A subset of nums is beautiful if it does not contain two integers with an absolute difference equal to k.
Return the number of non-empty beautiful subsets of the array nums.
A subset of nums is an array that can be obtained by deleting some (possibly none) elements from nums. Two subsets are different if and only if the chosen indices to delete are different.

题解
本题和求数组的全部子集有一些相似之处, 先排序, 排序可以使得在找与当前数字绝对值相差k的数时只需要看前面的数即可. 保存到当前位置处得到的全部合格的子数组(漂亮的). 在继续遍历时将新的数与之前的所有合格子数组比较, 看原来的子数组中是否有与新的数冲突的数. 若有则不能与新的数组合, 没有则可以组合. 这里为了快速寻找是否冲突, 可以用数组来保存之前的合格子数组, 将之前合格子数组中所有的数作为数组的下标.下标对应位置的值为1. 不包含的数的下标对应位置为0. 考虑数组中的数最大为1000. 这种方法是可以保存所有数的情况的.
代码
| |
总结
该方法时间复杂度比较高, 可参见下面的题解中讲解的动态规划解法, 这里要思考为什么同余的性质如此重要. 因为同余将数组中的数按照不同的性质分为了不同的组, 不同的组的数一定不会相差k因此可以随意组合. 最终结果相当于在这些组中任意选取组内一个可行组合进行组间组合. 这样通过将所有组的组内可行方案相乘就能得到最终结果. 而在组内, 通过排序, 因此各个数都同余, 只有相邻的数可能相差k, 不相邻的相差一定是k的2倍及以上, 这样就能用动态规划来求得组内的全部方案, 可以把问题转换为子问题, 如果不相邻的数也可能相差k, 那么问题就很难用动态规划来解决, 因为不知道什么时候才能解决一个子问题, 把相差k限制在相邻数, 我们就知道只要经过了这个相邻的数, 前面的数对后面一定没有影响了, 就解决了一个子问题, 这样相当于隐含携带了前面的数的信息. https://leetcode.cn/problems/the-number-of-beautiful-subsets/solutions/2177818/tao-lu-zi-ji-xing-hui-su-pythonjavacgo-b-fcgs/
day87 2024-05-24
1255. Maximum Score Words Formed by Letters
Given a list of words, list of single letters (might be repeating) and score of every character.
Return the maximum score of any valid set of words formed by using the given letters (words[i] cannot be used two or more times).
It is not necessary to use all characters in letters and each letter can only be used once. Score of letters ‘a’, ‘b’, ‘c’, … ,‘z’ is given by score[0], score[1], … , score[25] respectively.

题解
本题使用回溯算法, 遍历所有可能的组合并剪枝即可. 首先扫描保存所有可用的字母的个数. 循环当前的words数组, 判断当前词是否能由可用字母组成并计算score, 不能组成则跳到下一个词, 计算完成当前词的score后递归调用计算后面的词组成的词数组用剩余的可用字母能得到的最大值. 将其与当前词的score加和并更新全局最大值, 继续遍历下一个词. 注意这里的递归可能有重复状态, 但大部分是不重复的, 如第一个词用掉了两个a, 后面的词是在可用字母少了两个a的情况下的最大值. 这样求得的是包含第一个词的情况下能得到的最大值. 继续向后遍历, 此时求的是不包含第一个词的情况下的最大值, 意味着虽然也是求除第一个词之外数组中所有词能组成的最大值, 但此时能用全部可用字母, 刚才则是求少了两个a的情况, 因此得到的结果未必相同. 因为这两个a的影响我们不能预先知道, 所以不能直接记忆化上一次的结果拿来用. 可能的优化就是在剩余可用字母完全相同的情况下求包含相同的词的数组能取得的最大值可以记忆化.
代码
| |
day89 2024-05-25
140. Word Break II
Given a string s and a dictionary of strings wordDict, add spaces in s to construct a sentence where each word is a valid dictionary word. Return all such possible sentences in any order.
Note that the same word in the dictionary may be reused multiple times in the segmentation.

题解
为了快速检索分割出来的某个单词是否在词典中, 要先将词典数组转换为哈希表. 还可以注意到, 从原始字符串的某个下标开始能得到的所有可行分割的词的组合是固定的. 则可以扫描字符串, 分割出一个有效单词, 再对剩余字符串调用递归函数获取所有剩余字符串的可行分割, 在递归获取当前串的所有可行分割的过程中将当前下标对应的所有可行分割保存到全局记忆数组中. 后续若再次遇到从该下标开始分割, 直接从记忆数组中获取以该下标开始的所有可行分割串返回即可.
代码
| |
day90 2024-05-26
552. Student Attendance Record II
An attendance record for a student can be represented as a string where each character signifies whether the student was absent, late, or present on that day. The record only contains the following three characters:
‘A’: Absent. ‘L’: Late. ‘P’: Present. Any student is eligible for an attendance award if they meet both of the following criteria:
The student was absent (‘A’) for strictly fewer than 2 days total. The student was never late (‘L’) for 3 or more consecutive days. Given an integer n, return the number of possible attendance records of length n that make a student eligible for an attendance award. The answer may be very large, so return it modulo 109 + 7.

题解
本题为一道难题, 一看有不同的状态, 状态还受到一些限制, 显然首先想到动态规划. 关键在于如何从子问题到当前问题. 首先A只能出现一次, 所以可以通过A0和A1表示对A是否出现这一状态的记忆. L不能连续出现三次, 则L出现可以用L1和L2表示L连续出现1次和2次. P表示正常的出勤. 那么全部状态可以表示成如下图所示的6种(图中下标b表示前一天). 接下来考虑对于每一种情况(A,L,P)其出现时与前一天这6种状态中的哪些有关. 可以看到对于出现L如果当前L连续出现了两次并且A从未出现过, 那么这种状态只有在前一天也为L并且A从未出现过才会发生. 如果L出现了一次, 那么在这之前的状态肯定是非L的即为P, A从未出现过, 则状态数与A0P相同. 对于A0P来说, 其表示当前采用的字母为P, A从未出现, 则无论前一天状态是P还是L已经连续出现了1次或2次今天的状态都可以选择P. 这样将今天的状态与前一天的状态的关系对应起来即可得到只与前一天状态有关的状态转移方式. 实现这一状态转移过程即可. 注意在转移的过程中要及时的将存在加和的转移过程模10^9+7因为数字很快就会变得很大, 而中间模与最后模结果相同. 这样可以避免计算过程的数字溢出.

代码
| |
day91 2024-05-27
1608. Special Array With X Elements Greater Than or Equal X
You are given an array nums of non-negative integers. nums is considered special if there exists a number x such that there are exactly x numbers in nums that are greater than or equal to x.
Notice that x does not have to be an element in nums.
Return x if the array is special, otherwise, return -1. It can be proven that if nums is special, the value for x is unique.

题解
最简单的思路就是找到数组中的最大值, 再从最大值开始向下遍历各个整数, 并遍历数组查看是否满足条件. 但显然这样做时间复杂度很高. 如果先将数组排序, 则任一下标处的数后面的数必然大于等于这个数本身, 此时就可以用到数组末尾的距离来表示大于等于这个数的个数. 此时可以从后到前依次遍历并将当前下标到末尾的距离设为x, 并判断x是否大于前面的数, 如果大于则x满足条件. 对于这样在有序数组中依次遍历查找满足条件的x的值的问题都可以用二分法来加速解决. 设初始start为0, end为数组末尾下标, mid为二者和的一半. 因为题目中要求大于等于x的数的个数为x, 可以假设mid到数组末尾的距离为x, 判断这个数前面的数是否小于x并且当前mid下标对应的数大于等于x即可. 如果都满足则x为所求, 否则根据条件更新start或end的值.
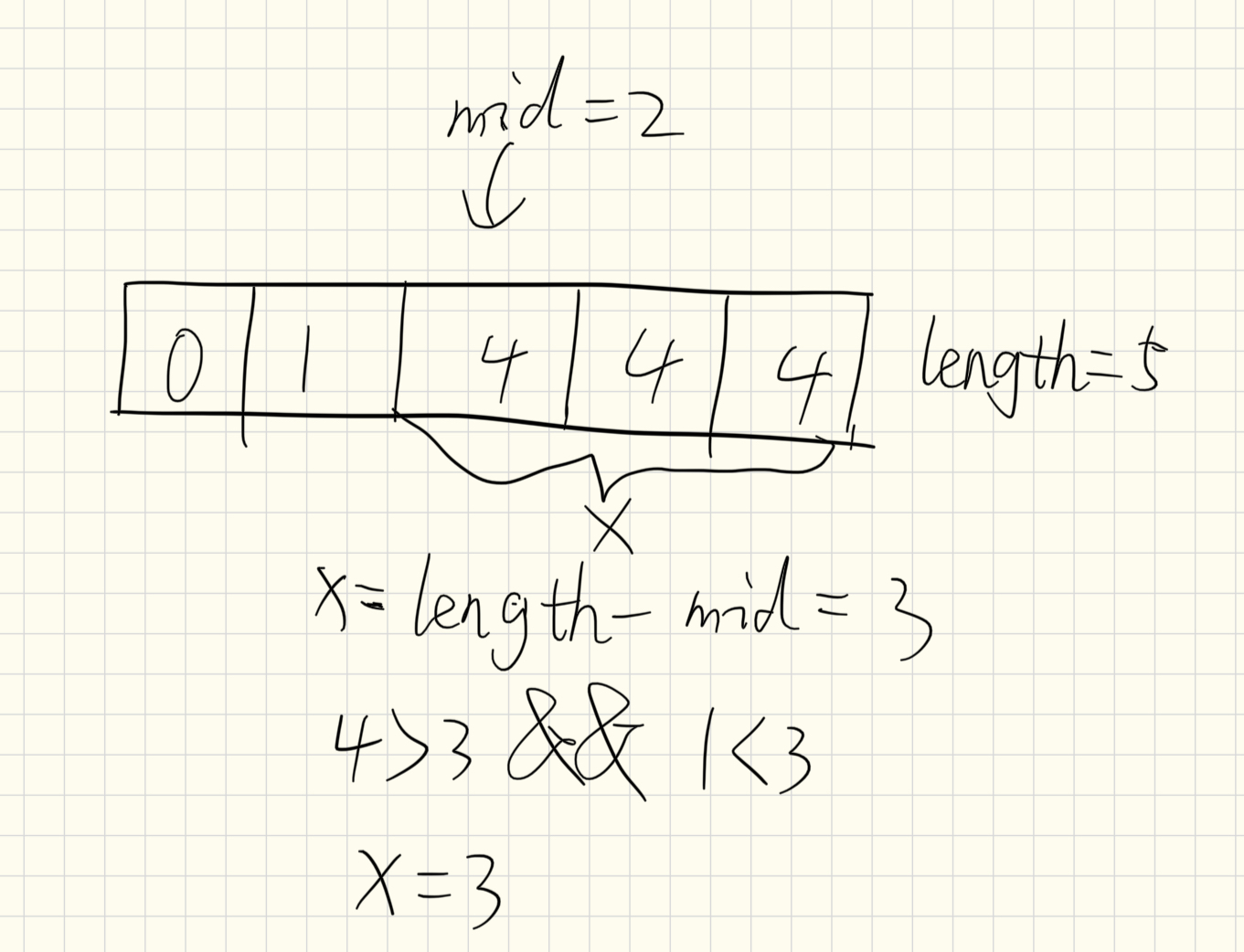
代码
| |
day92 2024-05-28
1208. Get Equal Substrings Within Budget
You are given two strings s and t of the same length and an integer maxCost.
You want to change s to t. Changing the ith character of s to ith character of t costs |s[i] - t[i]| (i.e., the absolute difference between the ASCII values of the characters).
Return the maximum length of a substring of s that can be changed to be the same as the corresponding substring of t with a cost less than or equal to maxCost. If there is no substring from s that can be changed to its corresponding substring from t, return 0.

题解
本题先计算出两个字符串各个位上的差值, 再使用滑动窗口找到窗口内和小于maxCost的最长窗口即可.
代码
| |
day93 2024-05-29
1404. Number of Steps to Reduce a Number in Binary Representation to One
Given the binary representation of an integer as a string s, return the number of steps to reduce it to 1 under the following rules:
If the current number is even, you have to divide it by 2.
If the current number is odd, you have to add 1 to it.
It is guaranteed that you can always reach one for all test cases.

题解
本题要注意寻找规律, 因为题目一定有解, 因此最后一定会变为类似于10000…这样的形式, 即开头为1, 后面全部为0, 这样在不断除以2最终才能得到1. 我们只需考虑对于后面的1, 需要几次给最后一位的1加1操作最终能得到1000…这样的形式. 也就是说, 我们整体考虑题目中给出的两种操作, 本来应该是按照条件奇数加一, 偶数除以二, 偶数除以二实际上就是右移一位, 使得0的数量减少一个, 现在相当于先执行所有的奇数加1操作(这里可以理解为每次给最后一位1加一, 使其进位), 将数字化为1000…这样的形式后, 0的个数就是需要除以二的次数. 观察可以发现, 需要执行加1操作的次数与第一个1和最后一个1之间的0的个数有关, 需要加1的次数正好与首末1之间的0的个数相差1. 这点可以理解为, 通过一系列的加1操作将首末1之间的0移到了整个字符串的最后面, 最终得到开头为连续的1的串, 再加1就能得到以1开头,其余全为0 的串. 如图说明了这个过程. 理解了这一点, 只需要扫描串, 记录首末1之间的0的个数, 最终结果即为首末1之间0的个数加1与串的长度的和. 注意处理串本身就是开头为连续1和串本身即为只有开头为1这两种情况. 只有开头为1直接返回长度减1, 存在大于1个的连续1则为串的长度加1.
代码
| |
总结
本题直接从最后一位开始向前遍历, 遇到0直接将结果加1, 遇到1设定一个标记进位的标记变量为1, 同时将结果加2, 如此重复即可. 注意在每次判断当前位是0还是1之前要将原本的当前位值加上进位的标记变量再判断.
day94 2024-05-30
1442. Count Triplets That Can Form Two Arrays of Equal XOR
Given an array of integers arr.
We want to select three indices i, j and k where (0 <= i < j <= k < arr.length).
Let’s define a and b as follows:
a = arr[i] ^ arr[i + 1] ^ … ^ arr[j - 1] b = arr[j] ^ arr[j + 1] ^ … ^ arr[k] Note that ^ denotes the bitwise-xor operation.
Return the number of triplets (i, j and k) Where a == b.

题解
题目中要求i-j和j-k之间的数组元素全部异或后的值相等, 而i<j<=k. 两个相同的值异或后的值为0, 因此可以得出结论, i-k之间的数异或后的值为0(i-j,j-k范围内的数异或后的值相同). i-k区间内的数异或后的值为0, 就意味着从头开始到i和从头开始到k这两个区间的数异或的值相等(不一定为0). 遍历数组, 计算到当前下标处的异或值. 并将异或值作为key, 下标作为value保存到map中, 计算得到异或值后查询map, 找到与当前下标异或值相等的全部下标, 并将这些区间内的所有可行分割(长度为n的区间有n-1种分割方法, 直观理解放木板到这个区间的数字之间, 一共能放几块就是几种分割方法)数目添加到结果中.
代码
| |
day95 2024-05-31
260. Single Number III
Given an integer array nums, in which exactly two elements appear only once and all the other elements appear exactly twice. Find the two elements that appear only once. You can return the answer in any order.
You must write an algorithm that runs in linear runtime complexity and uses only constant extra space.

题解
本题之前有一个前置问题, 即找到所有数中仅有一个出现了一次的数. 这个问题通过位运算的技巧, 两个相同的数异或之后得到的结果为0. 而唯一一个只出现了一次的数最终会被剩下. 那么对应有两个数都只出现了一次的情况怎么处理, 首先类似的,通过将所有的数异或最终实际上相当于只剩下两个数异或. 此时分辨不出来两个数分别是什么, 但仍保存了一些信息, 因为数字不同的位异或后的结果为1. 则可以通过对应的位为1了解到在对应位两个数不同. 则可以通过按照得到的两个数不同的位将所有数分割为两组, 考虑到在组内其他数个数均为两个, 则在组内使用对前置问题的解决方法即可分别得到两个数.
代码
| |
day96 2024-06-01
3110. Score of a String
You are given a string s. The score of a string is defined as the sum of the absolute difference between the ASCII values of adjacent characters.
Return the score of s.

题解
比较基础, 按照题目要求计算相邻字符的差的绝对值之和即可
代码
| |
day97 2024-06-02
344. Reverse String
Write a function that reverses a string. The input string is given as an array of characters s.
You must do this by modifying the input array in-place with O(1) extra memory.
Example 1:
Input: s = [“h”,“e”,“l”,“l”,“o”] Output: [“o”,“l”,“l”,“e”,“h”]
Example 2:
Input: s = [“H”,“a”,“n”,“n”,“a”,“h”] Output: [“h”,“a”,“n”,“n”,“a”,“H”]
题解
将字符串逆转也是一道简单题, 要求只能使用常数额外空间且直接在原始字符串上逆转, 因为原始字符串以数组形式保存, 可以分别从首尾开始向中间遍历数组并交换首尾的字符即可完成逆转操作.
代码
| |
day98 2024-06-03
2486. Append Characters to String to Make subsequence
You are given two strings s and t consisting of only lowercase English letters.
Return the minimum number of characters that need to be appended to the end of s so that t becomes a subsequence of s.
A subsequence is a string that can be derived from another string by deleting some or no characters without changing the order of the remaining characters.
Example 1:
Input: s = “coaching”, t = “coding” Output: 4 Explanation: Append the characters “ding” to the end of s so that s = “coachingding”. Now, t is a subsequence of s (“coachingding”). It can be shown that appending any 3 characters to the end of s will never make t a subsequence.
Example 2:
Input: s = “abcde”, t = “a” Output: 0 Explanation: t is already a subsequence of s (“abcde”).
Example 3:
Input: s = “z”, t = “abcde” Output: 5 Explanation: Append the characters “abcde” to the end of s so that s = “zabcde”. Now, t is a subsequence of s (“zabcde”). It can be shown that appending any 4 characters to the end of s will never make t a subsequence.
题解
本题从字符串s中删除任意位置的字符后再在末尾添加任意字符得到t, 这里从s中删除字符的位置是任意的,也就意味着只要在s中从头遍历并找到t的一个最长可行前缀即可。再用t的长度减去s中已经存在的前缀的长度级可得到需要补充的后缀长度。
代码
| |
day99 2024-06-04
409. Longest Palindrome
Given a string s which consists of lowercase or uppercase letters, return the length of the longest palindrome that can be built with those letters.
Letters are case sensitive, for example, “Aa” is not considered a palindrome.

题解
本题也是一道简单题, 最近几天的每日一题都比较简单, 因为是能组成的最长回文串, 与顺序无关, 因此只需统计字母个数即可. 遍历字符串并统计字母, 每当同一个字母有两个时就将结果加2并将字母个数重置为0. 遍历一遍后如果仍有字母剩余1个,则将结果加1表示奇数长度的回文串在中间添加的字母.
先统计全部字母的数量再最终求和会快一些, 减少了不必要的判断和加法操作.
代码
| |
day100 2024-06-05
1002. Find Common Characters
Given a string array words, return an array of all characters that show up in all strings within the words (including duplicates). You may return the answer in any order.

题解
本题也是一道简单题, 仍然是寻找在所有单词中都存在的字母, 重复的字母单独计算, 同样不要求顺序, 对于没有顺序要求的字符串问题, 计数往往是很好的解决方法, 因此只需依次遍历所有单词, 对单词中所有字母计数, 再与之前的字母计数比较, 取二者之间的较小值, 最后根据每个字母的计数个数输出答案即可. 注意题目限制字符串长度最多为100, 因此初始化为101保存字母个数的数组即可正常被更小的值刷新.
代码
| |
day101 2024-06-06
846. Hand of Straights
Alice has some number of cards and she wants to rearrange the cards into groups so that each group is of size groupSize, and consists of groupSize consecutive cards.
Given an integer array hand where hand[i] is the value written on the ith card and an integer groupSize, return true if she can rearrange the cards, or false otherwise.

题解
因为要将数组中的数分为几组连续相邻的数且组内个数为groupSize大小, 显然每次都扫描整个数组寻找当前数字的下一个相邻数字效率极低, 所以可以先排序, 排序后数组中的数从小到大排列, 如果相邻的数存在应该在数组中是相邻的, 因此从头遍历排序后的数组, 依次将相邻的数放入一个groupSize大小的判别数组中并在数组中删掉放入的数, 遇到相同的数先继续向后遍历寻找下一个不同的相邻数字, 直到填满整个判别数组为止, 如果找不到相邻的数则可直接返回false. 填满判别数组后再从头遍历数组, 清空判别数组, 重复上述操作. 直到数组中没有数且判别数组刚好填满为止.
代码
| |
总结
这种算法是可行的, 但由于大量的数组删除元素和数组连接操作, 使得实际耗时比较长. 本题还可以使用优先级队列(最小堆)来求解, 将元素全部放入最小堆中, 构造一个哈希表, 保存每个元素和其对应的元素个数. 每次从堆顶弹出一个元素, 即当前的最小元素, 如果弹出的元素不是相邻的数, 则返回false, 弹出后减少该元素在哈希表中对应的元素个数, 直到为0判断其前面是否还有其他更小的数, 如果有可直接返回false(这种情况下一定无法在group中再构成连续相邻的数了). 在函数开头可以先判断下数组的长度能否被groupSize整除, 不能直接返回false, 后面就可以不用再判断是否能填满最后一个group了. 开头的这个判断通过一些简单的方法过滤掉了不满足条件的解, 避免后续浪费时间对这些解进行判断, 做题时要先考虑一些这样可以通过简单判断排除不可行解的情况. 可以大大加快整体的运行效率.
| |
day102 2024-06-07
648. Replace Words
In English, we have a concept called root, which can be followed by some other word to form another longer word - let’s call this word derivative. For example, when the root “help” is followed by the word “ful”, we can form a derivative “helpful”.
Given a dictionary consisting of many roots and a sentence consisting of words separated by spaces, replace all the derivatives in the sentence with the root forming it. If a derivative can be replaced by more than one root, replace it with the root that has the shortest length.
Return the sentence after the replacement.

题解
读懂题是第一步, 本题要将句子中所有的单词替换为在词典中对应的它的前缀形式(如果字典中存在这个单词的前缀的话), 最直接的思路就是遍历句子中的所有单词, 将每个单词依次和词典中的所有单词比较, 看词典中是否存在它的前缀, 但这种方法无疑效率极低, 这个场景和我们日常查词典有些相似, 想想我们日常在词典中查一个单词是如何快速定位的, 当然是按照字母顺序在词典中先定位第一个字母的范围, 再定位第二个字母的范围…,最后找到需要的单词. 现在只要把这种方法表示出来就可以大大加快寻找前缀的速度. 这样就可以构造一棵词典树, 树的边表示不同的字母, 节点可以用来标定是否是一个可行单词. 再去查找某个单词的前缀的时候, 只需要去树中执行bfs找到最短的可行前缀即可.
代码
| |
总结
注意直接使用"+“在go中进行字符串连接是非常耗时的, 因此可以将原句子分割后得到字符串数组, 查询是否存在单词的可行前缀并直接替换对应数组中的字符串, 最后再调用strings.Join将数组中的所有字符串使用空格连接, 可以自行测试如果对数组中每个字符串在查找其可行前缀后都使用”+“连接到结果字符串上耗时远远大于这种方案.
day103 2024-06-08
523. Continuous Subarray Sum
Given an integer array nums and an integer k, return true if nums has a good subarray or false otherwise.
A good subarray is a subarray where:
its length is at least two, and the sum of the elements of the subarray is a multiple of k. Note that:
A subarray is a contiguous part of the array. An integer x is a multiple of k if there exists an integer n such that x = n * k. 0 is always a multiple of k.

题解
本题要求连续子数组和为k的倍数, 则实际有影响的为各个位置上的元素对k取模后的余数, 这种求连续子数组和满足某种条件的问题, 常常可以使用前缀和求解. 在这个问题中使用前缀和保存从数组开头到当前位置元素的所有数字对k取模后求和再对k取模的值, 并将对应的值和当前的下标保存到长度为k的数组中, 数组下标表示前缀和(因为最终要对k取模,因此取值范围一定在k以内), 对应的数组位置的值为这个前缀和对应nums数组中的下标. 这种用数组保存的方式比用map来保存要快得多.
代码
| |
总结
没有注意到k的取值范围, 因为k的取值范围非常大, 使用数组来保存前缀和对应的下标需要开始k大小的数组, 在实践中会导致超出leetcode的内存限制. 因此这里还是要用map来保存前缀和和对应的下标, 但思路仍然是相同的.
day104 2024-06-09
974. Subarray Sums Divisible by K
Given an integer array nums and an integer k, return the number of non-empty subarrays that have a sum divisible by k.
A subarray is a contiguous part of an array.

题解
本题和昨天的题目类似, 通过前缀和相同来得到能被k整除的连续子数组, 注意本题中k的范围为 $10^4$, 因此可以用数组来保存前缀和对k取模后得到某个余数对应的下标位置个数. 后续遇到相同余数在结果中加上之前相同余数的位置个数, 并更新该余数对应的位置个数.
代码
| |
总结
注意对负数取模的处理, 在这里为了将相同余数的位置个数保存到数组中, 要将负数取模后的数转换为正数(如对5取模得-4转换为1, 在求和过程中这二者的效果相同), 先取模再加一个k再取模(如果是正数通过再取模将加上的k消掉)即可
day105 2024-06-10
1051. Height Checker
A school is trying to take an annual photo of all the students. The students are asked to stand in a single file line in non-decreasing order by height. Let this ordering be represented by the integer array expected where expected[i] is the expected height of the ith student in line.
You are given an integer array heights representing the current order that the students are standing in. Each heights[i] is the height of the ith student in line (0-indexed).
Return the number of indices where heights[i] != expected[i].

题解
本题思路上很简单, 只需将数组复制一份并排序, 再与原数组比较即可. 这里主要意图应该是让你练习一下排序算法, 因此我们手动实现一下归并排序这种比较经典的排序算法. 归并算法是经典的分治法思想, 分治法分为"分"和"治"两部分, 分即将数组一分为二, 治即对于每个子数组进行排序, 最后将排好序的两个子数组合并(归并的"并”). 对于某一类分治法, 其时间复杂度可以使用主定理进行计算(感兴趣可自行了解).
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Master_theorem_(analysis_of_algorithms)
代码
| |
day 106 2024-06-11
1122. Relative Sort Array
Given two arrays arr1 and arr2, the elements of arr2 are distinct, and all elements in arr2 are also in arr1.
Sort the elements of arr1 such that the relative ordering of items in arr1 are the same as in arr2. Elements that do not appear in arr2 should be placed at the end of arr1 in ascending order.

题解
考虑数组中数字的大小范围在1000以内, 因此直接对数组排序可以使用计数排序算法. 本题中要求将数组1中的数字按照数组2中数字的顺序排序, 这部分也可以使用计数排序的思想, 即统计数组1中各个数的出现次数, 并保存在一个计数数组中, 这个数组中下标i处的值为数字i对应的数组1中出现的次数. 这种用下标指示值, 用元素指示个数的思路在前面的题中也多次出现. 得到计数数组后, 先将数组中包含在arr2的数按照arr2中的顺序放置, 并将对应位置次数归零, 再从头遍历数组, 按升序将其余数字放在末尾即可.
代码
| |
day107 2024-06-12
75. Sort Colors
Given an array nums with n objects colored red, white, or blue, sort them in-place so that objects of the same color are adjacent, with the colors in the order red, white, and blue.
We will use the integers 0, 1, and 2 to represent the color red, white, and blue, respectively.
You must solve this problem without using the library’s sort function.

题解
本题只有0,1,2三个数, 对只包含这三个数的数组进行排序, 直接在原数组上修改, 充分考虑题目条件, 没有必要使用排序算法来排序, 当题目中只有两个数的时候, 对整个数组排序相当于通过两变量交换将小的数都交换到前面, 大的都交换到后面. 现在有三个数, 则通过只需通过交换位置将所有的2都放到数组末尾, 将所有的0放到数组开头, 1自然就位于中间位置. 交换的思路也很简单, 通过两个变量分别标记被移到数组开头的0的个数和移到数组末尾的2的个数, 遇到0就将其移到之前的0的后面并将开头0的个数加一, 对2同理.
代码
| |
总结
思路是正确的, 但在实现时有一些细节要注意, 如遇到2将其交换到末尾时, 如果被交换过来的数也是2则要继续将其移到末尾, 直到交换过来的数不是2或者已经将当前下标后面的所有数都交换为2为止.
day108 2024-06-13
2037. Minimum Number of Moves to Seat Everyone
There are n seats and n students in a room. You are given an array seats of length n, where seats[i] is the position of the ith seat. You are also given the array students of length n, where students[j] is the position of the jth student.
You may perform the following move any number of times:
Increase or decrease the position of the ith student by 1 (i.e., moving the ith student from position x to x + 1 or x - 1) Return the minimum number of moves required to move each student to a seat such that no two students are in the same seat.
Note that there may be multiple seats or students in the same position at the beginning.

题解
本题总体思路比较直观, 因为找最小的移动次数让每个同学都坐在某个位置的椅子上, 因此只要找到同学位置和椅子位置最小的差值和就可以得到答案. 首先将椅子位置和同学位置均排序, 再从头遍历数组将二者差加和即得最终结果, 是一种贪心算法, 这里分析一下为什么排序后将椅子和同学的位置依次做差就能得到正确答案. 考虑数组中的任意两个位置, 假设椅子对应的位置为i和i+k, 同学对应的位置为j和j+m, 若则无论j,j+m和i的大小关系如何, 这两个同学挪到两个椅子的最小值均为|j-i|+|j+m-i-k|(可以自行考虑i,i+k,j,j+m这四个数的全部不同位置关系, 一一列举即可得出结论). 由两个位置的情况可推得一般情况, 即两个数组长度相同且均从小到大排序的情况下, 两个数组各个元素的差值的最小和就是各个位置元素差的和(还可以思考无论哪个同学坐到哪个位置上, 总要有另一个同学坐在另一个位置上从而将这两个同学的距离补上, 因此按照顺序一一就坐就是最优的).
代码
| |
day109 2024-06-14
945. Minimum Increment to Make Array Unique
You are given an integer array nums. In one move, you can pick an index i where 0 <= i < nums.length and increment nums[i] by 1.
Return the minimum number of moves to make every value in nums unique.
The test cases are generated so that the answer fits in a 32-bit integer.

题解
本题思路上和昨天的题目基本一致, 先排序再从头遍历排好序的数组, 将重复的数字增加到最小不重复为止(如2,2,2,3, 将第二个2增加到3,将第三个2增加到4, 将3增加到5). 使用一个变量记录当前已经遍历过的数字修改后不重复数字中的最大值. 对遍历的每个数字, 判断其与当前最大值的关系, 若相等则将最大值加一并将结果加一, 小于最大值将最大值加一并将结果加上当前数字与最大值的差值, 大于最大值将最大值更新为当前数字. 考虑排序在这里的作用, 排序给每一个数字都提供了隐含的信息, 即前面的数字都比当前数字小, 后面的数字都比当前数字大, 这一信息使得我们可以做出更好的决策. 在未排序前, 对数组中的数我们无法知道是应该保持原样还是增加到某个数字可以满足题目条件, 但在排序后, 只需要增加到最小不重复的数即可, 考虑两个数字2,4, 假如当前不重复需要数字4,5(注意题目中只允许增加, 不允许减小). 无论是将2增加到4,4增加到5. 还是4不变,2增加到5, 增加的差值均为3. 这是因为任何比4大的值, 2都需要先增加到4, 再增加到这个值. 这一过程无论是在同一个数字上完成还是拆分为在两个数字上完成, 过程中需要改变的差值都是一样的.
代码
| |
day110 2024-06-15
502. IPO
Suppose LeetCode will start its IPO soon. In order to sell a good price of its shares to Venture Capital, LeetCode would like to work on some projects to increase its capital before the IPO. Since it has limited resources, it can only finish at most k distinct projects before the IPO. Help LeetCode design the best way to maximize its total capital after finishing at most k distinct projects.
You are given n projects where the ith project has a pure profit profits[i] and a minimum capital of capital[i] is needed to start it.
Initially, you have w capital. When you finish a project, you will obtain its pure profit and the profit will be added to your total capital.
Pick a list of at most k distinct projects from given projects to maximize your final capital, and return the final maximized capital.
The answer is guaranteed to fit in a 32-bit signed integer.

题解
本题是一道难题, 思路总体还是比较清晰的, 本题目标是取k个不同的project, 使得最后能得到的利润最大. 每一个project都有对应的利润和成本. 要使最后的整体利润最大, 无疑只要在当前可以选择(即成本在当前已获得的资金范围内)的所有project中选择利润最大的, 再更新可选择的project, 再次选择利润最大的. 如此反复直到选择完全部的k个project即可. 有了这个思路, 我们要解决两个问题. 1. 如何高效的选择利润最大的project, 最大堆显然是一个不错的选择. 2. 如何更新可选择的project的范围, 我们将project的成本排序, 每次获得了更多的本金后就将小于当前本金的所有project的利润加入最大堆, 为了每次只放入新增加的project, 可以用一个标记变量标记之前已经选择过的project位置. 获得更多本金后从标记位置开始继续遍历数组, 并将成本小于本金的项的利润放入最大堆中. 代码实现以上解题思路即可.
代码
| |
总结
go中最大堆可以使用容器类heap来实现, 只要实现了heap接口的所有方法, 就可以直接使用这个堆了.
day111 2024-06-16
330. Patching Array
Given a sorted integer array nums and an integer n, add/patch elements to the array such that any number in the range [1, n] inclusive can be formed by the sum of some elements in the array.
Return the minimum number of patches required.

题解
本题是一道难题, 难点在于根据题目题意, 如何确定某个数组中数的和能够覆盖的数字范围. 按照我们一贯使用的思考方式, 先考虑一下简单情况, 若只有一个数字1, 则能覆盖的数字只有1, 添加上一个数字2, 则能覆盖的数字有1,2,1+2. 如果在1,2基础上再添加一个数字3, 则能覆盖的数字有1,2,1+2,3,1+3,2+3,1+2+3. 则由这几个简单例子可以发现, 如果之前能够覆盖的数字为集合{x}, 则加上一个数字r后能覆盖的数字为集合 $x \cup (x + r)$ . 若之前能够覆盖的为一个连续的区间[x,x+k],则加上数字r后能够覆盖的区间为 $ [x,x+k] \cup [x+r, x+k+r]$. 则此时想到可以用贪心算法, 如果已经覆盖了[x, x+k], 则只需要让x+r = x+k+1, 即新增加的数恰好可以使得新覆盖区间的开头为已经覆盖区间的末尾. 就能得到[x,x+k+r]的新覆盖区间. 如果r比这种情况小, 那么新覆盖的区间没有我们当前得到的区间大. 如果比这种情况大, 则x+r和x+k之间会有几个数字没有覆盖上, 还需要再用一个新的数覆盖一次, 显然很难使得添加数字的个数最小.
将这个思路在代码中实现, 初始化一个数字表示当前覆盖的区间最大值sum, 遍历数组, 设x为nums[i], 判断当前sum是否大于nums[i](即已经覆盖的区间是否包含当前这个数组中的数字). 如果小于, 则添加一个数字sum+1 前面分析中的x+k+1 (因为题目只要求添加的数字的最小个数,因此不需要真的添加到数组中, 只需扩大可行区间的范围即可), 将区间最大值扩展为sum+sum+1 前面分析中的x+k+r , 并将添加数字的个数加一. 再次判断与x的关系. 如此反复直到覆盖的区间包含x为止, 继续向下遍历. 遍历完成后, 判断当前区间是否已经可以覆盖n, 如果不能, 则按照之前的方法继续扩展区间直到能覆盖n为止.
代码
| |
day112 2024-06-17
633. Sum of Square Numbers
Given a non-negative integer c, decide whether there’re two integers a and b such that a2 + b2 = c.

题解
本题计算出c的平方根, 用两个变量low和high分别标记0和c的平方根(取下整), 计算两变量的平方和, 若比c大则减小high, 否则增大low, 直到得到平方和为c或者low=high为止.
代码
| |
总结
本题还有一些有趣的相关数学知识, 费马两平方和定理和两数平方和定理, 前者说明了一个奇素数何时能被写为两平方数之和. 满足条件的奇素数也被称为毕达哥拉斯质数, 后者给出了所有大于1的整数在什么情况下能被写为两平方数之和. 是前者的推广. 可参考
Fermat’s theorem on sums of two squares
day113 2024-06-18
826. Most Profit Assigning Work
You have n jobs and m workers. You are given three arrays: difficulty, profit, and worker where:
difficulty[i] and profit[i] are the difficulty and the profit of the ith job, and worker[j] is the ability of jth worker (i.e., the jth worker can only complete a job with difficulty at most worker[j]). Every worker can be assigned at most one job, but one job can be completed multiple times.
For example, if three workers attempt the same job that pays $1, then the total profit will be $3. If a worker cannot complete any job, their profit is $0. Return the maximum profit we can achieve after assigning the workers to the jobs.

题解
本题仍然使用贪心算法, 首先给worker排序, 在排好序后遍历worker数组, 并把当前worker可以做的工作中profit最大的分配给他, 即给结果加上可以做的工作中的最大profit, 这个最大profit可以使用一个变量来保存, 当遍历的下一个worker时, 根据他的工作能力更新可以做的工作中的最大值. 如此反复, 最终得到结果.
代码
| |
总结
为什么排序如此重要, 正如之前的题解中多次提到的, 一个排好序的数组在遍历的时候天然包含了更多信息, 即前面的数字比当前的小, 后面的比当前的大. 使用贪心的重要思想就是, 在当前能获得的结果中取最好的, 那么对于排好序的数组, 前面的必然比当前小, 我只需要依次遍历找到我能拿到的最大值即可. 如果没有排序, 那么我们每次都要将数组整体遍历一遍才能确定我当前能拿到的最大值是多少(后面可能有难度更小但利润更大的任务, 显然我们都想做这种任务). 每次都遍历一遍数组整体是 $n^2$ 的复杂度, 排好序后可以用下标标记之前遍历到哪里了, 只需要遍历一遍数组即可. 是 $nlogn(排序)+n(遍历数组) = O(nlogn) $ 的复杂度. 只有在排好序的数组里标记之前遍历到哪里才有意义, 未排序的数组标记之前遍历到哪里没什么意义(后面既可能有更大的, 也可能有更小的)
day114 2024-06-19
1482. Minimum Number of Days to Make m Bouquets
You are given an integer array bloomDay, an integer m and an integer k.
You want to make m bouquets. To make a bouquet, you need to use k adjacent flowers from the garden.
The garden consists of n flowers, the ith flower will bloom in the bloomDay[i] and then can be used in exactly one bouquet.
Return the minimum number of days you need to wait to be able to make m bouquets from the garden. If it is impossible to make m bouquets return -1.

题解
不能做出足够的花束的条件是很容易确定的, 只要花园里花的总数比需要的数量小, 则直接返回-1. 否则只要等待足够长的时间, 总能做出足够的花束. 如果等待时间为花盛开时间的最大值, 显然一定满足条件, 若为最小值, 不一定满足条件, 即实际上本题转化为在所有盛开时间中搜索能满足条件的最小值. 对于给定一个时间, 只需要遍历一遍bloomDay数组即可得知其是否满足条件. 这种搜索其实与在一个数组中搜索指定的数没有本质上的区别, 将数组排序后使用二分查找, 对于搜索某一固定数字, 我们采取的方式是如果中间值比目标大, 则将右边界设为中间值, 否则将左边界设为中间值. 如此反复. 而在本题中, 虽然不能直接比较目标值与中间值的相对大小, 但通过使用中间值对bloomDay数组遍历判断是否能做成足够数量的花束(设一个标记变量保存当前连续可使用的花的数量,大于等于k时将当前花束数量加1,最后判断花束数量是否大于等于m)我们可以了解到目标值与中间值的相对大小. 如果此中间值满足题目条件, 那么目标值应该小于等于这个中间值, 否则大于等于这个中间值, 因此回到了最熟悉的二分搜索部分.
代码
| |
day115 2024-06-20
1552. Magnetic Force Between Two Balls
In the universe Earth C-137, Rick discovered a special form of magnetic force between two balls if they are put in his new invented basket. Rick has n empty baskets, the ith basket is at position[i], Morty has m balls and needs to distribute the balls into the baskets such that the minimum magnetic force between any two balls is maximum.
Rick stated that magnetic force between two different balls at positions x and y is |x - y|.
Given the integer array position and the integer m. Return the required force.
题解
竟然是一道和<瑞克和莫蒂>的联动题(瑞克和莫蒂真的很好看, 强推!!), 要求我们分配这些球, 使得两个球的最小间隔最大. 典型的max-min问题. 解答这种问题因为题目中是要求分配球来获得最终的结果, 使得我们的思路往往起初就会停留在如何分配球这个问题上, 试图通过比较各种分配方式的最小间隔来找到最大的值, 但显然是低效的, 原因在于可能有很多种分配组合都对应着同一个最小间隔. 因此应该转换思路, 给定一个最小间隔, 判断是否有分配方式可以符合这个最小间隔, 只要有一个符合的分配方式, 那么这个最小间隔就是可以取得的, 相当于用这个分配方式代表了所有相同最小间隔的分配方式(代表元思想). 如何判断? 只要在排序后的数组从头到尾遍历, 并采用贪心算法, 和昨天的花束问题类似, 每当间隔大于等于给定的最小间隔就分配一个球, 最后看能分配的球的数量和给定的球的数量之间的相对大小. 大于给定的球则给定最小间隔可以取得. 如何得到最大值? 一样通过二分法, 通过上述判断方法判定中间数值与目标最大值的相对大小, 中间值能取得则将左边界设为中间值, 否则右边界设为中间值. 最终即可得到所求的最大值.
代码
| |
总结
本题和昨天的花束问题有几分相似之处, 体现了一种很重要的思想, 当通过某种组合寻找一由组合产生的属性值, 而多种组合对应同一个属性值时, 可以先假设一个属性值, 再去验证某个组合是否符合. 这样就把问题从求解问题转换为了验证问题. 这里其实和我们平常常用的证明思路正好相反, 平常很多问题证伪只需要举一个反例, 证实则要严格证明,而在今天的问题中, 我们只要找到一个能证实假设的距离成立的组合就足够了, 即证实只要举一个正例即可. 这种题要结合题目的要求, 很多实际生活问题只要能找到一个可行解即可. 这是我们能够用这种方法解题的基础.
很多问题在原问题不容易解决的时候都可以通过一些方式转换成等价的更容易解决的问题, 如计数问题中的自归约问题可将近似求解算法转换成某种采样算法, 通过采样即可得到原问题的近似解(蒙特卡罗)
day116 2024-06-21
1052. Grumpy Bookstore Owner
There is a bookstore owner that has a store open for n minutes. Every minute, some number of customers enter the store. You are given an integer array customers of length n where customers[i] is the number of the customer that enters the store at the start of the ith minute and all those customers leave after the end of that minute.
On some minutes, the bookstore owner is grumpy. You are given a binary array grumpy where grumpy[i] is 1 if the bookstore owner is grumpy during the ith minute, and is 0 otherwise.
When the bookstore owner is grumpy, the customers of that minute are not satisfied, otherwise, they are satisfied.
The bookstore owner knows a secret technique to keep themselves not grumpy for minutes consecutive minutes, but can only use it once.
Return the maximum number of customers that can be satisfied throughout the day.

题解
本题中minutes是固定的, 相当于固定长度的minutes可以放置在grumpy数组的任意位置, 将这些位置的数全部变为0, 显然我们需要遍历所有可以放置的位置从而找出能满足的顾客最大值, 因此可以采用滑动窗口从头开始遍历grumpy窗口, 并随着窗口滑动计算当前能满足的顾客数量. 考虑到窗口之外的能满足顾客数量是固定的, 且每次滑动实际上只需要增加窗口后一个的顾客数量且减去窗口最前面的顾客数量, 即可得到每次滑动后能满足的顾客总数. 则初始化先计算出窗口外能满足的顾客总数, 再单独计算窗口内满足的顾客数量. 再将二者加和即得当前能满足的顾客总数. 持续遍历, 按照之前的算法更新能满足的顾客总数并更新最大值.
代码
| |
day117 2024-06-22
1248. Count Number of Nice Subarrays
Given an array of integers nums and an integer k. A continuous subarray is called nice if there are k odd numbers on it.
Return the number of nice sub-arrays.

题解
这种连续子数组问题是老朋友了, 尤其是这种问符合某个条件的连续子数组个数, 这种题目都采用类似前缀和的思想. 计算从数组开始到当前下标的子数组中奇数的个数, 以奇数个数作为下标, 将从头开始包含这个奇数个数的子数组数目作为数组中的值. 只需要将j下标和j-k下标的数字相乘即可得到从j-k到j包含k个奇数的子数组个数. 从下标k开始遍历"前缀和"数组. 并按照前述方法计算包含k个奇数的子数组个数并加和即可得到最终结果.
代码
| |
总结
其实这种类型的问题核心也是一种转化问题的思路, 即对于求解某一性质为一定值的问题, 可以转化为求解两个区间再做差. 如求解某属性等于k的问题, 可以转化为求解某属性小于等于k和小于等于k-1两个区间后做差的问题. 这种转化适用求解一个区间比求解精准值要容易的多的场景(求解小于等于某个值 往往比求解等于某个值容易得多).
day118 2024-06-23
1438. Longest Continuous Subarray With Absolute Diff Less Than or Equal to Limit
Given an array of integers nums and an integer limit, return the size of the longest non-empty subarray such that the absolute difference between any two elements of this subarray is less than or equal to limit.

题解
本题虽是一道中等难度的题, 但实际比较复杂. 题目很好理解, 需要找到满足子数组内任意两数字差的绝对值小于等于k的所有子数组中最长子数组的长度. 将问题分解开, 首先解决如何确定某个子数组中任意两数字差绝对值是否小于等于k, 只需要知道这个子数组中的最大值和最小值, 二者的差小于等于k则子数组中任意两数字差绝对值都小于等于k. 那么解决这个问题可以使用滑动窗口, 记录当前窗口中的最大值和最小值, 如果满足小于等于k的条件, 则扩大窗口, 判断新加入的数字是否在最小值和最大值的范围内, 在则继续扩大窗口. 否则判断最值更新后当前窗口还能否继续满足小于等于k的条件, 如果不满足则缩小窗口直到满足为止. 满足则继续扩大窗口. 对于某一个特定的子数组, 获知其最小值和最大值比较容易, 遍历一遍数组即可得到. 但使用滑动窗口解题时, 如果每次扩大或者缩小窗口都对窗口内的数字进行遍历显然时间复杂度极高. 我们只需要根据扩大窗口时新增加的数字和缩小窗口时减少的数字来更新最值. 需要解决的问题是, 缩小窗口直到满足条件这一步骤中, 如何判断缩小窗口已经满足条件了呢. 以最小值被更新为例, 如果最小值更新和与当前最大值的差大于k, 则应该缩小窗口直到窗口内的最大值和最小值的差小于等于k. 这意味着, 我们缩小窗口时可能不仅要将窗口缩小到不包含当前最大值, 还可能继续缩小, 直到满足条件为止. 如当前最小值为2, k为3, 而当前窗口中最大值为8, 则我们应缩小窗口直到窗口内最大值小于等于5为止, 这期间我们可能要缩小到不包含8, 再缩小到不包含7, 再缩小到不包含6… 因此我们需要知道数字中大于5的数字都有什么. 这可以用单调队列来解决, 单调减队列保证了后面的数字一定比前面的数字小, 不满足条件的数字都被舍弃. 用一个哈希表保存当前窗口中所有数字和其对应的个数, 缩小窗口时, 减少哈希表中窗口左端数字对应的个数, 直到遇到当前单调队列的队首数字, 同样减少哈希表中的个数, 并判断减少后是否为0, 为0则将其从单调队列中弹出, 否则继续缩小窗口. 直到单调队列队首数字为满足条件的数字. 对于最大值被更新则做类似处理.
因此解答本题我们需要: 1. 哈希表 : 保存当前窗口中各个数字的个数 2. 单调减队列: 保存当前窗口中从最大值开始以及最大值右侧比最大值小且满足单调减顺序的数字(如对于7,5,6 队列中为7,6). 3. 单调增队列 : 保存窗口中从最小值开始及最小值右侧比最小值大且满足单调增顺序的数字(如对于5,7,6 队列中为5,6). 4. 滑动窗口: 解决核心问题
代码
| |
总结
最大值单调队列中的在最大值右侧这一含义为什么如此重要, 因为通过单调队列隐含了一个信息, 即位于当前窗口中单调队列中队列首的数字左侧的数字都比队首数字小, 这一信息使我们可以丢弃一些不必要保存的数字, 因为如果需要缩小窗口, 那么在缩小到这个最大值之前, 窗口中都包含这个最大值, 那么一定不满足要求, 只有在缩小到不包括这个最大值, 才可能满足要求. 这时候再根据单调队列中的数字继续依次判断. 这就是"单调"带来的隐含信息, 这一信息对于简化计算极为重要.
day119 2024-06-24
995. Minimum Number of K Consecutive Bit Flips
You are given a binary array nums and an integer k.
A k-bit flip is choosing a subarray of length k from nums and simultaneously changing every 0 in the subarray to 1, and every 1 in the subarray to 0.
Return the minimum number of k-bit flips required so that there is no 0 in the array. If it is not possible, return -1.
A subarray is a contiguous part of an array.

题解
本题为一道难题, 要解决最小的翻转次数之前先思考如何判断一个数组能否通过几次翻转最终使得数组内数字全为1, 再考虑如何求得翻转次数的最小值.
如何解决能否通过翻转使得数组内数字全为1的问题呢. 看上去数组中的0可能在任何一个位置出现, 我们也不知道101翻转后的010末尾的0能否和后面的数字组合到一起成为新的一串0. 想让计算机解题也不可能像我们看这个数组一样扫视过去大概估计哪些部分可以翻转, 再通过尝试修正一小部分错误就能得出判断. 计算机不会"估计". 但计算机会"硬算". 因此我们不必如此贪心想一步到位得出答案, 大可以从头开始, 每次只将一个0翻转为1, 遍历到下一个0, 翻转为1, 如此重复每次只将数组中最前面的0翻转为1. 最终如果整个数组都能变成1则该数组可以翻转为全1. 否则不能. 而翻转要相邻的k个位同时翻转, 可用一个固定窗口来表示相邻的k位. 遍历数组, 让窗口内窗口首部的数字为0, 翻转窗口, 将窗口移动到下一个0, 如此重复最终即可判断能否使数组内为全1.
巧合的是, 这种算法同时解决了最小的问题, 即通过这种方式移动窗口并翻转到最后翻转的次数就是最小次数. 原因是最终目标是将数组全部置为1, 因此想实现这个目标, 任何一个0都需要通过翻转变成1, 那么无论哪个位置的0迟早都要被翻转, 意味着任意位置的0对最终结果数量的贡献是均等的, 即时先翻转了后面的0, 前面遗留的0最后还是需要一次翻转, 因此直接从前到后依次翻转就能得到正确答案.
但到这里还没有结束, 这种算法每次都要将整个窗口内的全部数字翻转一遍, 最坏情况下, 窗口每次移动一位, 则总共需要翻转n*k次. 在k接近n时, 时间复杂度相当于 $n^2$ 级别. 这显然是不可取的, 考虑我们翻转的过程, 如果窗口只向后移动一位, 那么窗口后面的大部分数字经过两次翻转相当于没变. 这提示我们, 没必要真的每次都将每个数字翻转, 只需要记录这个数字被翻转了多少次, 在遍历到这个数字的时候根据翻转次数确定当前数字的值即可. 如何记录某个位置的数字被翻转了多少次? 因为每次翻转都是以一个窗口为单位的, 因此只需记录每次翻转时的窗口尾部到哪里就相当于记录了整个窗口内的数字都被翻转了一次. 用一个单调增数组保存每次翻转窗口尾部的位置, 每次新翻转都将新的尾部放入数组末尾. 对于遍历的每个数字, 将其当前位置和数组首的最小翻转窗口尾部比较, 小于等于这个最小尾部则单调数组的长度就是这个数字被翻转的次数.
代码
| |
day120 2024-06-25
1038. Binary Search Tree to Greater Sum Tree
Given the root of a Binary Search Tree (BST), convert it to a Greater Tree such that every key of the original BST is changed to the original key plus the sum of all keys greater than the original key in BST.
As a reminder, a binary search tree is a tree that satisfies these constraints:
The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys less than the node’s key. The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys greater than the node’s key. Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
题解
考虑到树为一棵二叉搜索树, 因此对于任何一个节点, 比它大的节点有其右子树的节点, 若其父节点为祖父节点的左子节点, 则还有其祖父节点以及祖父节点的右子树的节点. 以此类推. 考虑最简单的仅有三个节点的情况: 一个父节点和左右两个子节点. 对于左子节点而言, 需要加父节点和右子节点的值. 对于父节点要加右子节点的值. 右子节点不用处理. 因此通过对树遍历将问题转化为类似三个节点的情况. 左右子树均可视为一个节点. 从根节点开始, 对节点进行如下操作, 递归遍历右子树, 计算右子树所有节点的和返回. 将当前节点的值加上右子树的和, 将和传递给左子树并递归遍历左子树, 返回左子树所有节点的和. 最终返回根节点和左右两个子树的和. 注意更新节点值和计算子树和是分开的, 更新节点值要将传递的值和当前值以及右子树的和相加. 但返回时返回的是原来的节点值对应的子树和.
代码
| |
day121 2024-06-26
1382. Balance a Binary Search Tree
Given the root of a binary search tree, return a balanced binary search tree with the same node values. If there is more than one answer, return any of them.
A binary search tree is balanced if the depth of the two subtrees of every node never differs by more than 1.
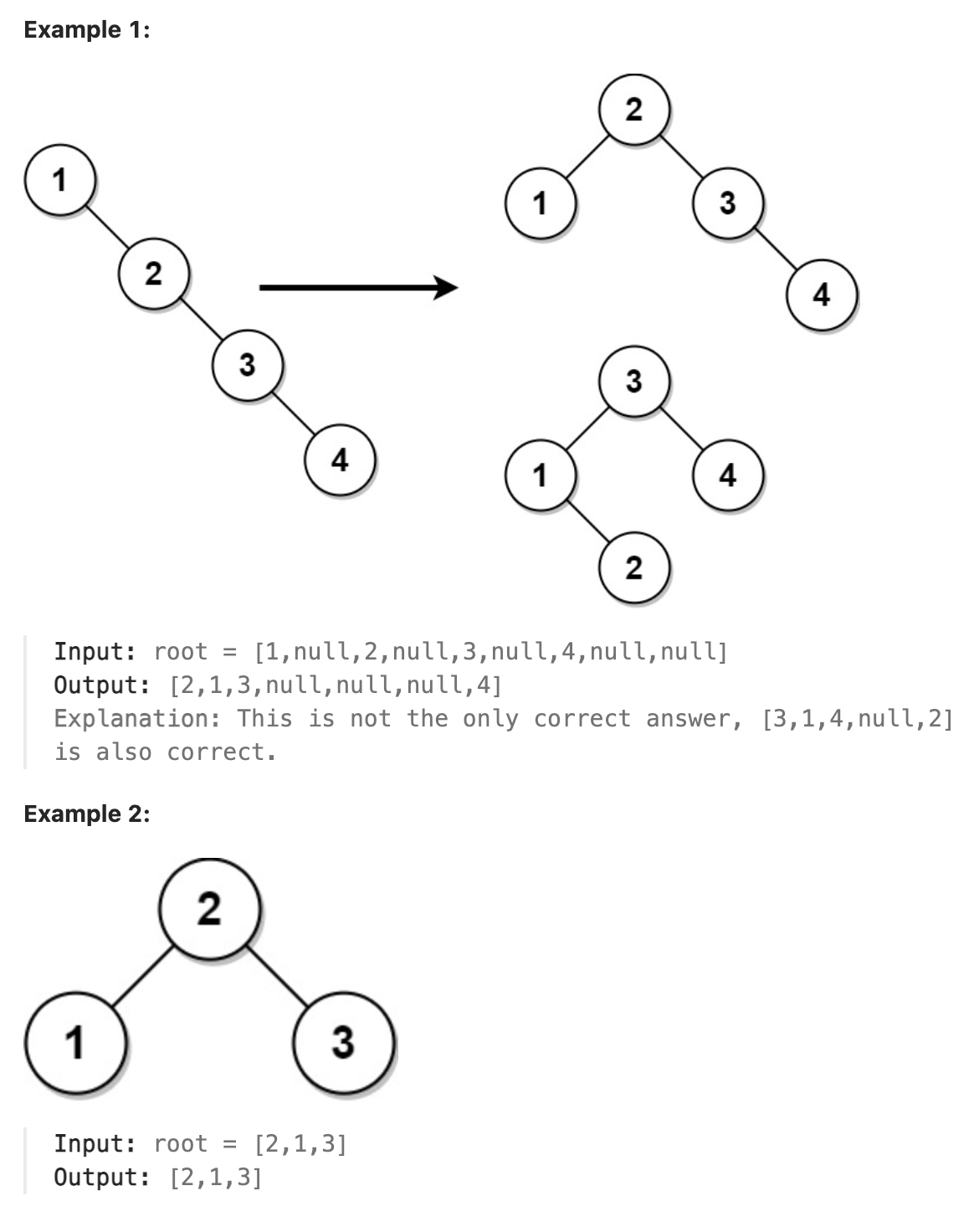
题解
本题要求将二叉搜索树转换为二叉平衡搜索树, 这就是在二叉平衡树新插入节点时常用的平衡操作. 但在本题中不需要使用常规的二叉平衡树中常用的左旋, 右旋等操作, 原因是二叉平衡树中常用的平衡操作是在插入一个新节点时用于调整树的平衡性的, 所以最多只需两次旋转即可调整平衡. 但在本题中, 树的不平衡性可能非常大, 且我们只需要在原来的树的基础上获得一棵新树. 只需考虑构造出一棵平衡树即可, 不需要考虑多次调整的情况.
因此遍历当前整棵二叉搜索树, 将树中的值从小到大保存到数组中, 二分法构造一棵新的平衡树就能得到最终结果.
代码
| |
day122 2024-06-27
1791. Find Center of Star Graph
There is an undirected star graph consisting of n nodes labeled from 1 to n. A star graph is a graph where there is one center node and exactly n - 1 edges that connect the center node with every other node.
You are given a 2D integer array edges where each edges[i] = [ui, vi] indicates that there is an edge between the nodes ui and vi. Return the center of the given star graph.
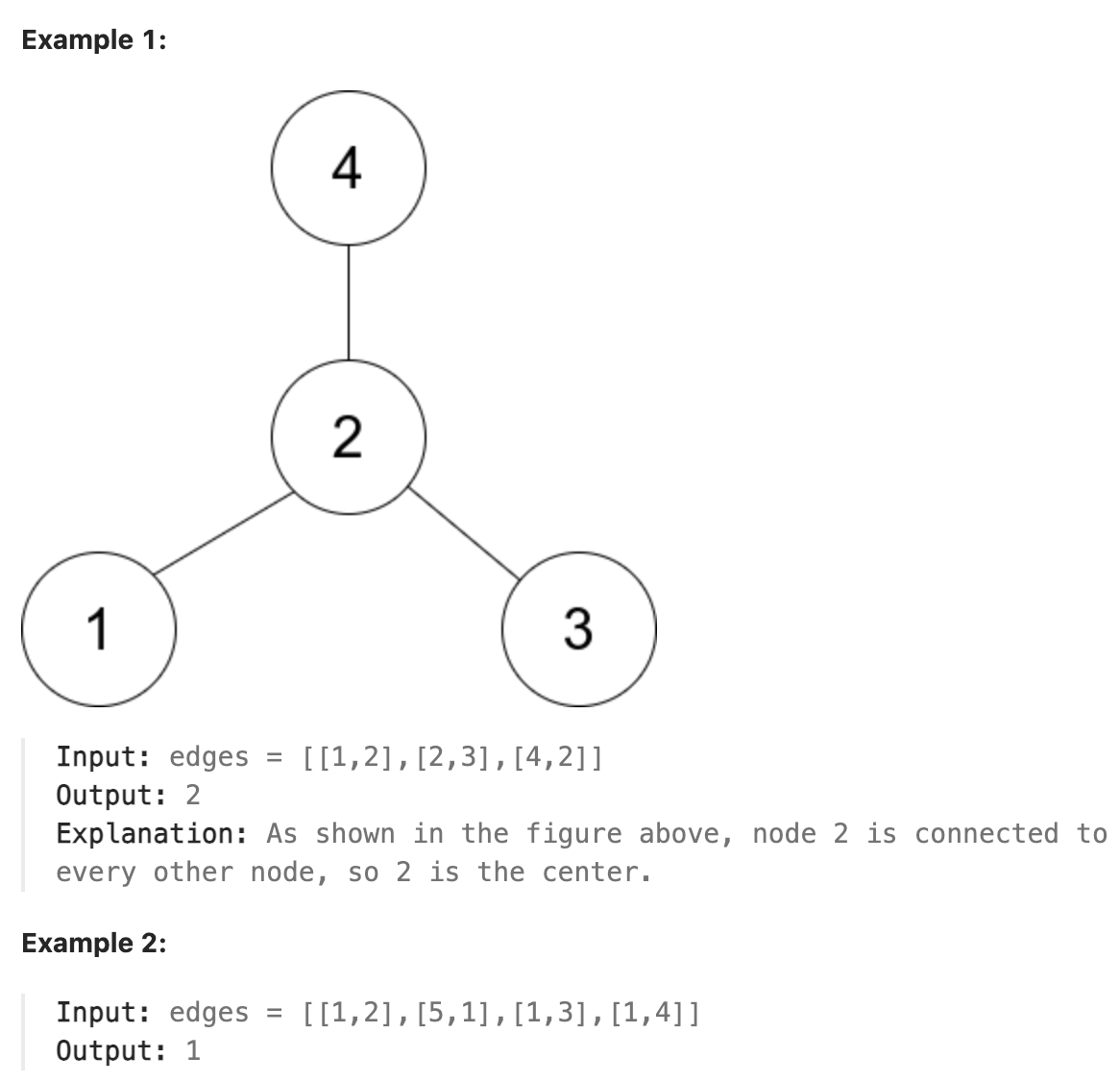
题解
本题n个节点共有n-1条边, 存在一个中心节点使得其余节点都与这个节点相连. 只需要看edges中的任意两条边, 找到这两条边共有的节点即为中心节点.
代码
| |
总结
考虑只有一个中心节点与其余n-1个节点相连, 但其余节点也可能相连的情况, 统计所有节点的度, 度最高的即为中心节点.
27. Remove Element
Given an integer array nums and an integer val, remove all occurrences of val in nums in-place. The order of the elements may be changed. Then return the number of elements in nums which are not equal to val.
Consider the number of elements in nums which are not equal to val be k, to get accepted, you need to do the following things:
Change the array nums such that the first k elements of nums contain the elements which are not equal to val. The remaining elements of nums are not important as well as the size of nums. Return k.

题解
本题最简单的解法当然是再创建一个相同大小的数组, 将原数组中非val的数依次复制到数组中. 另外一种方法则是双指针, 遍历数组, 头指针遇到val则与尾指针指向的非val值交换, 直到头尾指针相遇即可.
代码
| |
day123 2024-06-28
2285. Maximum Total Importance of Roads
You are given an integer n denoting the number of cities in a country. The cities are numbered from 0 to n - 1.
You are also given a 2D integer array roads where roads[i] = [ai, bi] denotes that there exists a bidirectional road connecting cities ai and bi.
You need to assign each city with an integer value from 1 to n, where each value can only be used once. The importance of a road is then defined as the sum of the values of the two cities it connects.
Return the maximum total importance of all roads possible after assigning the values optimally.
题解
本题要给每个节点赋值, 使得最终边的权重和(边连接的两个节点的权重和)最大. 统计出每个节点相连的边的数量, 从大到小排序, 按序依次从最大到最小赋值并计算权重和. 这里边的权重和可以转化为节点能贡献的权重和的和, 即用节点的权重乘以和这个节点相连的边的数量. 再依次对各个节点求值并加和.
题解
| |
day124 2024-06-29
2192. All Ancestors of a Node in a Directed Acyclic Graph
You are given a positive integer n representing the number of nodes of a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG). The nodes are numbered from 0 to n - 1 (inclusive).
You are also given a 2D integer array edges, where edges[i] = [fromi, toi] denotes that there is a unidirectional edge from fromi to toi in the graph.
Return a list answer, where answer[i] is the list of ancestors of the ith node, sorted in ascending order.
A node u is an ancestor of another node v if u can reach v via a set of edges.
题解
本题要求出每个节点的所有祖先节点, 按照节点标号从小到大列出. 既然是有向无环图, 那么本图可以进行拓扑排序. 统计所有节点的入度, 从入度为0的节点开始, 依次遍历入度为0的所有节点, 在其全部后继节点对应的祖先数组中中加入遍历的节点标号. 删掉与这些节点相连的边, 再次查看入度为0的的节点, 重复以上操作. 直到数组中只有入度为0的节点即剩余节点都没有后继节点为止.
但这种方式要重复向多个数组中加入相同的值. 如果在统计入度的时候将所有边反向并统计反向边对应的各个节点的入度, 则从入度为0的节点开始按入度从小到大遍历节点并将其所有后继节点(通过bfs进行遍历)放入其在结果数组中对应位置的数组内并排序即可.
代码
| |
day125 2024-06-30
1579. Remove Max Number of Edges to Keep Graph Fully Traversable
Alice and Bob have an undirected graph of n nodes and three types of edges:
Type 1: Can be traversed by Alice only. Type 2: Can be traversed by Bob only. Type 3: Can be traversed by both Alice and Bob. Given an array edges where edges[i] = [typei, ui, vi] represents a bidirectional edge of type typei between nodes ui and vi, find the maximum number of edges you can remove so that after removing the edges, the graph can still be fully traversed by both Alice and Bob. The graph is fully traversed by Alice and Bob if starting from any node, they can reach all other nodes.
Return the maximum number of edges you can remove, or return -1 if Alice and Bob cannot fully traverse the graph.
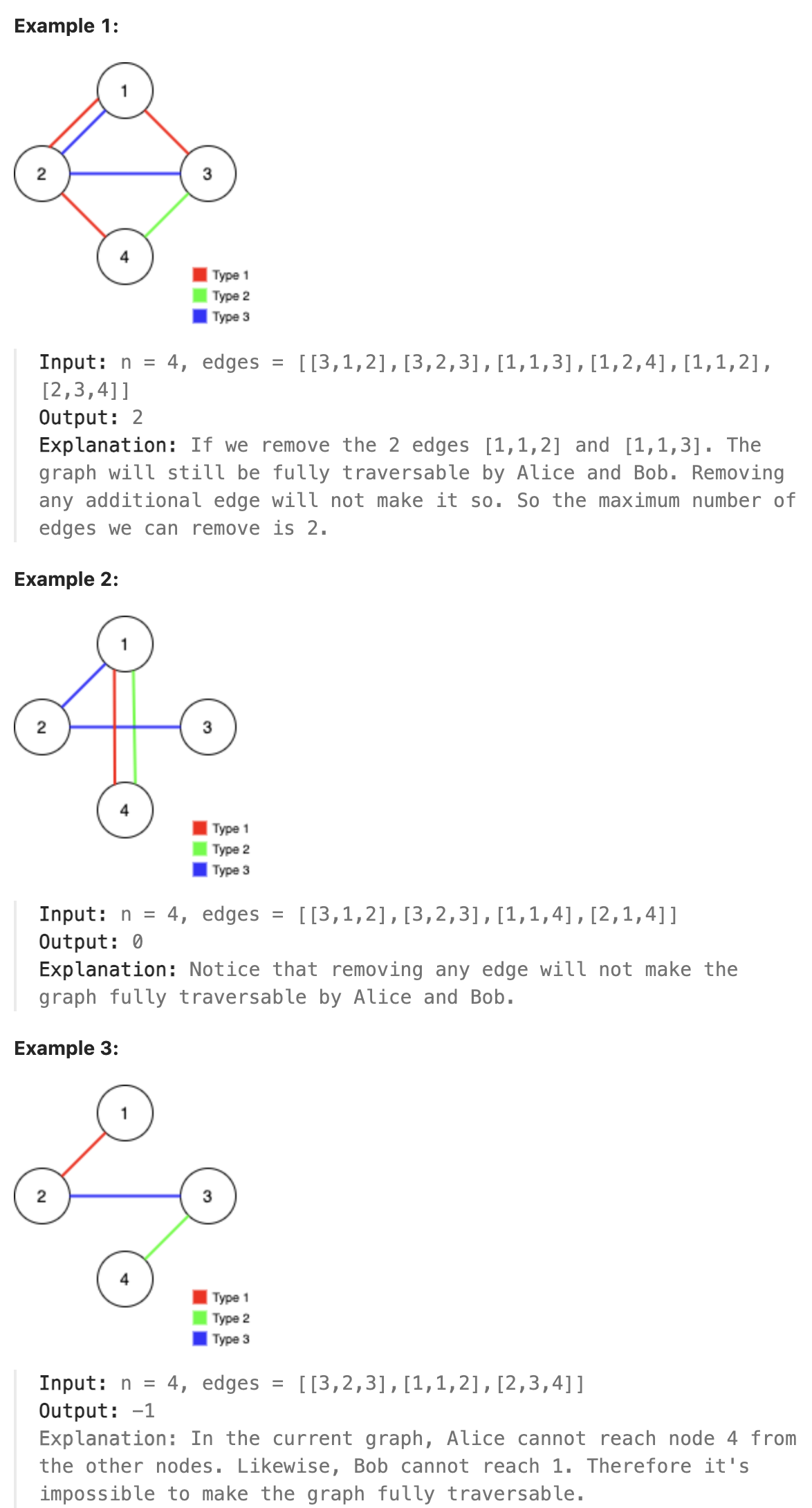
题解
本题是一道难题, type3的路径是Alice和Bob都可以使用的, 如果想让每个人都能遍历整个图并且使图中的边最少, 无疑首先要尽量使用type3的路径. 通过type3的路径能连通的点Alice和Bob不需要再使用type1和type2连通, 在type3的连通图中的type1和type2的边都可以删去. 不能删除的边是连通type3边构成的连通图之间连通的type1和type2的边. 使用并查集将type3的边构成的连通图中同一个连通图的节点用一个代表节点表示出来. 遍历type1的边, 将那些能将type3构成的不同连通图连通起来的边保留, 其余的均删除并计数, 若最后所有节点均在同一个集合中, 则Alice能遍历所有节点. 同理对type2的边也执行以上操作, 最终将删除的边数目加和即可得到最终结果.
代码
| |
总结
要熟悉并查集的实现, 能快速根据需要实现一个简单的并查集出来.
day126 2024-07-01
1550. Three Consecutive Odds
Given an integer array arr, return true if there are three consecutive odd numbers in the array. Otherwise, return false.

题解
本题是一道简单题, 设定一个标记位标记当前连续的奇数个数, 如果达到三个则返回true. 如果遍历到末尾还没有达到三个则返回false.
代码
| |
day127 2024-07-02
350. Intersection of Two Arrays II
Given two integer arrays nums1 and nums2, return an array of their intersection. Each element in the result must appear as many times as it shows in both arrays and you may return the result in any order.

题解
本题是一道简单题, 要获取在nums1和nums2中都出现的数组元素和其个数. 则可以用map记录nums1和nums2中出现的数字和出现次数. 遍历其中一个map, 在另一个map中查找当前map中的key出现的次数, 取比较小的次数n将对应key重复n次放入结果数组中.
代码
| |
day128 2024-07-03
1509. Minimum Difference Between Largest and Smallest Value in Three Moves
You are given an integer array nums.
In one move, you can choose one element of nums and change it to any value.
Return the minimum difference between the largest and smallest value of nums after performing at most three moves.

题解
本题可以改变三个数字的值和可以删掉三个数字效果上差不多, 问题变成了应该删掉哪三个数字, 显然为了让删掉后剩余数组中数字的极差最小, 应该从数组的最小值或者最大值中删除, 问题在于应该删掉的三个数字中哪些从最大值方向删除, 哪些从最小值方向删除. 考虑最终的目标为让极差最小, 从最小值方向删除和从最大值方向删除三个数字一共只有四种组合, 小3大0, 小1大2, 小2大1, 小0大3. 直接计算四种组合对应的减少极差的值, 比较大小选择能减少极差最大的组合并删除对应元素, 最后计算删除后数组的极差.
代码
| |
总结
这种方法属于暴力枚举的方式, 但在题目限制只能改变3个数的条件下, 需要枚举的情况极少, 因此可以奏效.
day129 2024-07-04
2181. Merge Nodes in Between Zeros
You are given the head of a linked list, which contains a series of integers separated by 0’s. The beginning and end of the linked list will have Node.val == 0.
For every two consecutive 0’s, merge all the nodes lying in between them into a single node whose value is the sum of all the merged nodes. The modified list should not contain any 0’s.
Return the head of the modified linked list.
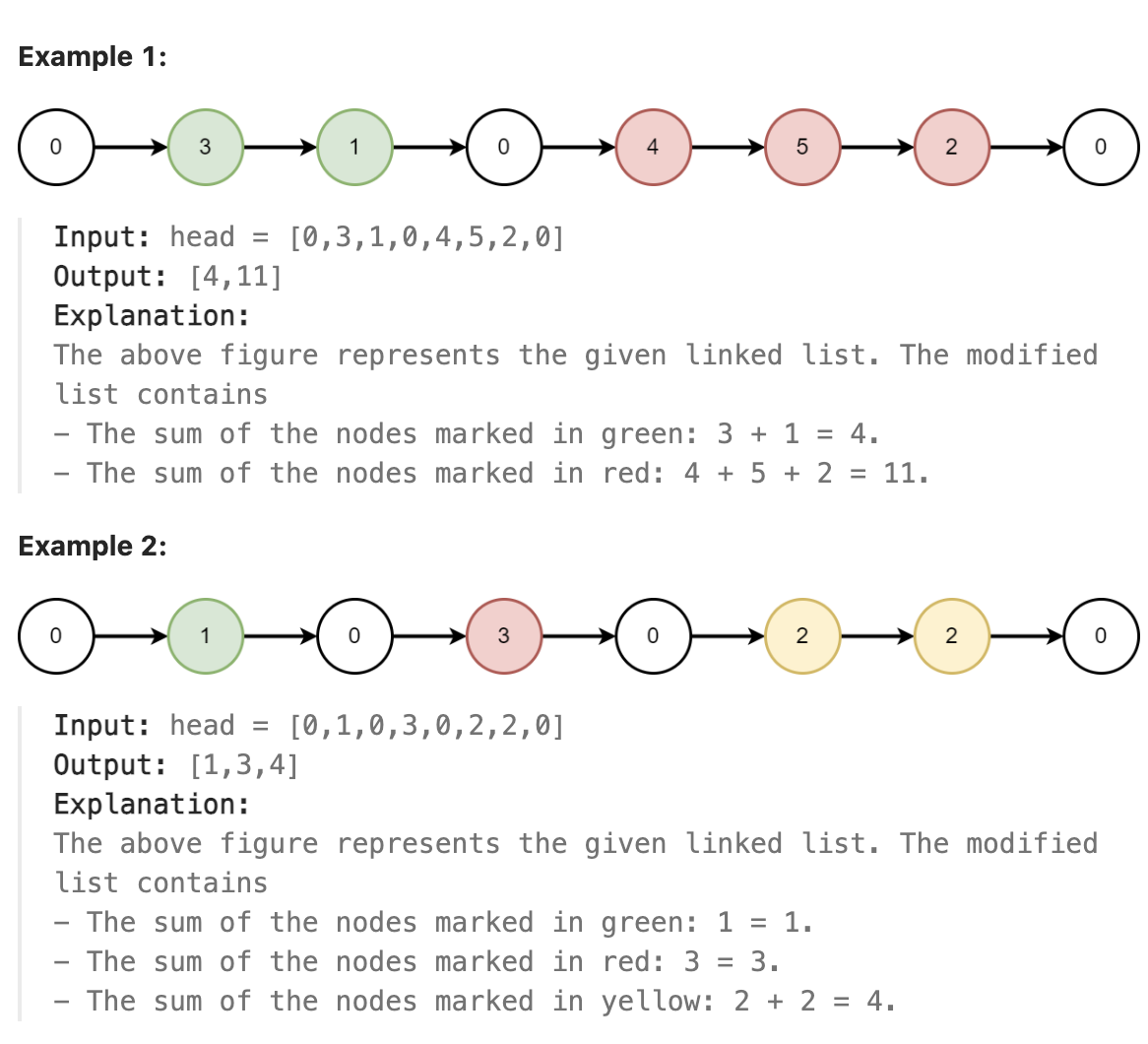
题解
本题要将0分隔的链表中两个0之间的数字求和合并为一个节点, 并删掉0节点, 则可以遍历链表, 遇到0记录起始0的节点指针, 对后面的非0数字求和, 再次遇到0则用和替换起始0节点的值, 并将这个节点的Next指针指向新遇到的0, 将新遇到的0设为起始0, 如此反复. 注意当出现连续0时, 直接忽视, 按照前述方法正常求和即可.
代码
| |
day130 2024-07-05
2058. Find the Minimum and Maximum Number of Nodes Between Critical Points
A critical point in a linked list is defined as either a local maxima or a local minima.
A node is a local maxima if the current node has a value strictly greater than the previous node and the next node.
A node is a local minima if the current node has a value strictly smaller than the previous node and the next node.
Note that a node can only be a local maxima/minima if there exists both a previous node and a next node.
Given a linked list head, return an array of length 2 containing [minDistance, maxDistance] where minDistance is the minimum distance between any two distinct critical points and maxDistance is the maximum distance between any two distinct critical points. If there are fewer than two critical points, return [-1, -1].
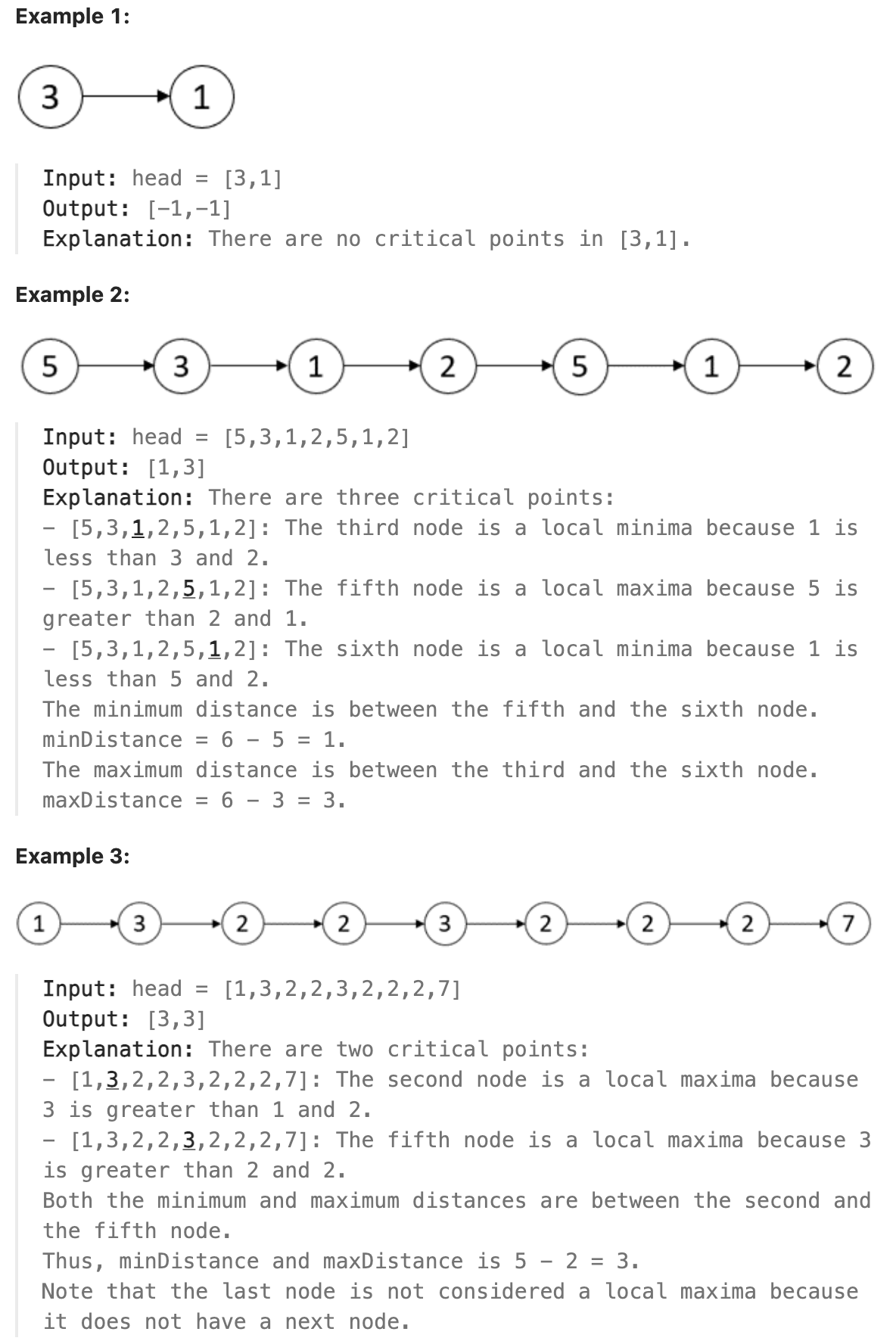
题解
本题使用双指针法, 一个指针指向前一个节点, 一个指针指向当前节点, 这样就可以判断当前节点是否是关键点(critical point). 将节点在链表中的位置也使用下标表示出来, 这样方便判断两个关键点之间的距离, 使用一个变量保存初始关键点的下标, 一个保存前一个关键点的下标, 每次遇到新的关键点计算与前一个关键点的距离并更新距离最小值. 遍历整个链表后, 用最后一个关键点下标和第一个关键点下标作差即得距离最大值.
代码
| |
day131 2024-07-06
2582. Pass the Pillow
There are n people standing in a line labeled from 1 to n. The first person in the line is holding a pillow initially. Every second, the person holding the pillow passes it to the next person standing in the line. Once the pillow reaches the end of the line, the direction changes, and people continue passing the pillow in the opposite direction.
For example, once the pillow reaches the nth person they pass it to the n - 1th person, then to the n - 2th person and so on. Given the two positive integers n and time, return the index of the person holding the pillow after time seconds.

题解
本题是简单题, 使用time对n-1(4个人只需传承3次即可到最后一人)求模和求商, 商的奇偶可以决定传递的起点是队首还是队尾, 求模得到的余数可以决定从本次传递起点开始传递了几次. 再使用对应的传递起点计算当前传递到哪个人.
代码
| |
2. Add Two Numbers
You are given two non-empty linked lists representing two non-negative integers. The digits are stored in reverse order, and each of their nodes contains a single digit. Add the two numbers and return the sum as a linked list.
You may assume the two numbers do not contain any leading zero, except the number 0 itself.
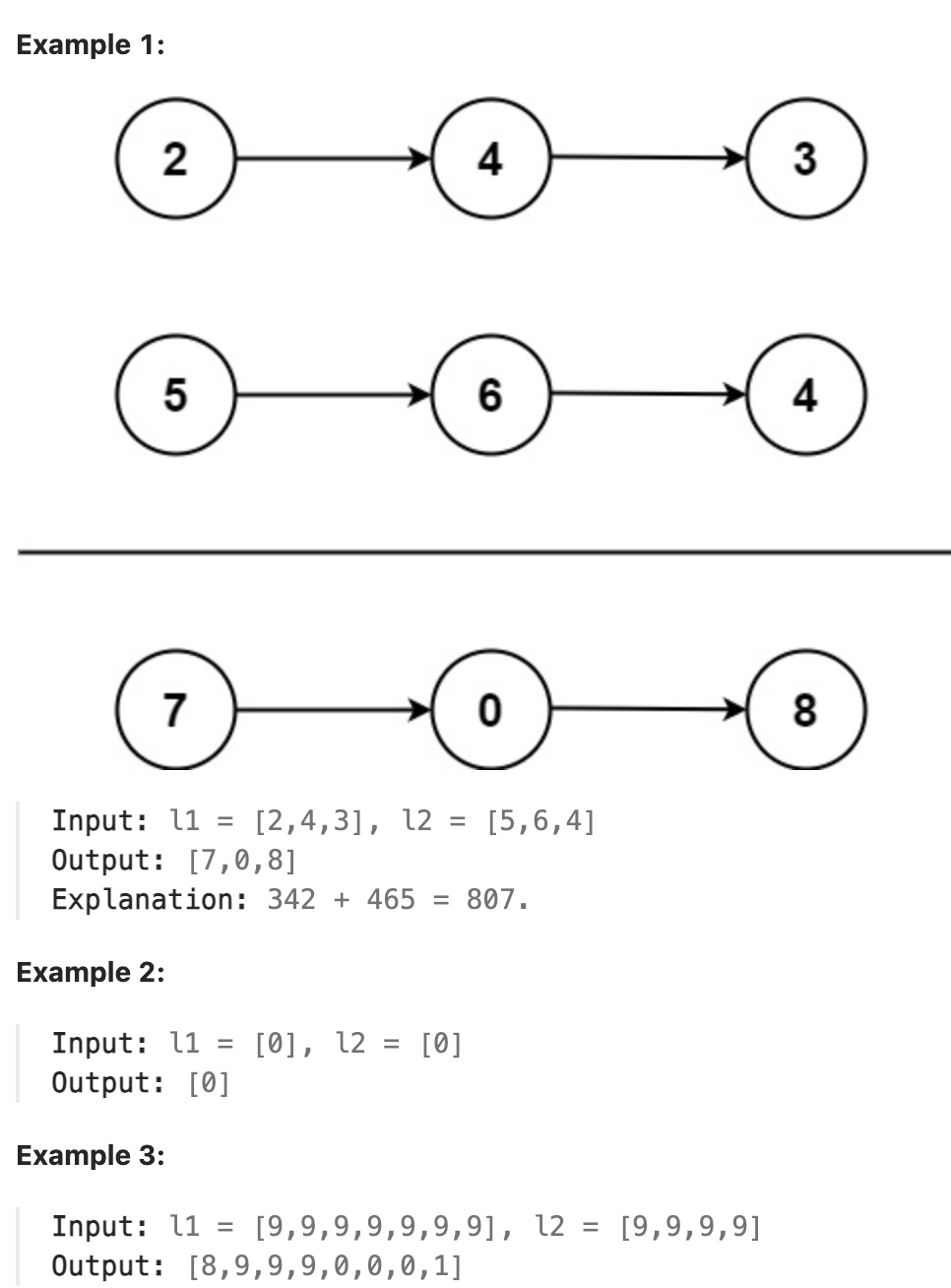
题解
本题在两个链表中较长的链表上直接加上另一个链表的中对应节点的值并用标志位标记进位. 当一个链表遍历结束时将另一个链表的剩余节点直接连接到链表后面, 注意处理进位.
代码
| |
day132 2024-07-07
1518. Water Bottles
There are numBottles water bottles that are initially full of water. You can exchange numExchange empty water bottles from the market with one full water bottle.
The operation of drinking a full water bottle turns it into an empty bottle.
Given the two integers numBottles and numExchange, return the maximum number of water bottles you can drink.
题解
本题是一道简单题, 和生活关联比较紧密, 只需通过循环不断判断当前手里的饮料喝完后的空瓶子数量能否换新的饮料, 将当前空瓶子个数(由余数和新换的饮料个数加和得到)除以numExchange, 商即为能换的新饮料数量, 保存余数用于下一次兑换饮料. 如此反复直至商为0. 每次将新换的饮料数量都加到最终结果中.
代码
| |
day133 2024-07-08
1823. Find the Winner of the Circular Game
There are n friends that are playing a game. The friends are sitting in a circle and are numbered from 1 to n in clockwise order. More formally, moving clockwise from the ith friend brings you to the (i+1)th friend for 1 <= i < n, and moving clockwise from the nth friend brings you to the 1st friend.
The rules of the game are as follows:
Start at the 1st friend. Count the next k friends in the clockwise direction including the friend you started at. The counting wraps around the circle and may count some friends more than once. The last friend you counted leaves the circle and loses the game. If there is still more than one friend in the circle, go back to step 2 starting from the friend immediately clockwise of the friend who just lost and repeat. Else, the last friend in the circle wins the game. Given the number of friends, n, and an integer k, return the winner of the game.
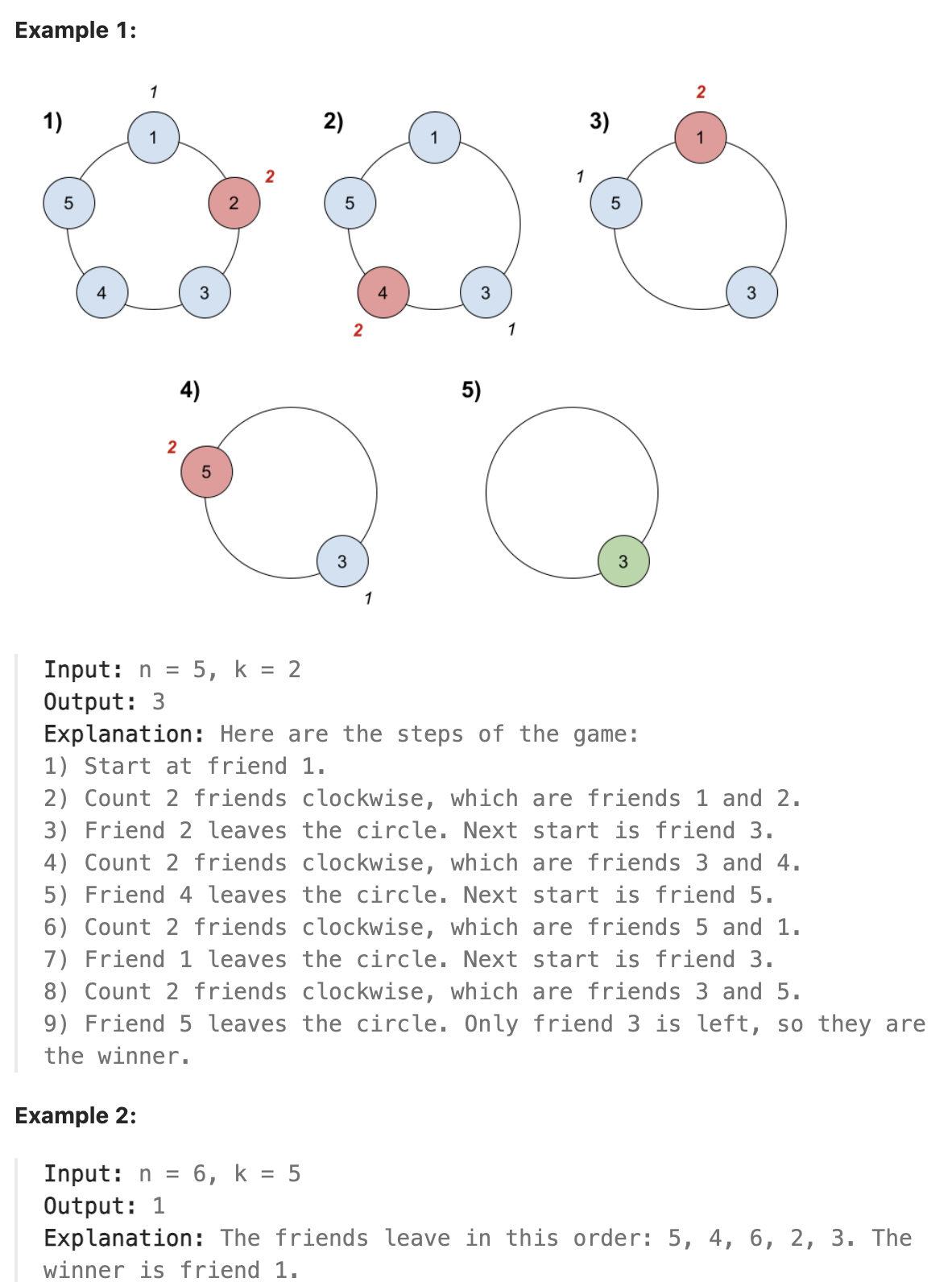
题解
本题直接模拟这一游戏过程即可, 直观思路是使用一个循环队列模拟圆桌上的所有人, 模拟游戏过程, 每次数到的人就将其从循环队列中删除, 循环队列可以使用一个数组来构建, 每次超出队列长度从头开始遍历即可. 数组初始化为1-n的节点值. 每次根据数到的下标直接删除数组中的这个元素. 直到数组中只有一个元素为止.
代码
| |
总结
本题也可以采用数学方法解决, 理解数学方法的关键还是在于问题的转化, 考虑之前循环队列的解法, 当我们已知队列中有两个人并且计数为k时的获胜者编号, 则当队列中有三个人时, 计数为k, 通过计数将某个人删除后问题又变为两个人并且计数为k时的获胜者编号, 只需要将原来的编号加上三个人时删掉的人的编号即可得到最终的编号. 这种解决方法将直观的从整体的队列根据计数挨个从队列中删除对应计数编号的人直到只剩一个人从而得到获胜者编号反向转换为从只有一个人时找到最终的获胜者编号到n-1时的获胜者编号最终到n个人时的获胜者编号. 是经典的递归解决问题的思想. 而在想明白这个思路后, 将递归部分转换为迭代, 即可得到最终的简单解法.
具体数学证明可见:
| |
day134 2024-07-09
1701. Average Waiting Time
There is a restaurant with a single chef. You are given an array customers, where customers[i] = [arrivali, timei]:
arrivali is the arrival time of the ith customer. The arrival times are sorted in non-decreasing order. timei is the time needed to prepare the order of the ith customer. When a customer arrives, he gives the chef his order, and the chef starts preparing it once he is idle. The customer waits till the chef finishes preparing his order. The chef does not prepare food for more than one customer at a time. The chef prepares food for customers in the order they were given in the input.
Return the average waiting time of all customers. Solutions within 10-5 from the actual answer are considered accepted.

题解
本题思路比较清晰, 直接模拟顾客来和等待上菜的过程, 用一个变量保存当前顾客能吃上菜的时间, 继续遍历,判断下一个顾客的到达时间是否在前一个顾客能吃上菜时间之前, 如果在之前, 则该顾客的等待时间为上一个顾客能吃上菜的时间减去当前顾客的到达时间与当前顾客菜的等待时间之和. 否则该顾客只需等待自己的菜品制作时间即可. 此处是典型的动态规划, 只需要保存前一个顾客能吃上菜的时间(之前最后一个顾客能吃上菜的时间)就已经包含了之前所有顾客等菜和菜品制作的信息. 根据前一个顾客的时间判断当前顾客的状态并更新当前最后一个顾客吃上菜的时间.
代码
| |
总结
本题其实就是先来先服务场景的简单应用.
day135 2024-07-10
1598. Crawler Log Folder
The Leetcode file system keeps a log each time some user performs a change folder operation.
The operations are described below:
“../” : Move to the parent folder of the current folder. (If you are already in the main folder, remain in the same folder). “./” : Remain in the same folder. “x/” : Move to the child folder named x (This folder is guaranteed to always exist). You are given a list of strings logs where logs[i] is the operation performed by the user at the ith step.
The file system starts in the main folder, then the operations in logs are performed.
Return the minimum number of operations needed to go back to the main folder after the change folder operations.
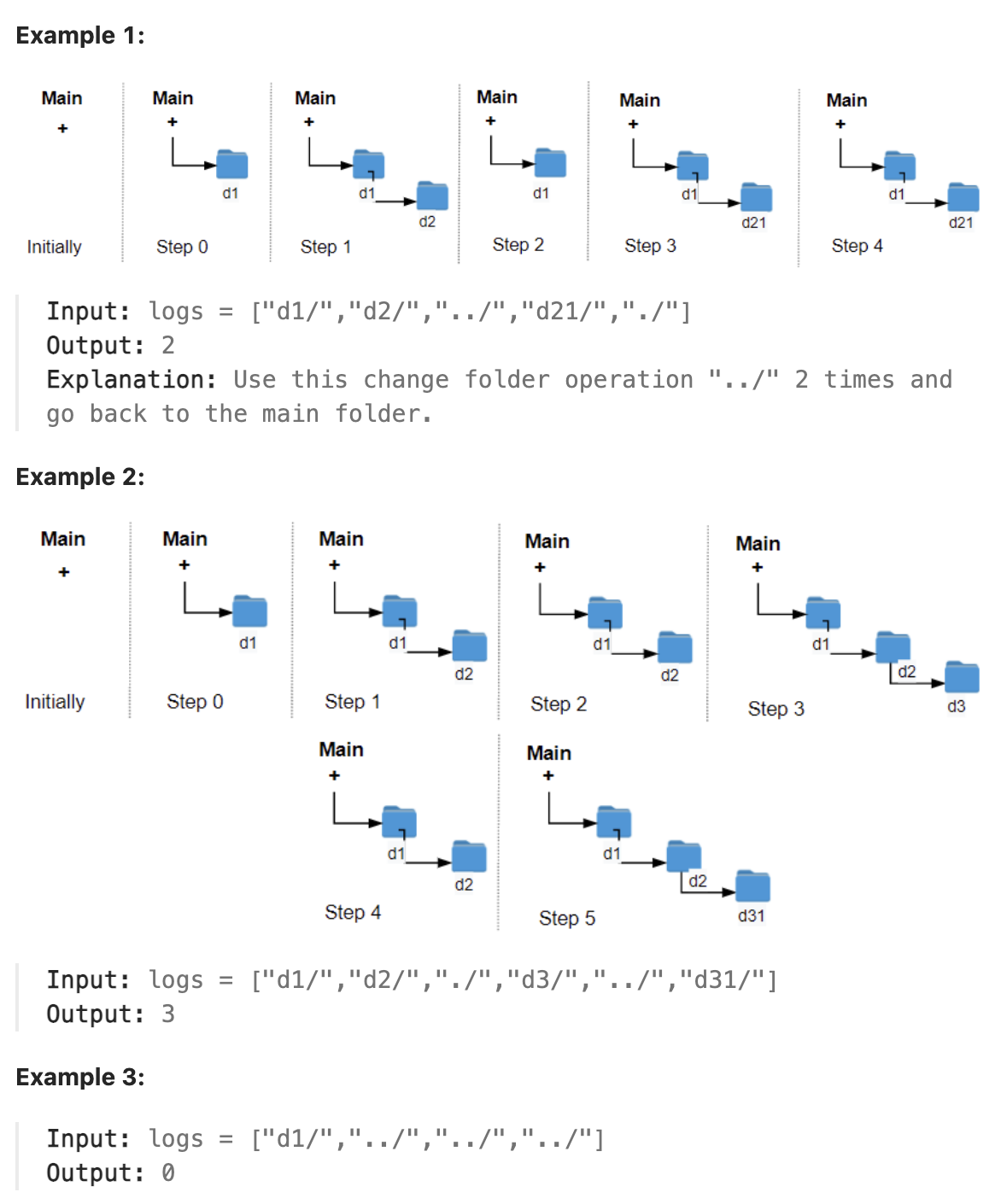
题解
本题为一道简单题, 只需用一个变量记录当前目录的深度, 遍历logs数组, 根据规定的操作修改深度数值即可, ../即为-1,x/即为+1, ./不变, 注意当深度已经为0时回到父目录的操作使得深度仍然为0.
代码
| |
3. Longest Substring Without Repeating Characters
Given a string s, find the length of the longest substring without repeating characters.

题解
本题用经典的滑动窗口求解, 当遇到重复字符时, 缩小窗口直到字符不重复. 继续扩大窗口. 更新窗口最大长度, 直到遍历完整个字符串为止. 要注意的是本题是不能有重复字符, 包括空格和特殊字符等, 因此用map是最方便的.
代码
| |
day136 2024-07-11
1190. Reverse Substrings Between Each Pair of Parentheses
You are given a string s that consists of lower case English letters and brackets.
Reverse the strings in each pair of matching parentheses, starting from the innermost one.
Your result should not contain any brackets.

题解
本题要将每个括号内的字符串都翻转, 则字符串被翻转偶数次后仍为原来的字符串本身, 因此可以用一个栈表示当前已经读入的待匹配的左括号和字符. 当匹配到右括号时, 就翻转匹配的左右括号之间的字符构成新的字符串, 并将这个字符串放入栈中, 继续向下匹配, 当再次匹配到右括号时, 重复此操作直到到字符串末尾为止, 即使用栈模拟整个字符串对应的括号内的翻转过程.
代码
| |
day137 2024-07-12
1717. Maximum Score From Removing Substrings
You are given a string s and two integers x and y. You can perform two types of operations any number of times.
Remove substring “ab” and gain x points. For example, when removing “ab” from “cabxbae” it becomes “cxbae”. Remove substring “ba” and gain y points. For example, when removing “ba” from “cabxbae” it becomes “cabxe”. Return the maximum points you can gain after applying the above operations on s.

题解
本题可以注意到由于x,y一个值比另一个值更大, 则ab,ba两个组合中只要优先选择组合成价值更大的组合就能得到最大值. 即通过贪心即可得到连续的ab串的最大值, 而优先组合可以通过栈来实现, 如果ab组合值更大, 遍历ab串并将读取的字符入栈, 当栈顶为a并且当前字符为b时将a出栈, 为a则继续入栈, 直到遍历到ab串末尾, 再将栈中剩余的a和b组合为ba. 这里可以不将只能和a组合成ba的b入栈, 而是用变量保存其个数, 最后直接通过个数计算结果即可. ba值更大同理.
代码
| |
day138 2024-07-13
2751. Robot Collisions
There are n 1-indexed robots, each having a position on a line, health, and movement direction.
You are given 0-indexed integer arrays positions, healths, and a string directions (directions[i] is either ‘L’ for left or ‘R’ for right). All integers in positions are unique.
All robots start moving on the line simultaneously at the same speed in their given directions. If two robots ever share the same position while moving, they will collide.
If two robots collide, the robot with lower health is removed from the line, and the health of the other robot decreases by one. The surviving robot continues in the same direction it was going. If both robots have the same health, they are both removed from the line.
Your task is to determine the health of the robots that survive the collisions, in the same order that the robots were given, i.e. final heath of robot 1 (if survived), final health of robot 2 (if survived), and so on. If there are no survivors, return an empty array.
Return an array containing the health of the remaining robots (in the order they were given in the input), after no further collisions can occur.
Note: The positions may be unsorted.

题解
本题是一道难题, 但核心算法只要熟悉栈操作即可, 本题机器人的位置并不是排好序的, 将机器人的编号和其位置, 方向, 血量绑定在同一个结构体后, 根据位置对结构体排序. 建立一个新栈(使用数组实现), 遍历机器人, 若机器人是向右运行的直接入栈. 向左则判断栈是否为空, 如果不为空则根据栈顶机器人的不同状态做出不同的操作, 若栈顶机器人运行方向向右且血量高于当前机器人, 则将栈顶机器人血量-1, 否则将当前机器人血量-1并弹出栈顶, 继续根据新栈顶做出不同操作. 直到栈顶机器人运行方向向左或者栈为空为止. 此时将当前机器人入栈.
代码
| |
day139 2024-07-14
726. Number of Atoms
Given a string formula representing a chemical formula, return the count of each atom.
The atomic element always starts with an uppercase character, then zero or more lowercase letters, representing the name.
One or more digits representing that element’s count may follow if the count is greater than 1. If the count is 1, no digits will follow.
For example, “H2O” and “H2O2” are possible, but “H1O2” is impossible. Two formulas are concatenated together to produce another formula.
For example, “H2O2He3Mg4” is also a formula. A formula placed in parentheses, and a count (optionally added) is also a formula.
For example, “(H2O2)” and “(H2O2)3” are formulas. Return the count of all elements as a string in the following form: the first name (in sorted order), followed by its count (if that count is more than 1), followed by the second name (in sorted order), followed by its count (if that count is more than 1), and so on.
The test cases are generated so that all the values in the output fit in a 32-bit integer.

题解
本题是一道难题, 关键在于如何处理括号, 从括号匹配问题开始, 对于这种有括号的问题, 栈一直是解决问题的核心. 括号代表着优先级的变化, 而栈的先入后出特性其实包含了隐含的优先级, 即后入栈的先出(优先级更高), 这与括号代表的优先级恰好一致(内层括号的优先级更高, 要先算). 本题通过使用栈将全部括号展开, 遇到左括号将其入栈, 继续遍历读入原子和对应的个数, 直到遇到右括号从栈顶向下遍历并将原子个数乘以右括号后面的数字, 直到遇到左括号为止, 删掉左括号. 这不是一个标准的栈操作, 但思想上仍是栈的思想. 将全部括号展开后, 从头遍历无括号的原子, 将相同原子个数合并最后输出.
代码
| |
day140 2024-07-15
2196. Create Binary Tree From Descriptions
You are given a 2D integer array descriptions where descriptions[i] = [parenti, childi, isLefti] indicates that parenti is the parent of childi in a binary tree of unique values. Furthermore,
If isLefti == 1, then childi is the left child of parenti. If isLefti == 0, then childi is the right child of parenti. Construct the binary tree described by descriptions and return its root.
The test cases will be generated such that the binary tree is valid.
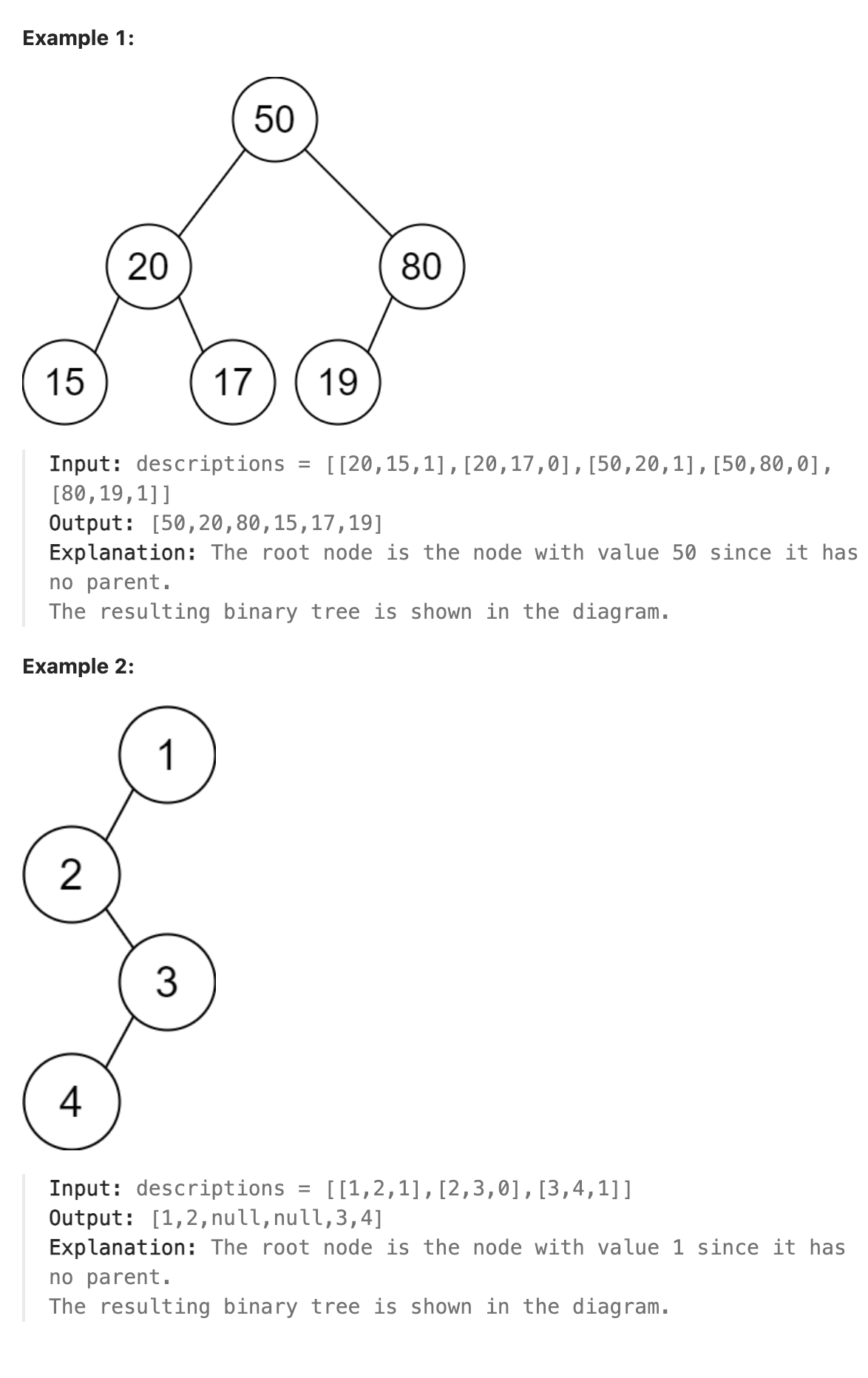
题解
本题先构建二叉树, 再找到二叉树的根. 构建二叉树并不困难, 可以将每个节点的指针都保存在map中, key为节点的值, value为节点的指针. 再根据描述构建每个节点. 找二叉树的根可以在构建二叉树的同时使用类似并查集的思想, 将当前描述的孩子节点的值作为下标, 父节点的值作为下标对应的值, 构造一个father数组. 若父节点作为下标之前没有指向任何值, 则将父节点的下标处的值指向父节点自身的值. 最终从任意一个节点值开始, 在father数组中查看其作为下标的值, 直到该下标处的值指向自身即为根节点的节点值. 返回根节点.
代码
| |
day141 2024-07-16
2096. Step-By-Step Directions From a Binary Tree Node to Another
You are given the root of a binary tree with n nodes. Each node is uniquely assigned a value from 1 to n. You are also given an integer startValue representing the value of the start node s, and a different integer destValue representing the value of the destination node t.
Find the shortest path starting from node s and ending at node t. Generate step-by-step directions of such path as a string consisting of only the uppercase letters ‘L’, ‘R’, and ‘U’. Each letter indicates a specific direction:
‘L’ means to go from a node to its left child node. ‘R’ means to go from a node to its right child node. ‘U’ means to go from a node to its parent node. Return the step-by-step directions of the shortest path from node s to node t.
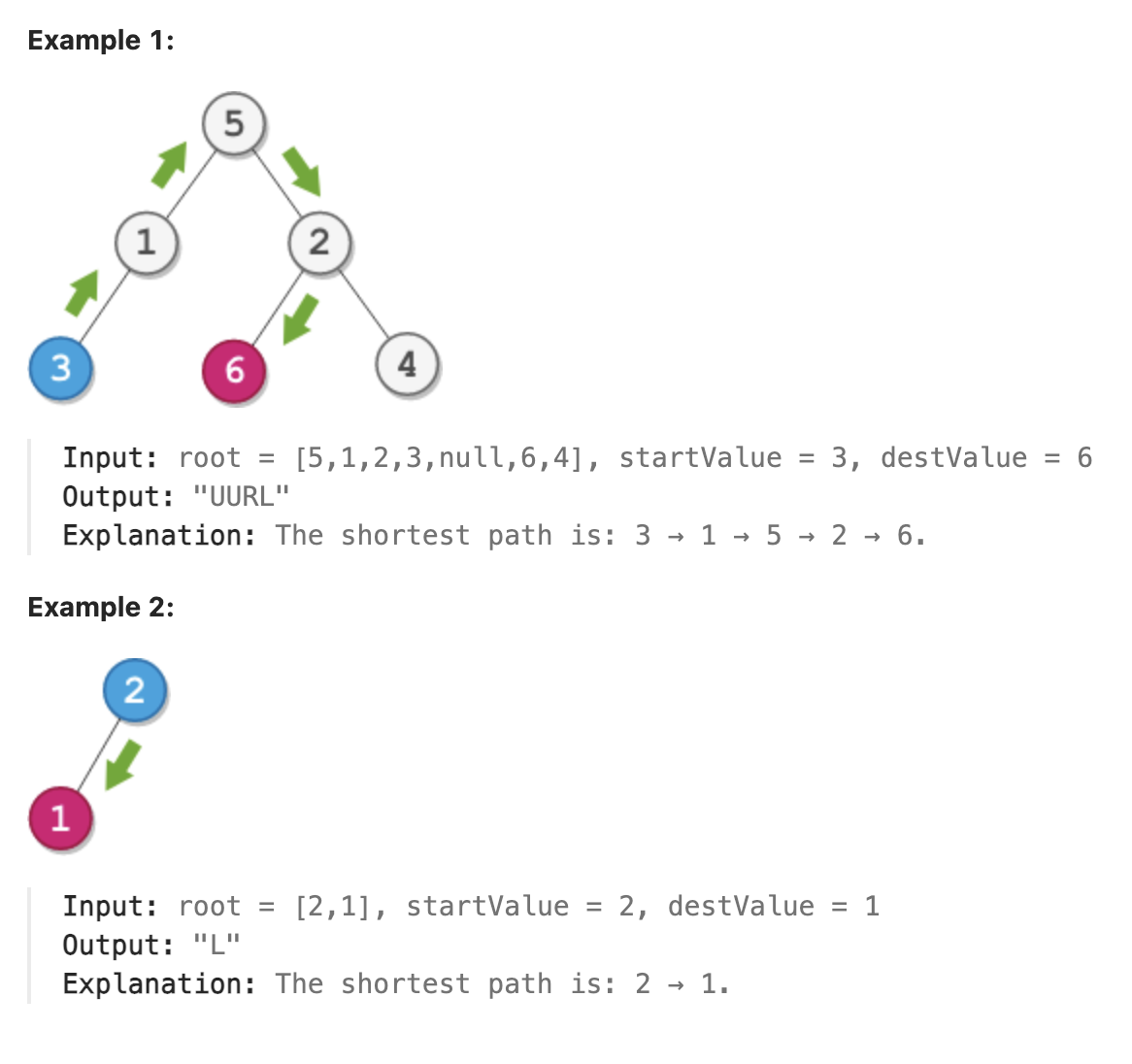
题解
本题正常遍历二叉树, 根据遍历过程记录’L’,‘R’直到分别找到起点和终点为止. 这里可以使用先根遍历, 如果根即为目标节点, 则设置对应的路径变量, 因为这里有两个目标节点, 需使用dfs查找两次分别找到到两个目标点的路径, 遍历过程中将之前经过的路径作为参数传递给递归函数. 这里使用字符数组要比使用字符串快得多.
得到起点和终点的路径后, 同时从头遍历二者的路径, 直到找到路径中的第一个不同点, 此时获取到达起点剩余路径的长度, 构造相同长度的重复’U’字符串并与终点的剩余路径连接即得到从起点到终点的路径.
代码
| |
day142 2024-07-17
1110. Delete Nodes And Return Forest
Given the root of a binary tree, each node in the tree has a distinct value.
After deleting all nodes with a value in to_delete, we are left with a forest (a disjoint union of trees).
Return the roots of the trees in the remaining forest. You may return the result in any order.
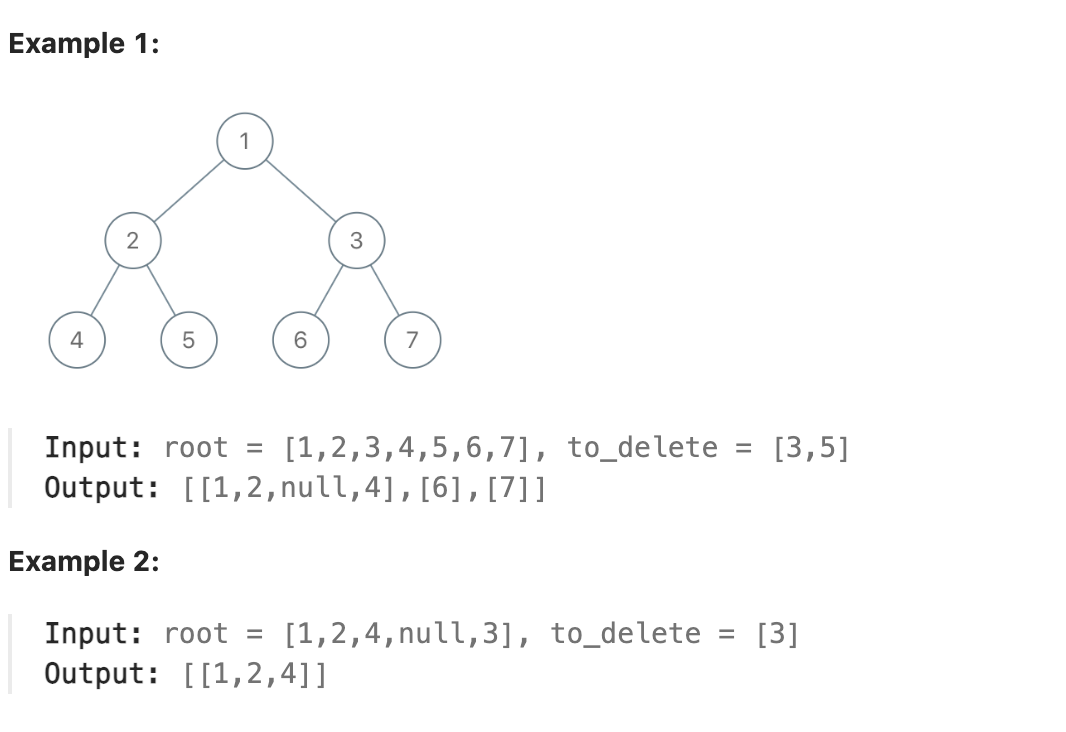
题解
本题关键在于了解什么样的节点会成为森林中树的根节点, 根据描述可以得出结论: 如果父节点是一个要被删除的节点且子节点不被删除, 那么这个子节点将成为森林中一棵树的根节点. 使用dfs遍历树并根据这一结论将根节点加入最终结果中, 注意处理当父节点不被删除但其子节点被删除时将父节点的这个子节点设置为空. 根据我们的结论, 每次只要对父节点和其左右子节点做出判断即可, 这样就转换为了仅包含父节点和左右子节点的小问题, 就可以使用递归来遍历整棵树得出最终结果.
代码
| |
day143 2024-07-18
1530. Number of Good Leaf Nodes Pairs
You are given the root of a binary tree and an integer distance. A pair of two different leaf nodes of a binary tree is said to be good if the length of the shortest path between them is less than or equal to distance.
Return the number of good leaf node pairs in the tree.
题解
考虑对于一个节点来说, 只要知道了到其左子树的所有叶子节点的距离, 和到其右子树的所有叶子节点的距离, 就可以将左子树的所有叶子节点距离和右子树所有叶子节点距离依次加和并与distance比较. 则通过后序遍历, 先遍历左右子树最后将左右子树的叶子节点的距离(数组)返回, 按照上面的思路与distance做比较, 直到遍历完整棵树为止. 这里可以将到叶子节点的最短距离记录下来用于优化, 当左右子树到叶子节点的最小值和已经大于distance时, 其余节点没必要继续进行比较. 直接返回即可.
代码
| |
总结
该种解法的时间复杂度与叶子节点的数量有关(约为节点总数乘以叶子节点数量的平方), 考虑节点总数最多为2的10次方, 则叶子节点最多为2的9次方即512个, 即便是平方的复杂度也在可以接受的范围内.
day144 2024-07-19
1380. Lucky Numbers in a Matrix
Given an m x n matrix of distinct numbers, return all lucky numbers in the matrix in any order.
A lucky number is an element of the matrix such that it is the minimum element in its row and maximum in its column.

题解
本题遍历两遍, 将每行最小的值的下标和每列最大的值的下标分别放入两个数组, 数组的下标代表对应的行数和列数, 遍历最小值数组, 根据对应的下标在最大值数组中找到对应的值看是否与最小值数组中的下标相同. 相同则表名找到了一个lucky number. 通过提前构建最大值数组, 可以仅遍历一遍数组即同时找到每行的最小值和每列的最大值, 只需在遍历行的时候将每个数与当前该列的最大值比较并更新即可通过一遍遍历完成任务.
代码
| |
day145 2024-07-20
1605. Find Valid Matrix Given Row and Column Sums
You are given two arrays rowSum and colSum of non-negative integers where rowSum[i] is the sum of the elements in the ith row and colSum[j] is the sum of the elements of the jth column of a 2D matrix. In other words, you do not know the elements of the matrix, but you do know the sums of each row and column.
Find any matrix of non-negative integers of size rowSum.length x colSum.length that satisfies the rowSum and colSum requirements.
Return a 2D array representing any matrix that fulfills the requirements. It’s guaranteed that at least one matrix that fulfills the requirements exists.

题解
本题使用贪心算法, 在填充每一行的数字时, 每次都取当前位置行和和列和的较小值. 再分别从行和和列和中减去当前取的值. 继续填充下一个位置的数字. 这样可以保证填充的每个数字都不会使当前行和列超过和的限制(实际按这个思路只要取小于等于二者较小值即可), 直接取二者中的较小值可以保证二者中的一个变为0. 避免了后续继续填充时可能会因行或列的和的限制而无法取得合适的数的问题(0对和没有影响). 而当和为0时只需将该位置填充为0即可.
代码
| |
day146 2024-07-21
2392. Build a Matrix With Conditions
You are given a positive integer k. You are also given:
a 2D integer array rowConditions of size n where rowConditions[i] = [abovei, belowi], and a 2D integer array colConditions of size m where colConditions[i] = [lefti, righti]. The two arrays contain integers from 1 to k.
You have to build a k x k matrix that contains each of the numbers from 1 to k exactly once. The remaining cells should have the value 0.
The matrix should also satisfy the following conditions:
The number abovei should appear in a row that is strictly above the row at which the number belowi appears for all i from 0 to n - 1. The number lefti should appear in a column that is strictly left of the column at which the number righti appears for all i from 0 to m - 1. Return any matrix that satisfies the conditions. If no answer exists, return an empty matrix.

题解
本题的条件实际上隐含了一种先后顺序, above在below的上面可以理解为above在below之前, 拓扑排序就是解决这种广义上的"顺序关系", 从a->b存在一种后继关系. 可以将above和below的关系视为有向图中的一条边, 从above指向below. 但本题中可能会出现环, 出现环即产生了冲突, 无法进行拓扑排序. 此时无解, 因此先判断由两个条件数组构建的有向图是否包含环, 包含环则无解, 不包含环继续进行拓扑排序, 得到拓扑排序后的数组, 按照数组中数对应的下标将其放入对应的行或者列. 注意对行进行拓扑排序得到的结果和对列进行拓扑排序得到的结果二者并不冲突. 所以分别排序并按顺序填入数组就能得到正确答案.
代码
| |
day147 2024-07-22
2418. Sort the People
You are given an array of strings names, and an array heights that consists of distinct positive integers. Both arrays are of length n.
For each index i, names[i] and heights[i] denote the name and height of the ith person.
Return names sorted in descending order by the people’s heights.

题解
本题先将人名和身高绑定成一个结构体, 再根据身高排序, 思路是比较简单, 因此手动实现快排用于身高排序.
代码
| |
day148 2024-07-23
1636. Sort Array by Increasing Frequency
Given an array of integers nums, sort the array in increasing order based on the frequency of the values. If multiple values have the same frequency, sort them in decreasing order.
Return the sorted array.

题解
本题可使用计数排序, 先使用map统计各个数字出现的次数, 再直接对原始数组进行排序, 首先根据出现的次数排序, 如果两个数字出现次数相同则根据数字大小排序, 将数字更大的放在前面, 这里只需根据上面的条件写好go内置的sort函数即可完成排序. 最后返回结果.
代码
| |
day149 2024-07-24
2191. Sort the Jumbled Numbers
You are given a 0-indexed integer array mapping which represents the mapping rule of a shuffled decimal system. mapping[i] = j means digit i should be mapped to digit j in this system.
The mapped value of an integer is the new integer obtained by replacing each occurrence of digit i in the integer with mapping[i] for all 0 <= i <= 9.
You are also given another integer array nums. Return the array nums sorted in non-decreasing order based on the mapped values of its elements.
Notes:
Elements with the same mapped values should appear in the same relative order as in the input. The elements of nums should only be sorted based on their mapped values and not be replaced by them.

题解
本题要解决两个问题, 一是将原始数字映射为其对应的映射数字, 二是将映射数字排序并按序排列对应的原始数字并返回. 将原始数字映射为对应数字只需每次除以10, 按位处理即可, 注意单独处理0的情况. 对映射后数字排序并反映到原来的数组上需要注意体重明确说明了对于映射数字相同的数字需保持原始数组的顺序, 因此需要稳定排序, 在go中使用sort.SliceStable即可进行稳定排序.
代码
| |
day150 2024-07-25
912. Sort an Array
Given an array of integers nums, sort the array in ascending order and return it.
You must solve the problem without using any built-in functions in O(nlog(n)) time complexity and with the smallest space complexity possible.

题解
本题是一道基础题, 要求手动实现一种排序方式进行排序, 之前已经实现过归并排序, 快排, 计数排序, 因此本次实现堆排序, 实现堆排序的关键在于构建一个最小堆.
代码
| |
